Environmental reporting may refer to:
Environmental reporting may refer to:
To invest is to allocate money in the expectation of some benefit/return in the future. In other words, to invest means owning an asset or an item with the goal of generating income from the investment or the appreciation of your investment which is an increase in the value of the asset over a period of time. When you invest it always requires a sacrifice of some present asset that you own today such as time, money, or effort.
Environmental full-cost accounting (EFCA) is a method of cost accounting that traces direct costs and allocates indirect costs by collecting and presenting information about the possible environmental, social and economical costs and benefits or advantages – in short, about the "triple bottom line" – for each proposed alternative. It is also known as true-cost accounting (TCA), but, as definitions for "true" and "full" are inherently subjective, experts consider both terms problematical.

The ecological footprint is a method promoted by the Global Footprint Network to measure human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people or an economy. It tracks this demand through an ecological accounting system. The accounts contrast the biologically productive area people use for their consumption to the biologically productive area available within a region or the world. In short, it is a measure of human impact on the environment.
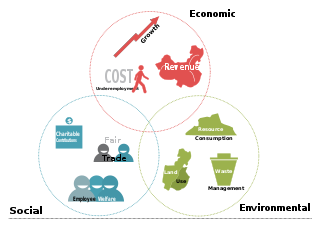
The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental and financial. Some organizations have adopted the TBL framework to evaluate their performance in a broader perspective to create greater business value. Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase in 1994.
The green gross domestic product is an index of economic growth with the environmental consequences of that growth factored into a country's conventional GDP. Green GDP monetizes the loss of biodiversity, and accounts for costs caused by climate change. Some environmental experts prefer physical indicators, which may be aggregated to indices such as the "Sustainable Development Index".

Life-cycle assessment or LCA is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life-cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of a manufactured product, environmental impacts are assessed from raw material extraction and processing (cradle), through the product's manufacture, distribution and use, to the recycling or final disposal of the materials composing it (grave).
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."

An annual report is a comprehensive report on a company's activities throughout the preceding year. Annual reports are intended to give shareholders and other interested people information about the company's activities and financial performance. They may be considered as grey literature. Most jurisdictions require companies to prepare and disclose annual reports, and many require the annual report to be filed at the company's registry. Companies listed on a stock exchange are also required to report at more frequent intervals.

Food miles is the distance food is transported from the time of its making until it reaches the consumer. Food miles are one factor used when testing the environmental impact of food, such as the carbon footprint of the food.
Sustainability reporting enables organizations to report on environmental and social performance. It is not just report generation from collected data; instead it is a method to internalize and improve an organization’s commitment to sustainable development in a way that can be demonstrated to both internal and external stakeholders.Sustainability reports help companies build consumer confidence and improve corporate reputations through social responsibility programs and transparent risk management.
Carbon accounting or greenhouse gas accounting refers to processes used to measure how much carbon dioxide equivalents an organization emits. It is used by states, corporations, and individuals to create the carbon credit commodity traded on carbon markets. Examples of products based on forms of carbon accounting may be found in national inventories, corporate environmental reports, and carbon footprint calculators.

The CDP is an international non-profit organisation based in the United Kingdom, Germany and the United States of America that helps companies and cities disclose their environmental impact. It aims to make environmental reporting and risk management a business norm, driving disclosure, insight, and action towards a sustainable economy. Since 2002 over 8,400 companies have publicly disclosed environmental information through CDP.

Sustainability accounting was originated about 20 years ago and is considered a subcategory of financial accounting that focuses on the disclosure of non-financial information about a firm's performance to external stakeholders, such as capital holders, creditors, and other authorities. Sustainability accounting represents the activities that have a direct impact on society, environment, and economic performance of an organisation. Sustainability accounting in managerial accounting contrasts with financial accounting in that managerial accounting is used for internal decision making and the creation of new policies that will have an effect on the organisation's performance at economic, ecological, and social level. Sustainability accounting is often used to generate value creation within an organisation.
Sustainability measurement is the quantitative basis for the informed management of sustainability. The metrics used for the measurement of sustainability are still evolving: they include indicators, benchmarks, audits, indexes and accounting, as well as assessment, appraisal and other reporting systems. They are applied over a wide range of spatial and temporal scales. Most recently, an article proposed a methodology for sustainability monitoring that is based on testing longitudinally normal distribution of intents and behaviors that pursue sustainability goals.
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is a ratio between net income and investment. A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favourably to its cost. As a performance measure, ROI is used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiencies of several different investments. In economic terms, it is one way of relating profits to capital invested.

Environmental issues are harmful effects of human activity on the biophysical environment. Environmental protection is a practice of protecting the natural environment on the individual, organizational or governmental levels, for the benefit of both the environment and humans. Environmentalism, a social and environmental movement, addresses environmental issues through advocacy, education and activism.
An environmental profit and loss account is a company's monetary valuation and analysis of its environmental impacts including its business operations and its supply chain from cradle-to-gate. An E P&L internalizes externalities and monetizes the cost of business to nature by accounting for the ecosystem services a business depends on to operate in addition to the cost of direct and indirect negative impacts on the environment. The primary purpose of an E P&L is to allow managers and stakeholders to see the magnitude of these impacts and where in the supply chain they occur.
Natural capital accounting is the process of calculating the total stocks and flows of natural resources and services in a given ecosystem or region. Accounting for such goods may occur in physical or monetary terms. This process can subsequently inform government, corporate and consumer decision making as each relates to the use or consumption of natural resources and land, and sustainable behaviour.
Social accounting is the process of communicating the social and environmental effects of organizations' economic actions to particular interest groups within society and to society at large. Social Accounting is different from public interest accounting as well as from critical accounting.

Cowspiracy: The Sustainability Secret is a 2014 documentary film which explores the impact of animal agriculture on the environment, and investigates the policies of a few environmental organizations on this issue. The film looks at various environmental concerns, including global warming, water use, deforestation, and ocean dead zones, and suggests that animal agriculture is the primary source of environmental destruction.