Michael Faraday was an early 19th-century British scientist (physicist and chemist).
Contents
Faraday may also refer to:
Michael Faraday was an early 19th-century British scientist (physicist and chemist).
Faraday may also refer to:

Michael Faraday was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism and electrolysis. Although Faraday received little formal education, as a self-made man, he was one of the most influential scientists in history. It was by his research on the magnetic field around a conductor carrying a direct current that Faraday established the concept of the electromagnetic field in physics. Faraday also established that magnetism could affect rays of light and that there was an underlying relationship between the two phenomena. He similarly discovered the principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and the laws of electrolysis. His inventions of electromagnetic rotary devices formed the foundation of electric motor technology, and it was largely due to his efforts that electricity became practical for use in technology.

William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. He was the professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, where he undertook significant research and mathematical analysis of electricity, was instrumental in the formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and contributed significantly to unifying physics, which was then in its infancy of development as an emerging academic discipline. He received the Royal Society's Copley Medal in 1883 and served as its president from 1890 to 1895. In 1892, he became the first scientist to be elevated to the House of Lords.
Franklin may refer to:
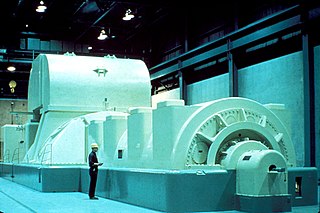
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motion-based power or fuel-based power into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all the power for electrical grids.

Sir Carl Wilhelm Siemens, anglicised to Charles William Siemens, was a German-British electrical engineer and businessman.
Porter may refer to:

A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block some electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of conductive material, or in the case of a Faraday cage, by a mesh of such materials. Faraday cages are named after scientist Michael Faraday, who first constructed one in 1836.

Siemens AG is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, distributed energy resources, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe, and holds the position of global market leader in industrial automation and industrial software.
Vega is a star in the constellation Lyra.

A cable layer or cable ship is a deep-sea vessel designed and used to lay underwater cables for telecommunications, for electric power transmission, military, or other purposes. Cable ships are distinguished by large cable sheaves for guiding cable over bow or stern or both. Bow sheaves, some very large, were characteristic of all cable ships in the past, but newer ships are tending toward having stern sheaves only, as seen in the photo of CS Cable Innovator at the Port of Astoria on this page. The names of cable ships are often preceded by "C.S." as in CS Long Lines.

Siemens Brothers and Company Limited was an electrical engineering design and manufacturing business in London, England. It was first established as a branch in 1858 by a brother of the founder of the German electrical engineering firm Siemens & Halske. The principal works were at Woolwich where cables and light-current electrical apparatus were produced from 1863 until 1968. The site between the Thames Barrier and Woolwich Dockyard has retained several buildings of historic interest. New works were built at Stafford in 1903 and Dalston in 1908.
Siemens Communications was the communications and information business arm of German industrial conglomerate Siemens AG, until 2006. It was the largest division of Siemens, and had two business units – Mobile Networks and Fixed Networks; and Enterprise.

A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundation upon which many other later electric-power conversion devices were based, including the electric motor, the alternating-current alternator, and the rotary converter.
The second CS Faraday was a cable ship built by Palmers Shipbuilding and Iron Company, Hebburn-on-Tyne, in 1922–23, as a replacement for the ageing CS Faraday built in 1874. Design of the new ship was influenced by long experience with the original ship.
Siemens Mobility is a division of Siemens. With its global headquarters in Munich, Siemens Mobility has four core business units: Mobility Management, dedicated to rail technology and intelligent traffic systems, Railway Electrification, Rolling Stock, and Customer Services.

The CS Faraday was a cable ship built for Siemens Brothers and launched in 1874.

Alexander Siemens was a German electrical engineer.
Two cable ships have been named CS Faraday after the scientist Michael Faraday: