
Emtricitabine, with trade name Emtriva, is a nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) for the prevention and treatment of HIV infection in adults and children.
Gilead Sciences, Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Foster City, California, that focuses on researching and developing antiviral drugs used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, influenza, and COVID-19, including ledipasvir/sofosbuvir and sofosbuvir. Gilead is a member of the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index and the S&P 500.
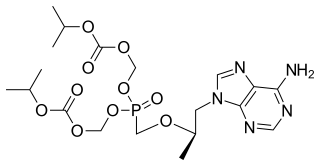
Tenofovir disoproxil, sold under the trade name Viread among others, is a medication used to treat chronic hepatitis B and to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals. It may be used for prevention of HIV/AIDS among those at high risk before exposure, and after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and together in combinations such as emtricitabine/tenofovir, efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir, and elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir. It does not cure HIV/AIDS or hepatitis B. It is available by mouth as a tablet or powder.
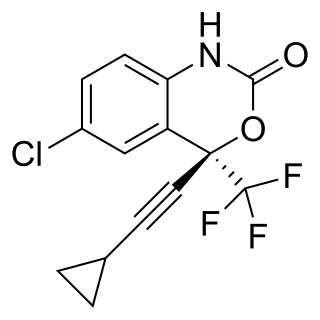
Efavirenz (EFV), sold under the brand names Sustiva among others, is an antiretroviral medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use with other antiretrovirals. It may be used for prevention after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and in combination as efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir. It is taken by mouth.

Emtricitabine/tenofovir, sold under the brand name Truvada among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS. It contains the antiretroviral medications emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil. For treatment, it must be used in combination with other antiretroviral medications. For prevention before exposure, in those who are at high risk, it is recommended along with safer sex practices. It does not cure HIV/AIDS. Emtricitabine/tenofovir is taken by mouth.

Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is the use of medications to prevent the spread of disease in people who have not yet been exposed to a disease-causing agent, usually a virus. The term typically refers to the use of antiviral drugs as a strategy for the prevention of HIV/AIDS. PrEP is one of a number of HIV prevention strategies for people who are HIV negative but who have a higher risk of acquiring HIV, including sexually active adults at increased risk of contracting HIV, people who engage in intravenous drug use, and serodiscordant sexually active couples.

Efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir, sold under the brand name Atripla among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication used to treat HIV/AIDS. It contains efavirenz, emtricitabine, and tenofovir disoproxil. It can be used by itself or together with other antiretroviral medications. It is taken by mouth.
Integrase inhibitors (INIs) are a class of antiretroviral drug designed to block the action of integrase, a viral enzyme that inserts the viral genome into the DNA of the host cell. Since integration is a vital step in retroviral replication, blocking it can halt further spread of the virus. Integrase inhibitors were initially developed for the treatment of HIV infection but have been applied to other retroviruses. The class of integrase inhibitors called integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) are in established medical use. Other classes, such as integrase binding inhibitors (INBIs), are still experimental.

Elvitegravir (EVG) is an integrase inhibitor used to treat HIV infection. It was developed by the pharmaceutical company Gilead Sciences, which licensed EVG from Japan Tobacco in March 2008. The drug gained approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on August 27, 2012 for use in adult patients starting HIV treatment for the first time as part of the fixed dose combination known as Stribild. On September 24, 2014 the FDA approved Elvitegravir as a single pill formulation under the trade name Vitekta. On November 5, 2015 the FDA approved the drug for use in patients affected with HIV-1 as a part of a second fixed dose combination pill known as Genvoya.

Rilpivirine, sold under the brand names Edurant and Rekambys, is a medication, developed by Tibotec, used for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is a second-generation non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) with higher potency, longer half-life and reduced side-effect profile compared with older NNRTIs such as efavirenz.

Cobicistat, sold under the brand name Tybost, is a medication for use in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus infection (HIV/AIDS). Its major mechanism of action is through the inhibition of human CYP3A proteins.
Emtricitabine/rilpivirine/tenofovir is a fixed-dose combination of antiretroviral drugs for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. The drug was co-developed by Gilead Sciences and Johnson & Johnson's Tibotec division and was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in August 2011, and by the European Medicines Agency in November 2011, for patients who have not previously been treated for HIV. It is available as a once-a-day single tablet.
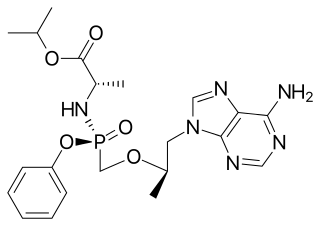
Tenofovir alafenamide, sold under the brand name Vemlidy, is a hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor medication for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in adults with compensated liver disease. It is taken by mouth.

John Charles Martin was an American billionaire businessman, and the former executive chairman (2016–2018) and CEO (1996–2016) of the American biotechnology company Gilead Sciences. He joined Gilead Sciences in 1990 as vice president for research and development. Gilead is known for developing drugs such as Atripla and commercializing Sovaldi (sofosbuvir) for the treatment of the liver virus hepatitis C. Martin is the recipient of a number of awards, including the Biotechnology Heritage Award (2017).

Abacavir/dolutegravir/lamivudine, sold under the brand name Triumeq among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is a combination of three medications with different and complementary mechanisms of action: abacavir, dolutegravir and lamivudine.
Efavirenz/lamivudine/tenofovir (EFV/3TC/TDF), sold under the brand name Symfi among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It combines efavirenz, lamivudine, and tenofovir disoproxil. As of 2019, it is listed by the World Health Organization as an alternative first line option to dolutegravir/lamivudine/tenofovir. It is taken by mouth.
Bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide, sold under the brand name Biktarvy, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. One tablet, taken orally once daily, contains 50 mg bictegravir, 200 mg emtricitabine, and 25 mg tenofovir alafenamide. It was approved for use in the United States in February 2018, and for use in the European Union in June 2018.
Doravirine/lamivudine/tenofovir, sold under the brand name Delstrigo, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It contains doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir disoproxil. It is taken by mouth.
Dolutegravir/lamivudine/tenofovir (DTG/3TC/TDF) is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication used to treat HIV/AIDS. It is a combination of dolutegravir, lamivudine, and tenofovir disoproxil. As of 2019, it is listed by the World Health Organization (WHO) as the first line treatment for adults, with tenofovir/lamivudine/efavirenz as an alternative. It is taken by mouth.
Lamivudine/tenofovir disoproxil, sold under the brand name Cimduo among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment of HIV/AIDS in adults and children weighing more than 35 kilograms (77 lb). It contains lamivudine and tenofovir disoproxil. It is taken by mouth.











