See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles about distinct geographical locations with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Fisher Island is a census-designated place in Florida.
Fisher Island, or Fishers Island, may also refer to:
Antarctica
Australia
Canada
Germany
USA
| This disambiguation page lists articles about distinct geographical locations with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Tasmania is an island state of Australia. It is located 240 km (150 mi) to the south of the Australian mainland, separated by Bass Strait. The state encompasses the main island of Tasmania, the 26th-largest island in the world, and the surrounding 334 islands. The state has a population of about 535,500 as of September 2019. Just more than forty percent of the population resides in the Greater Hobart precinct, which forms the metropolitan area of the state capital and largest city, Hobart.
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of the Environment. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. It conducts and supports collaborative research programs with other Australian and international organisations, such as the Bureau of Meteorology and Geoscience Australia, as well as administering and maintaining a presence in Australian Antarctic and sub-Antarctic territories.
Smooth means having a texture that lacks friction. It is the opposite of rough.

The Antarctic flora is a distinct community of vascular plants which evolved millions of years ago on the supercontinent of Gondwana. It is now found on several separate areas of the Southern Hemisphere, including southern South America, southernmost Africa, New Zealand, Australia and New Caledonia. Joseph Dalton Hooker was the first to notice similarities in the flora and speculated that Antarctica had served as either a source or a transitional point, and that land masses now separated might formerly have been adjacent.
Long Island is an island and geographical area of New York state.
Emilio Marcos Palma is an Argentine man who was the first documented person born on the continent of Antarctica.

The Furneaux Group is a group of approximately 100 islands located at the eastern end of Bass Strait, between Victoria and Tasmania, Australia. The islands were named after British navigator Tobias Furneaux, who sighted the eastern side of these islands after leaving Adventure Bay in 1773 on his way to New Zealand to rejoin Captain James Cook. Navigator Matthew Flinders was the first Westerner to explore the Furneaux Islands group in the Francis in 1798, and later that year in the Norfolk.
Egg Island may refer to the following places:

UTC+10:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +10:00. This time is used in:
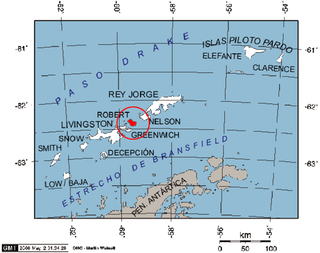
Robert Island or Mitchells Island or Polotsk Island or Roberts Island is an island 11 miles (18 km) long and 8 miles (13 km) wide, situated between Nelson Island and Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Robert Island is located at 62°24′S59°30′W. Surface area 132 km2 (51 sq mi). The name "Robert Island" dates back to around 1821 and is now established in international usage.
The following lists events that happened during 1928 in Australia.

Government in the Commonwealth of Australia is exercised on three levels: federal, states and territories, and local government.
Charity may refer to:
The following lists events that happened during 1913 in Australia.

The Great Dog Island, also known as Big Dog Island, and part of the Great Dog Group within the Furneaux Group, is a 354-hectare (870-acre) granite island, located in Bass Strait, lying south of the Flinders Island and north of the Cape Barren Island, in Tasmania, in south-eastern Australia.

Fisher Island is a small granite island, with an area of 0.9 ha, in south-eastern Australia. It is part of Tasmania’s Great Dog Island Group, lying in eastern Bass Strait between Flinders and Cape Barren Islands in the Furneaux Group. It is the site of a long-term, ongoing study of short-tailed shearwaters.
Smooth Island may refer to:

Maldonado Base, also Pedro Vicente Maldonado Base, is the Ecuadorian Antarctic research base situated at Guayaquil Bay, Greenwich Island. It is located in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It opened in 1990. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Clothier Harbour.

The biodiversity of Tasmania is of exceptional biological and paleoecological interest. A state of Australia, it is a large South Pacific archipelago of one large main island and a range of smaller islands. The terrain includes a variety of reefs, atolls, many small islands, and a variety of topographical and edaphic regions on the largest island, all of which promote the development of unusually concentrated biodiversity. During long periods geographically and genetically isolated, it is known for its unique flora and fauna. The region's climate is oceanic.

The Flora Antarctica or formally and correctly The Botany of the Antarctic Voyage of H.M. Discovery Ships Erebus and Terror in the years 1839–1843, under the Command of Captain Sir James Clark Ross, is a description of the many plants discovered on the Ross expedition, which visited islands off the coast of the Antarctic continent, with a summary of the expedition itself, written by Joseph Dalton Hooker and published in parts between 1844 and 1859 by Reeve Brothers in London. Hooker sailed on HMS Erebus as assistant surgeon.