
A dual carriageway (BrE) or a divided highway (AmE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are designed to higher standards with controlled access are generally classed as motorways, freeways, etc., rather than dual carriageways.
King's Highway 409, commonly referred to as Highway 409 and historically as the Belfield Expressway, is a 400-series highway in the Canadian province of Ontario that extends from Highway 401 in Toronto to Pearson International Airport, west of Highway 427, in Mississauga. It is a short freeway used mainly as a spur route for traffic travelling to the airport or Highway 427 northbound from Highway 401 westbound, as these route movements are not accommodated at the complex interchange between Highways 401 and 427.

The expressways of Singapore are special roads that allow motorists to travel quickly from one urban area to another. Construction of the system was authorized when construction of the Pan Island Expressway began in 1962. All of them are dual carriageways with grade-separated access. They usually have three to four lanes in each direction, although there are two-lane carriageways at many expressway intersections and five-lane carriageways in some places. There are ten expressways. Studies about the feasibility of additional expressways are ongoing.
The Hanlon Expressway or Hanlon Parkway is a high-capacity at-grade suburban limited-access road connecting Highway 401 with the city of Guelph in the Canadian province of Ontario. The 17 km (11 mi) route travels in a generally north–south direction on the city's west side. It is signed as Highway 6 for its entire length; from Wellington Street to Woodlawn Road it is concurrent with Highway 7. The speed limit alternates between 70 and 80 km/h.

The road hierarchy categorizes roads according to their functions and capacities. While sources differ on the exact nomenclature, the basic hierarchy comprises freeways, arterials, collectors, and local roads. Generally, the functional hierarchy can more or less correspond to the hierarchy of roads by their owner or administrator.

A limited-access road, known by various terms worldwide, including limited-access highway, dual-carriageway, expressway, and partial controlled-access highway, is a highway or arterial road for high-speed traffic which has many or most characteristics of a controlled-access highway, including limited or no access to adjacent property, some degree of separation of opposing traffic flow, use of grade separated interchanges to some extent, prohibition of slow modes of transport, such as bicycles, horse-drawn vehicles or ridden horses, or self-propelled agricultural machines; and very few or no intersecting cross-streets or level crossings. The degree of isolation from local traffic allowed varies between countries and regions. The precise definition of these terms varies by jurisdiction.

Federal Highways are a series of highways in Mexico. These highways link the nation's 32 federal entities with each other or with a neighboring country, and they are wholly or mostly built by Mexico's federal government with federal funds or through federal grants by individuals, states, or municipalities. Locally known as federal highway corridors, they are built and maintained by Mexico's Secretariat of Communications and Transportation. Federal Highways in Mexico can be classified into high-speed, limited access expressways and low-speed roads with non-limited access; not all corridors are completely improved.
Black Creek Drive is an expressway or arterial road in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. A four-lane route that runs north–south, it connects Weston Road and Humber Boulevard with Highway 401 via Highway 400, the latter of which it forms a southerly extension. Black Creek Drive officially transitions into Highway 400 at the Maple Leaf Drive overpass, southeast of the Jane Street interchange. The roadway is named after the Black Creek ravine, which it parallels for most of its route. It features a maximum speed limit of 70 km/h (43 mph). As part of the municipal system of expressways, it is patrolled by the Toronto Police Service.

A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway, and expressway. Other similar terms include throughway or thruway and parkway. Some of these may be limited-access highways, although this term can also refer to a class of highways with somewhat less isolation from other traffic.
The Federal Route 2 is a major east–west oriented federal highway in Malaysia. The 276.9 kilometres (172 mi) road connects Port Klang in Selangor to Kuantan Port in Pahang. The Federal Route 2 became the backbone of the road system linking the east and west coasts of Peninsula Malaysia before being surpassed by the East Coast Expressway E8.

A road is a thoroughfare, route, or way on land between two places that has been surfaced or otherwise improved to allow travel by foot or some form of conveyance, including a motor vehicle, cart, bicycle, or horse. Roads have been adapted to a large range of structures and types in order to achieve a common goal of transportation under a large and wide range of conditions. The specific purpose, mode of transport, material and location of a road determine the characteristics it must have in order to maximize its usefulness. Following is one classification scheme.

A two-lane expressway or two-lane freeway is an expressway or freeway with only one lane in each direction, and usually no median barrier. It may be built that way because of constraints, or may be intended for expansion once traffic volumes rise. The term super two is often used by roadgeeks for this type of road, but traffic engineers use that term for a high-quality surface road. Most of these roads are not tolled.

The Hunter Expressway is a 39.5-kilometre (24.5 mi) long controlled-access highway in New South Wales, Australia. It was previously known as the F3 to Branxton link or Kurri Kurri Corridor during the planning stage. It has two lanes in each direction, running generally north west from the Pacific Motorway at the Newcastle Link Road interchange to the eastern end of the Belford Bends Deviation on the New England Highway north of Branxton. The road allows traffic to bypass the Maitland area, Lochinvar, Greta and Branxton. The expressway opened on 22 March 2014.
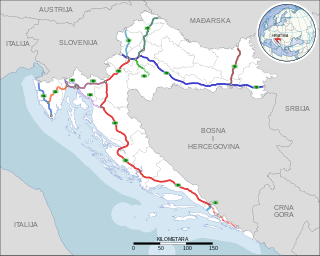
Highways in Croatia are the main transport network in Croatia. The Croatian classification includes several classes of highways:

Expressways are the highest class of roads in India. In July 2023, the total length of expressways in India was 5,930 km (3,680 mi), with 10,225.69 km (6,353.95 mi) under construction. These are controlled-access highways where entrance and exits are controlled by the use of cloverleaf or trumpet or grade separated interchanges that are incorporated into the design of the expressway and designed for maximum speed of 120 km/h, whereas National highways are flyover access or tolled, where entrance and exit is through the side of the flyover, at each intersection of highway with road, flyovers are provided to bypass the city/town/village traffic and these highways are designed for speed of 100 km/h. Some roads are not access-controlled expressways but are still named expressways, such as the Bagodara–Tarapur Expressway, Biju Expressway, these are actually state highways that are not declared by the central government as an Expressway, hence not an Expressway or National Highway.
This article describes the highway systems available in selected countries.

The Malaysian Expressway System is a network of national controlled-access expressways in Malaysia that forms the primary backbone network of Malaysian national highways. The network begins with the Tanjung Malim–Slim River tolled road which was opened to traffic on 16 March 1966, later North–South Expressway (NSE), and is being substantially developed. Malaysian expressways are built by private companies under the supervision of the government highway authority, Malaysian Highway Authority.
National Highway 66, commonly referred to as NH 66, is a mostly 4 lane 1640 km long busy National Highway that runs roughly north–south along the western coast of India, parallel to the Western Ghats. It connects Panvel, a city east of Mumbai to Cape Comorin (Kanyakumari), passing through the states of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
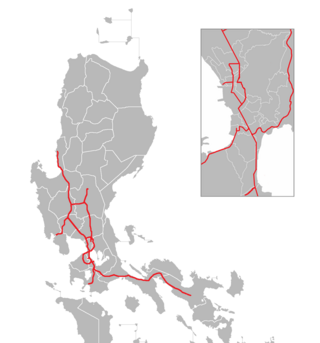
The Philippine expressway network, also known as the High Standard Highway Network, is a controlled-access highway network managed by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) which consists of all expressways and regional high standard highways in the Philippines.












