 | |
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Empagliflozin | SGLT2 inhibitor |
| Linagliptin | DPP-4 inhibitor |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Glyxambi |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Professional Drug Facts |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
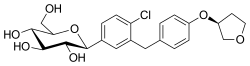
| Formula | C48H55ClN8O9 |
| Molar mass | 923.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Empagliflozin/linagliptin, sold under the brand name Glyxambi, is a fixed-dose combination anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. [5] [6] It is a combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin. [5] [6] It is taken by mouth. [5] [6]
Contents
The most common side effects include urinary infections, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infections . [5] [6]
It was approved for use in the United States in January 2015, [7] [8] for use in the European Union in November 2016, [6] and for use in Australia in December 2016. [2]