
The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, and stretching approximately 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) across eight Alpine countries : France, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at 4,810 m (15,781 ft) is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains about a hundred peaks higher than 4,000 metres (13,000 ft).

The alphorn or alpenhorn or alpine horn is a labrophone, consisting of a straight several-meter-long wooden natural horn of conical bore, with a wooden cup-shaped mouthpiece. It is used by mountain dwellers in the Swiss Alps, Austrian Alps, Bavarian Alps in Germany, French Alps, and elsewhere. Similar wooden horns were used for communication in most mountainous regions of Europe, from the Alps to the Carpathians. Alphorns are today used as musical instruments.

The geography of Switzerland encompasses the geographical features of Switzerland, a mountainous and landlocked country located in Western and Central Europe. Switzerland is world-famous for the beauty and uniqueness of its landscapes. It is surrounded by 5 countries: Austria and Liechtenstein to the east, France to the west, Italy to the south and Germany to the north. Switzerland has a maximum north–south length of 220 kilometres (140 mi) and an east–west length of about 350 kilometres (220 mi).
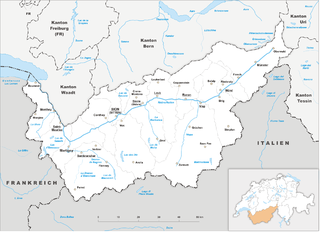
The canton of Valais is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland, situated in the southwestern part of the country, around the valley of the Rhône from its headwaters to Lake Geneva, separating the Pennine Alps from the Bernese Alps. The canton is simultaneously one of the driest regions of Switzerland in its central Rhône valley and among the wettest, having large amounts of snow and rain up on the highest peaks found in Switzerland. The canton of Valais is widely known for the Matterhorn and resort towns such as Crans-Montana, Saas Fee, Verbier and Zermatt. It is composed of 13 districts and its capital is Sion.

A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument used in fishing, whaling, sealing, and other marine hunting to catch large fish or marine mammals such as whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the target animal and securing it with barb or toggling claws, allowing the fishermen to use a rope or chain attached to the projectile to catch the animal. A harpoon can also be used as a weapon.

The French Alps are the portions of the Alps mountain range that stand within France, located in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur regions. While some of the ranges of the French Alps are entirely in France, others, such as the Mont Blanc massif, are shared with Switzerland and Italy.

Saint Nicholas of Flüe was a Swiss hermit and ascetic who is the patron saint of Switzerland. He is sometimes invoked as Brother Klaus. A farmer, military leader, member of the assembly, councillor, judge and mystic, he was respected as a man of complete moral integrity. Brother Klaus's counsel to the Diet of Stans (1481) helped to prevent war between the Swiss cantons.

The Gotthard Pass or St. Gotthard Pass at 2,106 m (6,909 ft) is a mountain pass in the Alps traversing the Saint-Gotthard Massif and connecting northern and southern Switzerland. The pass lies between Airolo in the Italian-speaking canton of Ticino, and Andermatt in the German-speaking canton of Uri, and connects further Bellinzona to Lucerne, Basel, and Zurich. The Gotthard Pass lies at the hearth of the Gotthard, an important north-south axis in Europe, and it is crossed by three major traffic tunnels, each being the world's longest at the time of their construction: the Gotthard Rail Tunnel (1882), the Gotthard Road Tunnel (1980) and the Gotthard Base Tunnel (2016). With the Lötschberg to the west, the Gotthard is one of the two main north-south routes through the Swiss Alps. Since the Middle Ages, transit across the Gotthard played an important role in Swiss history, the region north of Gotthard becoming the nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the early 14th century.

A flue pipe is an organ pipe that produces sound through the vibration of air molecules, in the same manner as a recorder or a whistle. Air under pressure is driven through a flue and against a sharp lip called a labium, causing the column of air in the pipe to resonate at a frequency determined by the pipe length. Thus, there are no moving parts in a flue pipe. This is in contrast to reed pipes, whose sound is driven by beating reeds, as in a clarinet. Flue pipes are common components of pipe organs.

The Grünhorn is a mountain in the Bernese Alps range of the Swiss Alps. It is located on the ridge between the two largest glaciers of the Alps: the Aletsch Glacier to the west and the Fiescher Glacier to the east. To the south lies the Gross Wannenhorn and, to the north, the Gross Fiescherhorn.

An organ pipe is a sound-producing element of the pipe organ that resonates at a specific pitch when pressurized air is driven through it. Each pipe is tuned to a specific note of the musical scale. A set of organ pipes of similar timbre comprising the complete scale is known as a rank; one or more ranks constitutes a stop.

Sennenhund, called Swiss mountain dogs or Swiss cattle dogs in English, are a type of dog originating in the Swiss Alps. The Sennenhund are farm dogs of the general molosser type. There are four breeds of Sennenhund, all sporting a unique tricolor coat. While the two larger ones share a heavy build and a calm temperament, the two smaller ones are more agile. The breeds range from medium in size to very large. The name Sennenhund refers to people called Senn or Senner, Swiss alpine herdsmen and dairymen, and does not translate as "mountain" or "cattle".

A flue is a duct, pipe, or opening in a chimney for conveying exhaust gases from a fireplace, furnace, water heater, boiler, or generator to the outdoors. Historically the term flue meant the chimney itself. In the United States, they are also known as vents for boilers and as breeching for water heaters and modern furnaces. They usually operate by buoyancy, also known as the stack effect, or the combustion products may be 'induced' via a blower. As combustion products contain carbon monoxide and other dangerous compounds, proper 'draft', and admission of replacement air is imperative. Building codes, and other standards, regulate their materials, design, and installation.
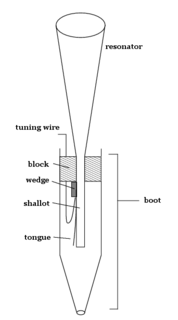
A reed pipe is an organ pipe that is sounded by a vibrating brass strip known as a reed. Air under pressure is directed towards the reed, which vibrates at a specific pitch. This is in contrast to flue pipes, which contain no moving parts and produce sound solely through the vibration of air molecules. Reed pipes are common components of pipe organs.

The two-flue harpoon or two-flue iron is a type of harpoon used in whaling for at least 1000 years. It appears in works of art dating back to the 14th century.
The one-flue harpoon or one-flue iron is a type of harpoon used in whaling after its introduction in the early 19th century when it replaced the two-flue harpoon. Due to the asymmetric design of the head for which it is named, the one-flue harpoon was less likely to cut its way out of the whale meat and blubber, and was therefore more successful in whaling.

The Ebnefluh is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, located on the border between the Swiss cantons of Bern and Valais. It lies towards the eastern end of the Lauterbrunnen Wall.

The Schlüechtli is a mountain of the Swiss Lepontine Alps, situated south of Versam in the canton of Graubünden. It lies between the valleys of Turischtobel and Safien, approximately 5 kilometres south of the anterior Rhine.
Dorothea Wyss, also known Dorothea von Flüe, married Niklaus von Flüe, the patron saint of Switzerland.
















