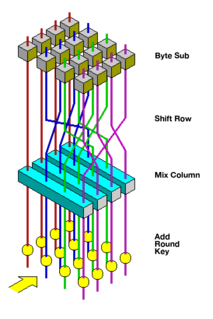
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael, is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001.

The Data Encryption Standard is a symmetric-key algorithm for the encryption of digital data. Although its short key length of 56 bits makes it too insecure for modern applications, it has been highly influential in the advancement of cryptography.
The Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) of the United States are a set of publicly announced standards that the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed for use in computer systems of non-military, American government agencies and contractors. FIPS standards establish requirements for ensuring computer security and interoperability, and are intended for cases in which suitable industry standards do not already exist. Many FIPS specifications are modified versions of standards the technical communities use, such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
The U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) used to rank cryptographic products or algorithms by a certification called product types. Product types were defined in the National Information Assurance Glossary which used to define Type 1, 2, 3, and 4 products. The definitions of numeric type products have been removed from the government lexicon and are no longer used in government procurement efforts.
The Federal Information Processing Standard Publication 6-4 is a five-digit Federal Information Processing Standards code which uniquely identified counties and county equivalents in the United States, certain U.S. possessions, and certain freely associated states.
The Federal Information Processing Standard Publication 140-2,, is a U.S. government computer security standard used to approve cryptographic modules. The title is Security Requirements for Cryptographic Modules. Initial publication was on May 25, 2001, and was last updated December 3, 2002.

The Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 is a United States federal law enacted in 2002 as Title III of the E-Government Act of 2002. The act recognized the importance of information security to the economic and national security interests of the United States. The act requires each federal agency to develop, document, and implement an agency-wide program to provide information security for the information and information systems that support the operations and assets of the agency, including those provided or managed by another agency, contractor, or other source.
The 140 series of Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) are U.S. government computer security standards that specify requirements for cryptography modules.
NSA Suite B Cryptography was a set of cryptographic algorithms promulgated by the National Security Agency as part of its Cryptographic Modernization Program. It was to serve as an interoperable cryptographic base for both unclassified information and most classified information.
SHA-2 is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and first published in 2001. They are built using the Merkle–Damgård construction, from a one-way compression function itself built using the Davies–Meyer structure from a specialized block cipher.

IDEF0, a compound acronym, is a function modeling methodology for describing manufacturing functions, which offers a functional modeling language for the analysis, development, reengineering and integration of information systems, business processes or software engineering analysis.

FIPS 201 is a United States federal government standard that specifies Personal Identity Verification (PIV) requirements for Federal employees and contractors.

IT security standards or cyber security standards are techniques generally outlined in published materials that attempt to protect the cyber environment of a user or organization. This environment includes users themselves, networks, devices, all software, processes, information in storage or transit, applications, services, and systems that can be connected directly or indirectly to networks.
Information technology risk, IT risk, IT-related risk, or cyber risk is any risk related to information technology. While information has long been appreciated as a valuable and important asset, the rise of the knowledge economy and the Digital Revolution has led to organizations becoming increasingly dependent on information, information processing and especially IT. Various events or incidents that compromise IT in some way can therefore cause adverse impacts on the organization's business processes or mission, ranging from inconsequential to catastrophic in scale.
NIST Special Publication 800-53 provides a catalog of security and privacy controls for all U.S. federal information systems except those related to national security. It is published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, which is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce. NIST develops and issues standards, guidelines, and other publications to assist federal agencies in implementing the Federal Information Security Modernization Act of 2014 (FISMA) and to help with managing cost effective programs to protect their information and information systems.
The Federal Information Processing Standard Publication 140-3,, is a U.S. government computer security standard used to approve cryptographic modules. The title is Security Requirements for Cryptographic Modules. Initial publication was on March 22, 2019 and it supersedes FIPS 140-2.
Managed Trusted Internet Protocol Service (MTIPS) was developed by the US General Services Administration (GSA) to allow US Federal agencies to physically and logically connect to the public Internet and other external connections in compliance with the Office of Management and Budget's (OMB) Trusted Internet Connection (TIC) Initiative.

The Risk Management Framework (RMF) is a United States federal government guideline, standard and process for risk management to help secure information systems developed by National Institute of Standards and Technology. The Risk Management Framework (RMF), illustrated in the diagram to the right, provides a disciplined and structured process that integrates information security, privacy and risk management activities into the system development life cycle.
The National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence (NCCoE) is a US government organization that builds and publicly shares solutions to cybersecurity problems faced by U.S. businesses. The center, located in Rockville, Maryland, was established in 2012 through a partnership with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the state of Maryland, and Montgomery County. The center is partnered with nearly 20 market-leading IT companies, which contribute hardware, software and expertise.
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is an assessment framework and assessor certification program designed to increase the trust in measures of compliance to a variety of standards published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology






