Related Research Articles

The Tellermine 42 (T.Mi.42) was a German metal-cased anti-tank blast mine used during the Second World War. The mine was a development of the Tellermine 35 with improved resistance to blast. It was followed by the simplified Tellermine 43.

The PROM-1 is a Yugoslavian manufactured bounding anti-personnel mine. It consists of a cylindrical body with a pronged fuze inserted into the top of the mine. It is broadly similar in operation to the German S-mine.
The PMN series of blast anti-personnel mines were designed and manufactured in the Soviet Union. They are one of the most widely used and commonly found devices during demining operations. They are sometimes nicknamed "black widow" because of their dark casings.
The TMD-44 and TMD-B are simple rectangular Soviet wooden box cased anti-tank blast mines, they were both used during the Second World War. Both mines are similar in design, differing only in fuzing mechanism. The wooden construction of both the mines makes them unpredictable as rot and insects can eat away the wooden case, reducing activation pressure to as little as 3 kg. Both mines are found in a number of countries including Afghanistan, Angola, Chad, Cuba, Egypt, Korea, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, Yemen, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
The PT Mi-K is a Czechoslovakian metal-cased anti-tank blast landmine. The mine uses a metal grid instead a pressure plate, this gives it resistance to overpressure. The mine is no longer produced, but is found in Afghanistan, Cambodia, Eritrea, Namibia, Nicaragua and the Western Sahara.
The M7 is a small, metal-cased United States anti-tank blast mine that was used during the Second World War. It was based on the British Hawkins grenade. Approximately 2.5 million were produced before production ceased, and although it has long since been withdrawn from U.S. service, it can be found in Angola, Burma, Cambodia, Chad, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Korea, Lebanon, Myanmar, Somalia, Thailand, and Zambia.

The FMK-3 is a fibreglass cased Argentine anti-tank blast mine. It is produced by Direccion General de Fabricaciones Militares. The mine actually uses a FMK-1 anti-personnel mine as a fuze, the FMK-1 is modified with a pressure cap to increase the activation pressure. Argentina's stock of FMK-1 mines was modified in 2003 to prevent their use as anti-personnel mines, this involved welded an additional plastic pressure cap onto the mine. The mine has very little metal content, although an optional detection ring is provided with the FMK-1.
The M21 is a circular United States anti-tank landmine that uses a Misznay Schardin effect warhead. The mine uses an M607 pressure fuse, which can be adapted as a tilt rod fuze. The mine is triggered either by pressure, or by the tilt rod being forced beyond 20 degrees from the vertical by a force of more than 1.7 kg, either of these actions results in pressure being transferred via a bearing cap to a Belleville spring, which inverts, driving the firing pin into the M46 detonator. The M46 charge first ignites a black powder charge, which blows off the mine's cover, and clears any earth or debris that may have been on top of the mine. A fraction of a second later the main warhead detonates, driving and compressing a steel plate upwards, with enough force to penetrate 76 mm of armour at a distance of 530 mm. Approximately 200,000 M21 mines were produced in the U.S. and licensed copies, the K441 and K442, were produced in South Korea.
The P2 Mk2 and P3 Mk2 are Pakistani plastic cased minimum metal anti-tank blast mines. The P2 Mk2 has a square case with a central circular ribbed pressure plate, the P3 is circular with a central circular pressure plate. Both mines use anti-personnel mines as the fuse, typically the either the P4 Mk1 or P2 Mk2 anti-personnel mines. The anti-personnel mine sits in a cavity below the pressure plate, when enough pressure is place on the pressure plate of the mine, it collapses onto the anti-personnel mine triggering it and the main charge which sits below it. A yellow canvas carrying strap is normally fitted to the side of the mine. The mines have a secondary fuse well on the bottom which can be used with anti-handling devices. A GLM-2 electronic booby trap can be fitted to the cavity under the pressure plate. The mine is supplied with a steel disc which makes the mine more easily detectable, although this is seldom used. Since 1997 only a detectable version of the mine has been produced, and to comply with the Convention on Conventional Weapons amended protocol II, Pakistani stocks of the mine are being retrofitted with steel detection discs. The mines are found in Afghanistan, Angola, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Pakistan, Somalia, and Tajikistan.

The TMA-1 and TMA-1A are circular, plastic cased Yugoslavian minimum metal anti-tank blast mine. The mine consists of an upper plastic pressure plate, and the lower body containing the main charge. The pressure plate has eight triangular raised sectors, and a central fuze cap. The pressure plate is held in place by four plastic pins, which when suffient pressure is applied, shear allowing the pressure plate to collapse onto the mine body, triggering the UANU-1 fuze. A secondary fuze well is provided in the base of the mine, allowing the use of anti-handling devices. The mine is found in Bosnia, Croatia and Kosovo.

