External links
![]() Media related to English Dialect Society at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to English Dialect Society at Wikimedia Commons
The English Dialect Society was the first dialect society founded in England. It was founded in 1873, but wound up after the publication of Joseph Wright's English Dialect Dictionary had begun.
Such a society was first proposed by Aldis Wright in 1870. It was founded in 1873 with W. W. Skeat as its secretary. The society's publications were divided into four series: bibliographies, reprinted glossaries, original glossaries and miscellanies. One unsatisfactory feature of the publications is that they are often arranged by counties whereas dialect boundaries rarely coincide with county boundaries. Some of the material published by the society was included in Joseph Wright's English Dialect Dictionary. Collectors of dialect words were discouraged from proposing etymologies on the ground that in so doing they might distort the meaning of the words they were collecting. In 1876 the society's headquarters was transferred from Cambridge to Manchester where it remained until a further transfer to Oxford in 1893. The society's library remained at Manchester and was presented to the Manchester Free Library. It consisted of some 800 books and pamphlets. John Howard Nodal became honorary secretary and director of the society in 1874. He continued in office to the dissolution of the society in 1896. The following year the first of the regional dialect societies in England was founded in Yorkshire. As of October 2021, this still exists as the Yorkshire Dialect Society.
The publications include:
![]() Media related to English Dialect Society at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to English Dialect Society at Wikimedia Commons

Pitmatic – originally 'pitmatical' – is a group of traditional Northern English dialects spoken in rural areas of the Great Northern Coalfield in England.

Sir Arthur Thomas Quiller-Couch was a British writer who published using the pseudonym Q. Although a prolific novelist, he is remembered mainly for the monumental publication The Oxford Book of English Verse 1250–1900 and for his literary criticism. He influenced many who never met him, including American writer Helene Hanff, author of 84, Charing Cross Road and its sequel, Q's Legacy. His The Oxford Book of English Verse was a favourite of John Mortimer's fictional character Horace Rumpole.

West Country English is a group of English language varieties and accents used by much of the native population of the West Country, an area found in the southwest of England.
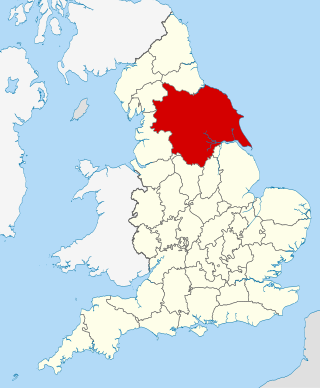
Yorkshire dialect, also known as Yorkshire English, Broad Yorkshire, Tyke, or Yorkie, is a grouping of several regionally neighbouring dialects of English spoken in the Yorkshire area of Northern England. The varieties have roots in Old English and are influenced to a greater extent by Old Norse than Standard English is. Yorkshire experienced drastic dialect levelling in the 20th century, eroding many traditional features, though variation and even innovations persist, at both the regional and sub-regional levels. Organisations such as the Yorkshire Dialect Society and the East Riding Dialect Society exist to promote the survival of the more traditional features.
The "Lyke-Wake Dirge" is a traditional English folk song and dirge listed as number 8194 in the Roud Folk Song Index. The song tells of the soul's travel, and the hazards it faces, on its way from earth to purgatory, reminding the mourners to practise charity during lifetime. Though it is from the Christian era and features references to Christianity, much of the symbolism is thought to be of pre-Christian origin.

Arthur Coke Burnell was an English civil servant who served in the Madras Presidency who was also a scholar in Sanskrit and Dravidian languages. He catalogued the Sanskrit manuscripts in southern India, particularly those in the collections of the Tanjore court collections. He was, with Henry Yule, a co-compiler of the Hobson-Jobson, a compendium of Anglo-Indian terms.
Robert Morton Nance (1873–1959) was a British writer and leading authority on the Cornish language, a nautical archaeologist, and joint founder of the Old Cornwall Society.
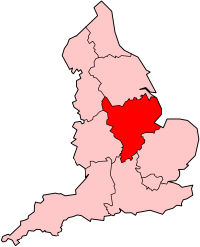
East Midlands English is a dialect, including local and social variations spoken in most parts of East Midlands England. It generally includes areas east of Watling Street, north of an isogloss separating it from variants of Southern English and East Anglian English, and south of another separating it from Northern English dialects.

Ranter Go Round is a primitive, traditional, English gambling game and children's game using playing cards that also nowadays goes under the name of Chase the Ace.
Margaret Ann Courtney was a Cornish poet and folklorist based in Penzance, Cornwall.

The Lancashire dialect refers to the Northern English vernacular speech of the English county of Lancashire. The region is notable for its tradition of poetry written in the dialect.

Joan the Wad is a mythological character in Cornish folklore. She is the Queen of the Pixies, which are tiny mythical creatures usually associated with the counties of Cornwall and Devon in England.

Jonathan Couch was a British naturalist, the only child of Richard and Philippa Couch, of a family long resident at Polperro, a small fishing village between Looe and Fowey, on the south coast of Cornwall. A blue plaque on the wall of Warren cottage commemorates his birthplace.
Charles Chorley was an English journalist, man of letters and translator from several languages.
John Howard Nodal (1831–1909) was an English journalist, linguistic and writer on dialect.
The Cornish dialect is a dialect of English spoken in Cornwall by Cornish people. Dialectal English spoken in Cornwall is to some extent influenced by Cornish grammar, and often includes words derived from the Cornish language. The Cornish language is a Celtic language of the Brythonic branch, as are the Welsh and Breton languages. In addition to the distinctive words and grammar, there are a variety of accents found within Cornwall from the north coast to that of the south coast and from east to west Cornwall. Typically, the accent is more divergent from Standard British English the further west through Cornwall one travels. The speech of the various parishes being to some extent different from the others was described by John T. Tregellas and Thomas Quiller Couch towards the end of the 19th century. Tregellas wrote of the differences as he understood them and Couch suggested the parliamentary constituency boundary between the East and West constituencies, from Crantock to Veryan, as roughly the border between eastern and western dialects. To this day, the towns of Bodmin and Lostwithiel as well as Bodmin Moor are considered the boundary.
A crowdy-crawn is a wooden hoop covered with sheepskin used as a percussion instrument in western Cornwall at least as early as 1880. It is similar to the Irish bodhrán. It is used by some modern Cornish traditional music groups as a solo or accompaniment instrument. The name crowdy-crawn is derived from the Cornish "croder croghen," literally "skin sieve," sometimes shortened to "crowd."

Black pudding is a distinct national type of blood sausage originating in the United Kingdom and Ireland. It is made from pork or occasionally beef blood, with pork fat or beef suet, and a cereal, usually oatmeal, oat groats, or barley groats. The high proportion of cereal, along with the use of certain herbs such as pennyroyal, serves to distinguish black pudding from blood sausages eaten in other parts of the world.

Louisa Sarah Ann Parr was a British writer who published some of her work under the name Mrs Olinthus Lobb.

A riddle drum is a makeshift frame drum used in traditional English folk music. Originally, they were large agricultural riddle sieves used for winnowing corn, made from sheepskin stretched across a wooden frame. Agricultural workers found these made excellent percussion instruments, and developed unique rhythms and playing styles.