A faucet (or "tap" or "spigot") is a valve controlling the release of a liquid or gas.
Faucet may also refer to:
- Bitcoin faucet, a bitcoin dispenser
- Bithynia tentaculata , or faucet snail, a species of freshwater snail
A faucet (or "tap" or "spigot") is a valve controlling the release of a liquid or gas.
Faucet may also refer to:
A helix is a spiral-like space curve.

Bithynia tentaculata, common names the mud bithynia or common bithynia, or faucet snail is a relatively small species of freshwater snail with gills and an operculum, an aquatic prosobranch gastropod mollusk in the family Bithyniidae.

Jeffrey David Berwick is a Canadian-Dominican entrepreneur, libertarian and anarcho-capitalist activist.

A bidet shower—also known as a handheld bidet, commode shower, toilet shower, health faucet, bum shower, jet spray, Muslim shower, shatafa or bum gun—is a hand-held triggered nozzle that is placed near the toilet and delivers a spray of water used for anal cleansing and cleaning of the genitals after using the toilet for defecation and urination, popularised by Arab nations where the bidet shower is a common bathroom accessory. The device is similar to that of a kitchen sink sprayer.

Block Inc. is an American financial technology company founded in 2009 by Jack Dorsey and Jim McKelvey. It is a public company listed on the New York Stock Exchange.

Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency. Bitcoin transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain. The cryptocurrency was invented in 2008 by an unknown entity under the name Satoshi Nakamoto. The currency began use in 2009, when its implementation was released as open-source software.
Satoshi Nakamoto is the name used by the presumed pseudonymous person or persons who developed Bitcoin, authored the bitcoin white paper, and created and deployed bitcoin's original reference implementation. As part of the implementation, Nakamoto also devised the first blockchain database. Nakamoto was active in the development of bitcoin up until December 2010.
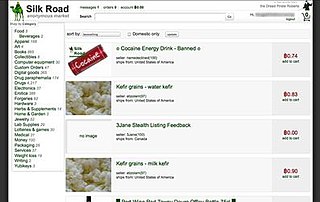
Silk Road was an online black market and the first modern darknet market. It was launched in 2011 by its American founder Ross Ulbricht under the pseudonym "Dread Pirate Roberts". He managed the entire marketplace from his personal laptop, which was seized by the FBI on 1 October 2013. As part of the dark web, Silk Road operated as a hidden service on the Tor network, allowing users to buy and sell products and services between each other anonymously. All transactions were conducted with bitcoin, a cryptocurrency which aided in protecting user identities. The website was known for its illegal drug marketplace, among other illegal and legal product listings. Between February 2011 and July 2013, the site facilitated sales amounting to 9,519,664 Bitcoins.

A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a digital currency designed to work as a medium of exchange through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it. It is a decentralized system for verifying that the parties to a transaction have the money they claim to have, eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries, such as banks, when funds are being transferred between two entities.
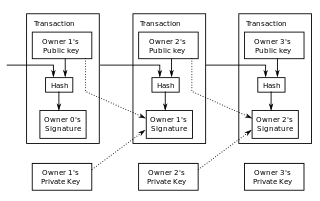
The Bitcoin network is a peer-to-peer network of nodes which implement the Bitcoin protocol. The protocol itself implements a highly available, public, and decentralized ledger. The nodes verify that each update to the ledger follows the rules of the Bitcoin protocol.

Gavin Andresen is a software developer known for his involvement with bitcoin. He is based in Amherst, Massachusetts.

Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, a digital asset that uses cryptography to control its creation and management rather than relying on central authorities. Originally designed as a medium of exchange, Bitcoin is now primarily regarded as a store of value. The history of bitcoin started with its invention and implementation by Satoshi Nakamoto, who integrated many existing ideas from the cryptography community. Over the course of bitcoin's history, it has undergone rapid growth to become a significant store of value both on- and offline. From the mid-2010s, some businesses began accepting bitcoin in addition to traditional currencies.
A blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records (blocks) that are securely linked together via cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Since each block contains information about the previous block, they effectively form a chain, with each additional block linking to the ones before it. Consequently, blockchain transactions are irreversible in that, once they are recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks.
A cryptocurrency tumbler or cryptocurrency mixing service is a service that mixes potentially identifiable or "tainted" cryptocurrency funds with others, so as to obscure the trail back to the fund's original source. This is usually done by pooling together source funds from multiple inputs for a large and random period of time, and then spitting them back out to destination addresses. As all the funds are lumped together and then distributed at random times, it is very difficult to trace exact coins. Tumblers have arisen to improve the anonymity of cryptocurrencies, usually bitcoin, since the digital currencies provide a public ledger of all transactions. Due to its goal of anonymity, tumblers have been used to money launder cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin is a digital asset designed by its pseudonymous inventor, Satoshi Nakamoto, to work as a currency.

Bitcoin Cash is a cryptocurrency that is a fork of Bitcoin. Bitcoin Cash is a spin-off or altcoin that was created in 2017.
A cryptocurrency bubble is a phenomenon where the market increasingly considers the going price of cryptocurrency assets to be inflated against their hypothetical value. The history of cryptocurrency has been marked by several speculative bubbles.
Nano is a cryptocurrency characterized by a directed acyclic graph data structure and distributed ledger, making it possible for Nano to work without intermediaries. To agree on what transactions to commit, it uses a voting system with weight based on the amount of currency an account holds.
In blockchain technology, a testnet is an instance of a blockchain powered by the same or a newer version of the underlying software, to be used for testing and experimentation without risk to real funds or the main chain. Testnet coins are separate and distinct from the official (mainnet) coins, don't have value, and can be obtained freely from faucets.
Cryptojacking is the act of exploiting a computer to mine cryptocurrencies, often through websites, against the user's will or while the user is unaware. One notable piece of software used for cryptojacking was Coinhive, which was used in over two-thirds of cryptojacks before its March 2019 shutdown. The cryptocurrencies mined the most often are privacy coins—coins with hidden transaction histories—such as Monero and Zcash.