
Palestinian refugee camps are camps set up by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UNRWA) in Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to accommodate Palestinian refugees registered with UNRWA, who fled or were expelled during the 1948 Palestinian exodus after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War or in the aftermath of the Six-Day War in 1967, and their patrilineal descendants. There are 68 Palestinian refugee camps, 58 official and 10 unofficial, ten of which were established after the Six-Day War while the others were established in 1948 to 1950s.
Issues relating to the State of Israel and aspects of the Arab–Israeli conflict and more recently the Iran-Israel conflict occupy repeated annual debate times, resolutions and resources at the United Nations. Since its founding in 1948, the United Nations Security Council, has adopted 79 resolutions directly related to the Arab–Israeli conflict as of January 2010.
The United Nations Mission of Observers in Tajikistan (UNMOT) was a peacekeeping mission established by the United Nations Security Council in December 1994 and extended on several occasions until its mandate expired in May 2000. Its purpose was to monitor peace agreements during and after the Tajikistan Civil War. The observers were first deployed in the wake of the ceasefire, in 1994, between the ruling government of Tajikistan, led by Emomali Rahmonov, and the United Tajik Opposition. After the UN-sponsored armistice ended the war in 1997, the UN expanded the mission's original mandate to monitor the peace and demobilization. The mission was headquartered in Dushanbe, Tajikistan.
Commission of inquiry may refer to:
In 2006 the Israel Defense Forces launched Operation "Autumn Clouds" beginning on 1 November 2006, following numerous rocket and mortar attacks on southern Israel, when the Israeli Defense Forces entered the Gaza Strip triggering sporadic fighting near Beit Hanoun. The operation was the first military endeavor undertaken by the Israeli military since Operation "Summer Rains" in the summer of 2006. The operation was launched to stop Palestinian rocket attacks into Israel.
The 2006 shelling of Beit Hanoun by the Israeli Defence Force (IDF) happened on 8 November, when shells hit a row of houses in the Gaza Strip town of Beit Hanoun, killing at least 19 Palestinians and wounding more than 40. The shelling followed the IDF's withdrawal from the Gaza Strip in completion of a week-long operation codenamed Operation "Autumn Clouds", which the Israeli government stated had been intended to stop the Qassam rocket attacks on Israel by Palestinian militants. The Israeli government apologized and attributed the incident to a technical malfunction.

UN Watch is a Geneva-based non-governmental organization whose stated mission is "to monitor the performance of the United Nations by the yardstick of its own Charter". It is an accredited NGO in Special Consultative Status to the UN Economic and Social Council and an Associate NGO to the UN Department of Public Information.

The United Nations Department of Political and Peacebuilding Affairs (DPPA) is a department of the Secretariat of the United Nations (UN) with responsibility for monitoring and assessing global political developments and advising and assisting the UN Secretary General and his envoys in the peaceful prevention and resolution of conflict around the world. The department manages field-based political missions in Africa, Central Asia, and the Middle East, and has in recent years been increasing its professional capacities in conflict mediation and preventive diplomacy. DPPA also oversees UN electoral assistance to Member States of the organization. Established in 1992, the department's responsibilities also include providing secretariat support to the UN Security Council and two standing committees created by the General Assembly concerning the Rights of the Palestinian People and Decolonization. DPPA is based at the UN Headquarters in New York City.
Issues relating to the State of Palestine and aspects of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict occupy continuous debates, resolutions, and resources at the United Nations. Since its founding in 1948, the United Nations Security Council, as of January 2010, has adopted 79 resolutions directly related to the Arab–Israeli conflict.
A United Nations fact-finding mission, also called a United Nations commission of inquiry, is a United Nations mission carried out with the intention to discover facts. They are often sent to troubled areas. Fact-finding missions have been sent by the UN to a number of trouble-spots over the past 50 years, on a pragmatic, occasional, case-by-case basis. There are legal and political parameters for fact-finding, which stresses its value and opens the door for more comprehensive, ongoing use of this tool, particularly by the Secretary-General.
The Azizabad airstrike was carried out by the United States Air Force on Friday 22 August 2008 in the village of Azizabad which is located in Shindand district, Herat Province, Afghanistan. The airstrike killed an estimated 78 to 92 civilians, mostly children, and a number of structures in the village including homes were damaged or destroyed, although there remains some dispute about the accuracy of these figures. A Taliban commander was the intended target of the airstrike.

