Related Research Articles
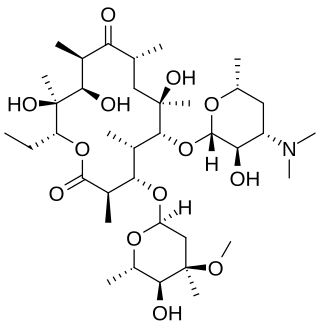
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used during pregnancy to prevent Group B streptococcal infection in the newborn, as well as to improve delayed stomach emptying. It can be given intravenously and by mouth. An eye ointment is routinely recommended after delivery to prevent eye infections in the newborn.

Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for humans. It is a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal, retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids. Vitamin A has multiple functions: it is essential for embryo development and growth, for maintenance of the immune system, and for vision, where it combines with the protein opsin to form rhodopsin – the light-absorbing molecule necessary for both low-light and color vision.

Acne, also known as acne vulgaris, is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to lack of confidence, anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide.

A scar is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation.

Isotretinoin, also known as 13-cis-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication primarily used to treat severe acne. It is also used to prevent certain skin cancers, and in the treatment of other cancers. It is used to treat harlequin-type ichthyosis, a usually lethal skin disease, and lamellar ichthyosis. It is a retinoid, meaning it is related to vitamin A, and is found in small quantities naturally in the body. Its isomer, tretinoin, is also an acne drug.

Seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Dandruff is a milder form of the condition without inflammation.
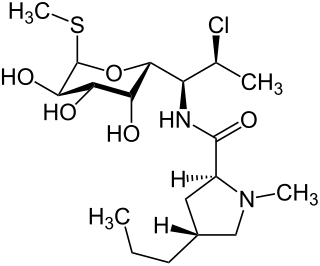
Clindamycin is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media, and endocarditis. It can also be used to treat acne, and some cases of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In combination with quinine, it can be used to treat malaria. It is available by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as a cream or a gel to be applied to the skin or in the vagina.

Tretinoin, also known as all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For leukemia, it is taken by mouth for up to three months. Topical tretinoin is also the most extensively investigated retinoid therapy for photoaging.
ATC code D10Anti-acne preparations is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup D10 is part of the anatomical group D Dermatologicals.

The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth.
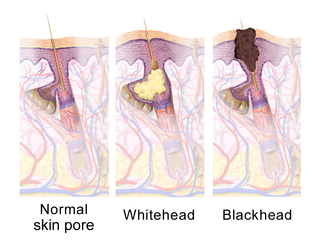
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word "comedo" comes from the Latin comedere, meaning "to eat up", and was historically used to describe parasitic worms; in modern medical terminology, it is used to suggest the worm-like appearance of the expressed material.

Azelaic acid (AzA) is a organic compound with the formula HOOC(CH2)7COOH. This saturated dicarboxylic acid exists as a white powder. It is found in wheat, rye, and barley. It is a precursor to diverse industrial products including polymers and plasticizers, as well as being a component of a number of hair and skin conditioners. AzA inhibits tyrosinase.

Clindamycin/benzoyl peroxide is a topical gel used for the treatment of acne. It is a combination of clindamycin, an antibiotic, and benzoyl peroxide, an antiseptic.
Benzamycin is a topical gel containing of 5% benzoyl peroxide and 3% erythromycin. Its main usage is to fight acne. Benzamycin is a prescription medication.
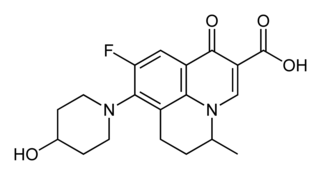
Nadifloxacin is a topical fluoroquinolone antibiotic for the treatment of acne vulgaris. It is also used to treat bacterial skin infections.
Acne conglobata is a highly inflammatory disease presenting with comedones, nodules, abscesses, and draining sinus tracts.
Acne miliaris necrotica is a rare condition consisting of follicular vesicopustules, sometimes occurring as solitary lesions that are usually very itchy. The condition affects middle aged and elderly individuals. Affected areas can include the scalp, frontal hairline, face, and chest.

A pimple is a kind of comedo that results from excess sebum and dead skin cells getting trapped in the pores of the skin. In its aggravated state, it may evolve into a pustule or papules. Pimples can be treated by acne medications, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatories prescribed by a physician, or various over the counter remedies purchased at a pharmacy.
Infantile acne is a form of acneiform eruption that occurs in infants from 6 weeks to 1 year of age. Typical symptoms include inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions, papules and pustules most commonly present on the face. No cause of infantile acne has been established but it may be caused by increased sebaceous gland secretions due to elevated androgens, genetics and the fetal adrenal gland causing increased sebum production. Infantile acne can resolve by itself by age 1 or 2 however treatment options include topical benzyl peroxide, topical retinoids and topical antibiotics in most cases.

Glyceryl octyl ascorbic acid (GO-VC) is an amphipathic derivative of vitamin C consisting of two ether linkages: a 1-octyl at position 2 and a glycerin at position 3. The chemical name is 2-glyceryl-3-octyl ascorbic acid. The isomer in which these two groups are swapped is also known.
References
- 1 2 "Isotrexin Gel (isotretinoin 0.05%/erythromycin 2%)" (PDF). mhra.gov.uk. Stiefel Laboratories Ltd.
- ↑ Marshall H (10 May 2017). "Isotrexin gel (isotretinoin, erythromycin)". Netdoctor. Retrieved 2016-05-10.