A monolithic kernel is an operating system architecture where the entire operating system is working in kernel space. The monolithic model differs from other operating system architectures in that it alone defines a high-level virtual interface over computer hardware. A set of primitives or system calls implement all operating system services such as process management, concurrency, and memory management. Device drivers can be added to the kernel as modules.

An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs.
Multi-user software is software that allows access by multiple users of a computer. Time-sharing systems are multi-user systems. Most batch processing systems for mainframe computers may also be considered "multi-user", to avoid leaving the CPU idle while it waits for I/O operations to complete. However, the term "multitasking" is more common in this context.
In computing, a file server is a computer attached to a network that provides a location for shared disk access, i.e. shared storage of computer files that can be accessed by the workstations that are able to reach the computer that shares the access through a computer network. The term server highlights the role of the machine in the client–server scheme, where the clients are the workstations using the storage. It is common that a file server does not perform computational tasks, and does not run programs on behalf of its clients.
It is designed primarily to enable the storage and retrieval of data while the computation is carried out by the workstations.

An email client, email reader or more formally mail user agent (MUA) is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email.
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call system. The NFS is an open standard defined in Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used for the transfer of computer files between a client and server on a computer network.

Squid is a caching and forwarding HTTP web proxy. It has a wide variety of uses, including speeding up a web server by caching repeated requests, caching web, DNS and other computer network lookups for a group of people sharing network resources, and aiding security by filtering traffic. Although primarily used for HTTP and FTP, Squid includes limited support for several other protocols including Internet Gopher, SSL, TLS and HTTPS. Squid does not support the SOCKS protocol.
Independent Computing Architecture (ICA) is a proprietary protocol for an application server system, designed by Citrix Systems. The protocol lays down a specification for passing data between server and clients, but is not bound to any one platform. Citrix's ICA is an alternative to Microsoft's Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
In computer networking, Server Message Block (SMB), one version of which was also known as Common Internet File System, operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used for providing shared access to files, printers, and serial ports and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an authenticated inter-process communication mechanism. Most usage of SMB involves computers running Microsoft Windows, where it was known as "Microsoft Windows Network" before the introduction of Active Directory. Corresponding Windows services are LAN Manager Server and LAN Manager Workstation.

In computing, Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop-sharing system that uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) to remotely control another computer. It transmits the keyboard and mouse events from one computer to another, relaying the graphical-screen updates back in the other direction, over a network.
A shell account is a user account on a remote server, traditionally running under the Unix operating system, which gives access to a shell via a command-line interface protocol such as telnet or SSH.
A remote access services (RAS) is any combination of hardware and software to enable the remote access tools or information that typically reside on a network of IT devices.
Windows Services for UNIX (SFU) is a discontinued software package produced by Microsoft which provided a Unix environment on Windows NT and some of its immediate successor operating-systems.
NIS+ is a directory service developed by Sun Microsystems to replace its older 'NIS'. It is designed to eliminate the need for duplication across many computers of configuration data such as user accounts, host names and addresses, printer information and NFS disk mounts on individual systems, instead using a central repository on a master server, simplifying system administration. NIS+ client software has been ported to other Unix and Unix-like platforms.
Files transferred over Shell protocol (FISH) is a network protocol that uses Secure Shell (SSH) or Remote Shell (RSH) to transfer files between computers and manage remote files.

Virtuoso Universal Server is a middleware and database engine hybrid that combines the functionality of a traditional Relational database management system (RDBMS), Object-relational database (ORDBMS), virtual database, RDF, XML, free-text, web application server and file server functionality in a single system. Rather than have dedicated servers for each of the aforementioned functionality realms, Virtuoso is a "universal server"; it enables a single multithreaded server process that implements multiple protocols. The free and open source edition of Virtuoso Universal Server is also known as OpenLink Virtuoso. The software has been developed by OpenLink Software with Kingsley Uyi Idehen and Orri Erling as the chief software architects.
In computing, Self-certifying File System (SFS) is a global and decentralized, distributed file system for Unix-like operating systems, while also providing transparent encryption of communications as well as authentication. It aims to be the universal distributed file system by providing uniform access to any available server, however, the usefulness of SFS is limited by the low deployment of SFS clients. It was developed in the June 2000 doctoral thesis of David Mazières.
Unbound is a validating, recursive, and caching DNS resolver product from NLnet Labs. It is distributed free of charge in open-source form under the BSD license.
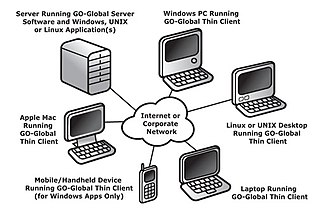
GraphOn GO-Global is remote access/application publishing software that allows users to access and run Windows, Linux, and UNIX applications installed on a central server. GO-Global displays the application's user interface on personal computers and other client devices running a variety of operating systems, including UNIX, Linux, Mac OS X, Windows, Windows Mobile, and Pocket PC. GO-Global can be used to Web-enable existing applications without the need to modify existing code. Applications appear on the client device either in a Web browser or within a loose window on the desktop.








