Related Research Articles

The Continuation War was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany, against the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1941 to 1944, as a part of World War II. In Soviet historiography, the war was called the Finnish Front of the Great Patriotic War. Germany regarded its operations in the region as part of its overall war efforts on the Eastern Front and provided Finland with critical material support and military assistance, including economic aid.

The Winter War was a war between the Soviet Union (USSR) and Finland. It began with a Soviet invasion of Finland on 30 November 1939, three months after the outbreak of World War II, and ended three and a half months later with the Moscow Peace Treaty on 13 March 1940. Despite superior military strength, especially in tanks and aircraft, the Soviet Union suffered severe losses and initially made little headway. The League of Nations deemed the attack illegal and expelled the Soviet Union from the organisation.

The Finnish Army is the land forces branch of the Finnish Defence Forces. The Finnish Army is divided into six branches: the infantry, field artillery, anti-aircraft artillery, engineers, signals, and materiel troops. The commander of the Finnish Army since 1 August 2017 is Lieutenant General Petri Hulkko.

The siege of Leningrad was a prolonged military blockade undertaken from the south by the Army Group North of Nazi Germany against the Soviet city of Leningrad on the Eastern Front in World War II. The Finnish army invaded from the north, co-operating with the Germans until Finland had recaptured territory lost in the recent Winter War, but refused to make further approaches to the city. Also co-operating with the Germans since 1942 in August: the Spanish Blue Division that was transferred to the southeastern flank of the siege of Leningrad, just south of the Neva near Pushkin, Kolpino and its main intervention was in Krasny Bor in the Izhora River area.
The II Corps was a unit of the Finnish Army during the Winter War.

Operation Silver Fox from 29 June to 17 November 1941, was a German–Finnish military operation during the Continuation War on the Eastern Front of World War II against the Soviet Union. The objective of the offensive was to cut off and capture the key Soviet Port of Murmansk through attacks from Finnish and Norwegian territory.
Mountain Corps Norway was a German army unit during World War II. It saw action in Norway and Finland.

The 5th SS Panzer Division "Wiking" was a Panzer division among the thirty-eight Waffen-SS divisions of Nazi Germany. It was recruited from foreign volunteers in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Estonia, the Netherlands and Belgium under the command of German officers. During the course of World War II, the division served on the Eastern Front. It surrendered in May 1945 to the American forces in Austria.

The Battle of Narva was a military campaign between the German Army Detachment "Narwa" and the Soviet Leningrad Front fought for possession of the strategically important Narva Isthmus on 2 February – 10 August 1944 during World War II.
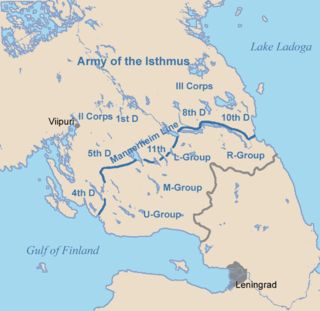
The Army of the Isthmus was a formation of the Finnish Army during the Winter War. It was stationed on the Karelian Isthmus and was the largest formation of the Finnish Army, as it was charged to defend the important isthmus.
The IV Corps was a formation of the Finnish Army during the Winter War against the Soviet Union. It defended the area north of Lake Ladoga against Soviet attacks. It was commanded by Major General Juho Heiskanen and from 4 December 1939 by Major General Woldemar Hägglund. The IV Corps defeated superior Soviet troops by using motti tactics.
The III Corps was a unit of the Finnish Army during the Winter War. The III Corps with the II Corps formed the Army of the Isthmus. For most of the war it defended the Mannerheim Line on the northern side of the River Vuoksi against Soviet attacks.
The 8th Army was a field army of the Soviet Red Army during the Second World War.

The 44th Kievskaya of the Red Banner Rifle Division of Nikolay Shchors, or 44th Kievskaya for short, was an elite military formation of the Soviet Union.
The 17th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Soviet Union's Red Army during World War II.
The 49th Rifle Division was a Soviet Army infantry division, formed three times. First formed as a territorial division in 1931, the 49th Rifle Division's first formation became a regular division by 1939 and fought in the Winter War. For its actions during the war, it was awarded the Order of the Red Banner. However, the 49th Rifle Division was wiped out during the first ten days of Operation Barbarossa. Its second formation occurred in December 1941 and fought at Stalingrad, Kursk, the Vistula-Oder Offensive and the Battle of Berlin. The second formation was disbanded in 1946. The division was reformed in 1955 by renaming the 295th Rifle Division and became the 49th Motor Rifle Division in 1957.
The 50th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Red Army from 1936 to 1946. The division took part in the Soviet invasion of Poland and the Winter War. After Germany launched Operation Barbarossa, the 50th fought in the Battle of Moscow, the Battles of Rzhev, the Donbass Strategic Offensive, the Dnieper–Carpathian Offensive, the First and Second Jassy–Kishinev Offensive, the Vistula–Oder Offensive and the Berlin Offensive.

The Battle of Porlampi, also known as the Battle of Porlammi, was a military engagement fought between the Finnish Army and Red Army from 30 August to 1 September 1941 on the Karelian Isthmus. The battle was fought near the town of Porlampi during the second month of the Continuation War. The battle was a Finnish victory and effectively ended the reconquest of Karelia.
References
- Kilin, Juri; Raunio, Ari (2007). Talvisodan taisteluja (in Finnish). Karttakeskus. ISBN 978-951-593-068-2.
- Trotter, William R. (2002) [1991]. The Winter War: The Russo–Finnish War of 1939–40 (5th ed.). London: Aurum Press. ISBN 1-85410-881-6.
| This World War II article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This article about the military of Finland is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |