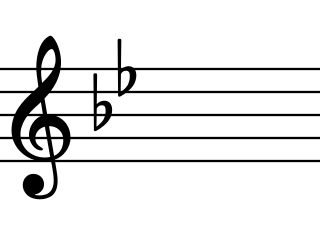In music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps, depending on their position in the scale. This pattern ensures that, in a diatonic scale spanning more than one octave, all the half steps are maximally separated from each other.

In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios of frequencies. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals consist of tones from a single harmonic series of an implied fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth.
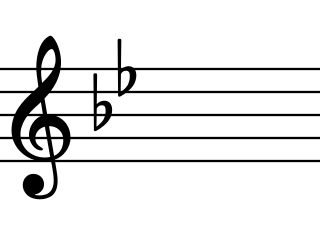
In Western musical notation, a key signature is a set of sharp, flat, or rarely, natural symbols placed on the staff at the beginning of a section of music. The initial key signature in a piece is placed immediately after the clef at the beginning of the first line. If the piece contains a section in a different key, the new key signature is placed at the beginning of that section.

Music notation or musical notation is any system used to visually represent aurally perceived music played with instruments or sung by the human voice through the use of written, printed, or otherwise-produced symbols, including notation for durations of absence of sound such as rests.
In music, an octave or perfect octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems". The interval between the first and second harmonics of the harmonic series is an octave.
In music theory, a scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch. A scale ordered by increasing pitch is an ascending scale, and a scale ordered by decreasing pitch is a descending scale.

A clef is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical staff. Placing a clef on a staff assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines or four spaces, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces.
In Western musical notation, the staff or stave (UK) is a set of five horizontal lines and four spaces that each represent a different musical pitch or in the case of a percussion staff, different percussion instruments. Appropriate music symbols, depending on the intended effect, are placed on the staff according to their corresponding pitch or function. Musical notes are placed by pitch, percussion notes are placed by instrument, and rests and other symbols are placed by convention.
In music, sharp, dièse, or diesis means, "higher in pitch". More specifically, in musical notation, sharp means "higher in pitch by one semitone ". A sharp is the opposite of a flat, a lowering of pitch. The ♯ symbol itself is conjectured to be a condensed form of German ligature ſch or the symbol ƀ.
In music, flat means "lower in pitch". Flat is the opposite of sharp, which is a raising of pitch. In musical notation, flat means "lower in pitch by one semitone ", notated using the symbol ♭ which is derived from a stylised lowercase 'b'.

In music theory, a perfect fifth is the musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so.

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of pitches consisting of multiple notes that are sounded simultaneously, or nearly so. For many practical and theoretical purposes, arpeggios and other types of broken chords may also be considered as chords in the right musical context.

In music theory, the circle of fifths is a way of organizing the 12 chromatic pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths.. If C is chosen as a starting point, the sequence is: C, G, D, A, E, B, F♯, C♯, A♭, E♭, B♭, F. Continuing the pattern from F returns the sequence to its starting point of C. This order places the most closely related key signatures adjacent to one another. It is usually illustrated in the form of a circle.
In musical notation, a bar is a segment of music bounded by vertical lines, known as bar lines, usually indicating one of more recurring beats. The length of the bar, measured by the number of note values it contains, is normally indicated by the time signature.
In music, an accent is an emphasis, stress, or stronger attack placed on a particular note or set of notes, or chord, either as a result of its context or specifically indicated by an accent mark. Accents contribute to the articulation and prosody of a performance of a musical phrase. Accents may be written into a score or part by a composer, or added by the performer as part of their interpretation of a musical piece.

Piano tuning is the act of adjusting the tension of the strings of an acoustic piano so that the musical intervals between strings are in tune. The meaning of the term 'in tune', in the context of piano tuning, is not simply a particular fixed set of pitches. Fine piano tuning requires an assessment of the vibration interaction among notes, which is different for every piano, thus in practice requiring slightly different pitches from any theoretical standard. Pianos are usually tuned to a modified version of the system called equal temperament.
Svara is a word that connotes simultaneously a breath, a vowel, the sound of a musical note corresponding to its name, and the successive steps of the octave or saptaka. More comprehensively, it is the ancient Indian concept about the complete dimension of musical pitch. Most of the time a svara is identified as both musical note and tone, but a tone is a precise substitute for sur, related to tunefulness. Traditionally, Indians have just seven svaras/notes with short names, e.g. saa, re/ri, ga, ma, pa, dha, ni which Indian musicians collectively designate as saptak or saptaka. It is one of the reasons why svara is considered a symbolic expression for the number seven.
Musicians use various kinds of chord names and symbols in different contexts to represent musical chords. In most genres of popular music, including jazz, pop, and rock, a chord name and its corresponding symbol typically indicate one or more of the following:
- the root note,
- the chord quality,
- whether the chord is a triad, seventh chord, or an extended chord,
- any altered notes,
- any added tones, and
- the bass note if it is not the root.

Swaralipi is any system used in sheet music in order to represent aurally perceived music through the use of written notes for Indian classical music.