Related Research Articles

In music, there are two common meanings for tuning:

A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a beater including attached or enclosed beaters or rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or struck against another similar instrument. Excluding zoomusicological instruments and the human voice, the percussion family is believed to include the oldest musical instruments. In spite of being a very common term to designate instruments, and to relate them to their players, the percussionists, percussion is not a systematic classificatory category of instruments, as described by the scientific field of organology. It is shown below that percussion instruments may belong to the organological classes of idiophone, membranophone, aerophone and chordophone.

Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the greater category of wind instruments. Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and reed instruments. The main distinction between these instruments and other wind instruments is the way in which they produce sound. All woodwinds produce sound by splitting the air blown into them on a sharp edge, such as a reed or a fipple. Despite the name, a woodwind may be made of any material, not just wood. Common examples of other materials include brass, silver, cane, and other metals such as gold and platinum. The saxophone, for example, though made of brass, is considered a woodwind because it requires a reed to produce sound. Occasionally, woodwinds are made of earthen materials, especially ocarinas.
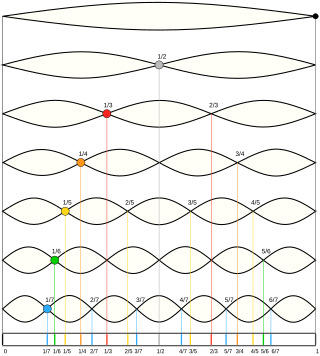
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the fundamental frequency of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the 1st harmonic; the other harmonics are known as higher harmonics. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a harmonic series.

In musical instrument classification, string instruments or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner.

In organology, the study of musical instruments, many methods of classifying instruments exist. Most methods are specific to a particular cultural group and were developed to serve that culture's musical needs. Culture-based classification methods sometimes break down when applied outside that culture. For example, a classification based on instrument use may fail when applied to another culture that uses the same instrument differently.
Hornbostel–Sachs or Sachs–Hornbostel is a system of musical instrument classification devised by Erich Moritz von Hornbostel and Curt Sachs, and first published in the Zeitschrift für Ethnologie in 1914. An English translation was published in the Galpin Society Journal in 1961. It is the most widely used system for classifying musical instruments by ethnomusicologists and organologists. The system was updated in 2011 as part of the work of the Musical Instrument Museums Online (MIMO) Project.

An aerophone is a musical instrument that produces sound primarily by causing a body of air to vibrate, without the use of strings or membranes, and without the vibration of the instrument itself adding considerably to the sound.

An idiophone is any musical instrument that creates sound primarily by the vibration of the instrument itself, without the use of air flow, strings (chordophones), membranes (membranophones) or electricity (electrophones). It is the first of the four main divisions in the original Hornbostel–Sachs system of musical instrument classification. The early classification of Victor-Charles Mahillon called this group of instruments autophones. The most common are struck idiophones, or concussion idiophones, which are made to vibrate by being struck, either directly with a stick or hand or indirectly, with scraping or shaking motions. Various types of bells fall into both categories. A common plucked idiophone is the Jew's harp.

A mute is a device attached to a musical instrument which changes the instrument's tone quality (timbre) or lowers its volume. Mutes are commonly used on string and brass instruments, especially the trumpet and trombone, and are occasionally used on woodwinds. Their effect is mostly intended for artistic use, but they can also allow players to practice discreetly. Muting can also be done by hand, as in the case of palm muting a guitar or grasping a triangle to dampen its sound.
A multiphonic is an extended technique on a monophonic musical instrument in which several notes are produced at once. This includes wind, reed, and brass instruments, as well as the human voice. Multiphonic-like sounds on string instruments, both bowed and hammered, have also been called multiphonics, for lack of better terminology and scarcity of research.
Stretched tuning is a detail of musical tuning, applied to wire-stringed musical instruments, older, non-digital electric pianos, and some sample-based synthesizers based on these instruments, to accommodate the natural inharmonicity of their vibrating elements. In stretched tuning, two notes an octave apart, whose fundamental frequencies theoretically have an exact 2:1 ratio, are tuned slightly farther apart. "For a stretched tuning the octave is greater than a factor of 2; for a compressed tuning the octave is smaller than a factor of 2."

An experimental musical instrument is a musical instrument that modifies or extends an existing instrument or class of instruments, or defines or creates a new class of instrument. Some are created through simple modifications, such as cracked cymbals or metal objects inserted between piano strings in a prepared piano. Some experimental instruments are created from household items like a homemade mute for brass instruments such as bathtub plugs. Other experimental instruments are created from electronic spare parts, or by mixing acoustic instruments with electric components.

A wind instrument is a musical instrument that contains some type of resonator in which a column of air is set into vibration by the player blowing into a mouthpiece set at or near the end of the resonator. The pitch of the vibration is determined by the length of the tube and by manual modifications of the effective length of the vibrating column of air. In the case of some wind instruments, sound is produced by blowing through a reed; others require buzzing into a metal mouthpiece, while yet others require the player to blow into a hole at an edge, which splits the air column and creates the sound.

A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who plays a musical instrument is known as an instrumentalist. The history of musical instruments dates to the beginnings of human culture. Early musical instruments may have been used for rituals, such as a horn to signal success on the hunt, or a drum in a religious ceremony. Cultures eventually developed composition and performance of melodies for entertainment. Musical instruments evolved in step with changing applications and technologies.

There are several overlapping schemes for the classification of percussion instruments.

The conservation and restoration of musical instruments is performed by conservator-restorers who are professionals, properly trained to preserve or protect historical and current musical instruments from past or future damage or deterioration. Because musical instruments can be made entirely of, or simply contain, a wide variety of materials such as plastics, woods, metals, silks, and skin, to name a few, a conservator should be well-trained in how to properly examine the many types of construction materials used in order to provide the highest level or preventive and restorative conservation.

Music technology is the study or the use of any device, mechanism, machine or tool by a musician or composer to make or perform music; to compose, notate, playback or record songs or pieces; or to analyze or edit music.