The United Nations Fact Finding Mission on the Gaza Conflict, also known as the Goldstone Report, was a United Nations fact-finding mission established in April 2009 pursuant to Resolution A/HRC/RES/S-9/1 of the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) of 12 January 2009, following the Gaza War as an independent international fact-finding mission "to investigate all violations of international human rights law and international humanitarian law by the occupying Power, Israel, against the Palestinian people throughout the Occupied Palestinian Territory, particularly in the occupied Gaza Strip, due to the current aggression". South African jurist Richard Goldstone was appointed to head the mission. The other co-authors of the Report were Hina Jilani, Christine Chinkin and Desmond Travers.
Peter Fitzgerald is an Irish deputy police commissioner of the Irish Garda Inspectorate and author of the United Nations initial report known as the Fitzgerald Report "Report of the Fact-Finding Mission to Lebanon inquiring into the causes, circumstances and consequences of the assassination of former Prime Minister Rafik Hariri, 25 February - 24 March 2005".
Desmond Travers is a retired Irish Army colonel. During his years with the army he served with various United Nations and European Union peacekeeping forces. Since his retirement from the army in 2001, he has taught military affairs at the Institute for International Criminal Investigations in The Hague. He also served on the institutes board of directors. In 2009 together with Richard Goldstone, Christine Chinkin, and Hina Jilani, he was appointed to the United Nations Fact Finding Mission on the Gaza Conflict. The report that the mission subsequently published is commonly referred to as the Goldstone Report and Travers is credited as one of the four co-authors.
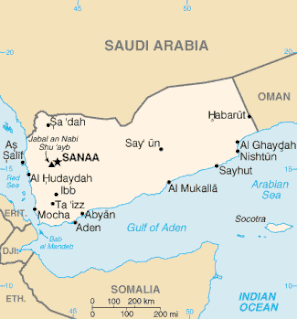
United Nations Security Council resolution 924, adopted unanimously on 1 June 1994, after considering the civil war in Yemen between the Yemeni government and Yemeni Socialist Party, the Council called for the immediate cessation of hostilities and for a fact-finding mission to be sent to the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1405, adopted unanimously on 19 April 2002, after recalling resolutions 242 (1967), 338 (1973), 1397 (2002), 1402 (2002) and 1403 (2002), the Council emphasised the necessity of humanitarian access to the Palestinian population.
The Khan al-Assal chemical attack was a chemical attack in Khan al-Assal, Aleppo, Syria on 19 March 2013, which according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights resulted in at least 26 fatalities including 16 government soldiers and 10 civilians, and more than 86 injuries. Immediately after the incident, the Syrian government and opposition accused each other of carrying out the attack, but neither side presented clear documentation. The Syrian government asked the United Nations to investigate the incident, but disputes over the scope of that investigation led to lengthy delays. In the interim, the Syrian government invited Russia to send specialists to investigate the incident. Samples taken at the site led them to conclude that the attack involved the use of sarin, which matched the assessment made by the United States. Russia held the opposition responsible for the attack, while the US held the government responsible. UN investigators finally arrived on the ground in Syria in August, but their arrival coincided with the much larger-scale 2013 Ghouta attacks which took place on 21 August, pushing the Khan al-Assal investigation "onto the backburner" according to a UN spokesman. The UN report, which was completed on 12 December, found "likely use of chemical weapons in Khan al-Assal" and assessed that organophosphate poisoning was the cause of the "mass intoxication".
The OPCW-UN Joint Mission in Syria was jointly established on 16 October 2013 by the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) and the United Nations (UN) to oversee the elimination of the Syrian chemical weapons program. The Joint Mission continued the work of the OPCW-UN advance team that had arrived in Damascus on 1 October 2013.
The OPCW Fact-Finding Mission in Syria is a mission of the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) to investigate some possible cases of the use of toxic chemicals in Syria during the civil war, including chlorine. The 21 August 2013 Ghouta chemical attack used sarin. The OPCW-Director General Ahmet Üzümcü announced the creation of the mission on 29 April 2014. This initial mission was headed by Malik Ellahi. The Syrian Government agreed to the Mission.





