Fluoroaniline may refer to three compounds with the formula FC6H4NH2:
Fluoroaniline may refer to three compounds with the formula FC6H4NH2:
Compound may refer to:
German(s) may refer to:
Quinolone may refer to:
Acrylic may refer to:
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Copper oxide is a compound from the two elements copper and oxygen.
Volatility or volatile may refer to:
Copper sulfate may refer to:
Sulfur oxide refers to many types of sulfur and oxygen containing compounds such as SO, SO2, SO3, S7O2, S6O2, S2O2, etc.
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Iron sulfide or Iron sulphide can refer to range of chemical compounds composed of iron and sulfur.
There are two isomers of propanol.
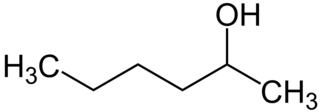
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomeric organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH:
Linolenic acid is a type of naturally-occurring fatty acid. It can refer to either of two octadecatrienoic acids, or a mixture of the two. Linolenate is often found in vegetable oils; traditionally, such fatty acylates are reported as the fatty acids:
Butyne is an alkyne that contains 4 carbon and 6 hydrogen. It contains one triple bond and has two isomeric organic chemical compounds:
Pentyne may refer to:
Dioxin may refer to:
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid.
Halobenzenes are a group of aryl halides consisting of a benzene ring with halogen atoms as substituents.
4-Fluoroaniline is an organofluorine compound with the formula FC6H4NH2. A colorless liquid, it is one of three isomers of fluoroaniline. It is used as a precursor to various potential and real applications.