The TMA-2 is a rectangular plastic cased Yugoslavian minimum metal anti-tank blast mine. It is very similar in appearance and size to the PT-56, which it replaced. The mine consists of two sections, an upper ribbed pressure plate with two large circular fuze caps, and a lower base section containing the main charge and two primary fuze wells containing UANU-1 fuzes. A secondary fuze well is provided in the base of the mine for an anti-handling device.
The TMA-5 and TMA-5A are rectangular plastic cased Yugoslavian minimum metal anti-tank blast mines. The mine's top surface has a single circular threaded fuze cap in the center, covering the fuze well. Additionally there is a small compartment for storing the fuze when disarmed. The corners of the mine have small posts to permit stacking of the mine. Although the mine does not have a secondary fuze well, it could easily be fitted with an improvised one in the field. The mine uses a single black plastic UANU-1 fuze.
The TMD-1 and TMD-2 are Yugoslavian wooden cased anti-tank blast mines, similar to the Russian TMD-B. The box consists of a wooden box, which contains the main cast TNT main charge. A webbing carrying handle is provided on one side of the mine. The fuze is placed in a central detonation well under the centre board of three that are fixed to the top of the mine. When sufficient pressure is placed on the boards, they collapse inwards, pressing on the installed fuze triggering the mine.

The VS-JAP is an Italian bounding anti-personnel mine. It is the latest of the Valmara family of bounding mines that includes the Valmara 59 and Valmara 69. The mine has a waterproof plastic faceted cylindrical body with a three-pronged cap, with a central fixing point for a tripwire. The fuze is triggered via downward or sideways pressure.

The FMK-1 is a small circular Argentina anti-personnel blast mine which, when fitted with a stiffened pressure plate, is also used as the fuze for the FMK-3 and FMK-5 anti-tank mines. The mine has a circular plastic body, with a number of small ribs running vertically around the outside of the mine, with the circular detonator and striker protruding on each side. The pressure plate has a distinctive six pointed star shape ribbing for stiffness. The bottom of the mine has small base plug inside which a small stud is installed. The stud increases the activation pressure of the mine. A metal detector disc can be added to the bottom of the mine, but it is not often used. It is actually in service with the Argentine Army.
The T-AB-1 is a rectangular plastic cased Brazilian anti-tank blast mine. The mine uses a T-AB-1 anti-personnel mine as a fuze. The AP mine is inserted into the body of the AT mine under a large stiff ABS plastic pressure plate. The pressure plate is fastened in place by a number of shear pins, which are designed to give way under a pressure of 200 kg. The AP mine under the pressure plate is then triggered, triggering the mine's main charge.
The Min AP NM AE T1 is a small Brazilian minimum metal anti-personnel mine. The mine has a plastic case in the form of a truncated cone. with a small protruding fuse and pressure plate. The small size of the pressure plate gives the mine some blast resistance. The main charge is in the form of a small inverted cone which generates a shaped charge effect when detonated.
The TM-44 was a circular metal-cased Soviet anti-tank landmine used during the Second World War. The mine's case consisted of a short cylinder with the entire top surface being used as a pressure plate. The mine was normally painted olive drab and was broadly similar to the earlier, smaller, TM-41 mine.

The Anti-Tank Mine General Service Mark II was a British anti-tank blast mine used during the Second World War. It consisted of a body about 7.5 in (190 mm) in diameter and 3.25 in (83 mm). The mine has a central fuze well accessed from the bottom, with a main charge in a cavity around the well consisting of about 4 lb (1.8 kg) of TNT. The mine is fitted with a thin brass cover, which acts as a pressure plate. The cover is suspended over the main body of the main by four leaf springs. A Sorbo ring can be fitted between the cover and the mine body, which absorbs shock and blast and allows the mines to be planted as close as two feet (0.61 m) without causing sympathetic detonation.
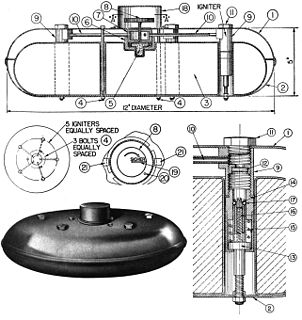
The L.P.Z. mine or Leichte Panzermine was a circular, metal-cased German anti-tank mine produced during the Second World War. The mine was accepted into service in 1941, and were intended for use by Paratroops. Production of the mine ended in 1942 with only 31,700 mines produced. The mines were first used during Operation Merkur, the airborne invasion of Crete and were still in use at the end of the war.
References
- Jane's Mines and Mine Clearance 2005-2006