
Shuffling is a procedure used to randomize a deck of playing cards to provide an element of chance in card games. Shuffling is often followed by a cut, to help ensure that the shuffler has not manipulated the outcome.
In the card game contract bridge, the Losing-Trick Count (LTC) is a method of hand evaluation that is generally only considered suitable to be used in situations where a trump suit has been established and when shape and fit are more significant than high card points (HCP) in determining the optimum level of the contract. The method is generally not considered suitable for no trump or misfit hands; also, the trump suit is generally considered to require at least eight cards in length with no partner holding fewer than three.

Card manipulation, commonly known as card magic, is the branch of magic that deals with creating effects using sleight of hand techniques involving playing cards. Card manipulation is often used in magical performances, especially in close-up, parlor, and street magic. Some of the most recognized names in this field include Dai Vernon, Tony Slydini, Ed Marlo, S.W. Erdnase, Richard Turner, John Scarne, Ricky Jay and René Lavand. Before becoming world-famous for his escapes, Houdini billed himself as "The King of Cards". Among the more well-known card tricks relying on card manipulation are Ambitious Card, and Three-card Monte, a common street hustle also known as Find the Lady.
A trick deck is a deck of playing cards that has been altered in some way to allow magicians to perform certain card tricks where sleight of hand would be too difficult or impractical.

Mentalism is a performing art in which its practitioners, known as mentalists, appear to demonstrate highly developed mental or intuitive abilities. Mentalists perform a theatrical act that includes special effects that may appear to employ psychic or supernatural forces but that is actually achieved by "ordinary conjuring means", natural human abilities, and an in-depth understanding of key principles from human psychology or other behavioral sciences. Performances may appear to include hypnosis, telepathy, clairvoyance, divination, precognition, psychokinesis, mediumship, mind control, memory feats, deduction, and rapid mathematics.

Out of This World is a card trick created by magician Paul Curry in 1942, in which an audience member is asked to sort a deck into piles of red and black cards, without looking at the faces. Many performers have devised their own variations of this trick. It is often billed as "the trick that fooled Winston Churchill" due to a story describing how it was performed for him during World War II. The method behind the trick is simple and essentially self-working, and can be enhanced by the presentation of the performer and the use of other principles of magic.

Card throwing is the art of throwing standard playing cards with great accuracy or force. It is performed both as part of stage magic shows and as a competitive physical feat among magicians, with official records existing for longest distance thrown, fastest speed, highest throw, greatest accuracy, and the greatest number of cards in one minute.
This is a glossary of conjuring terms used by magicians.
These terms are used in contract bridge, using duplicate or rubber scoring. Some of them are also used in whist, bid whist, the obsolete game auction bridge, and other trick-taking games. This glossary supplements the Glossary of card game terms.
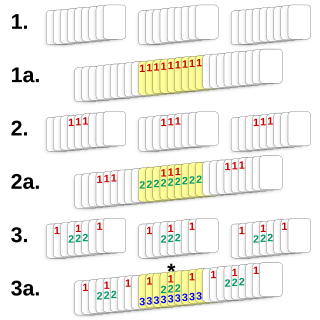
The Twenty-One Card Trick, also known as the 11th card trick or three column trick, is a simple self-working card trick that uses basic mathematics to reveal the user's selected card.
Spelling Bee may refer to one of several card tricks that revolve around the spelling of card types, audience member names, or words suggested by the audience. Many make use of decks prepared in advance in order to provide the illusion of spelling card names in a particular sequence. Jean Hugard's Encyclopedia of Card Tricks lists a number of such spelling-based tricks, many of which are considered to be self-working.
The Circus Card Trick is a self-working card trick where the performer uses verbal misdirection to prompt the participant into betting that the performer has failed to execute the trick correctly. The performer exploits the ambiguous wording of their patter to win the bet in a manner unexpected by the audience. It is often recommended for beginning magicians due to its entertaining and self-working nature.
A bridge maxim is a rule of thumb in contract bridge acting as a memory aid to best practice gained from experience rather than theory.

Penn & Teller's Cruel Tricks for Dear Friends is a 1987 direct-to-video program hosted by magicians Penn & Teller. Produced by The Mofo Video Corp. and released by Lorimar Home Video, the tape features seven different swindles or tricks that the home viewer can use to fool their friends. The tape was a companion piece to their best-selling book of the same name, released two years later. All of the tricks involve using a portion of the videotape.

Mark Wilson's Complete Course in Magic is a book on magic written by magician Mark Wilson. The book is a popular reference for magicians and has been in print since its first issue in 1975.

Chink-a-chink is a simple close-up magic coin trick in which a variety of small objects, usually four, appear to magically transport themselves from location to location when covered by the performer's hands, until the items end up gathered together in the same place. Variations, especially the Sympathetic Coins, also known as Coins-n-Cards, have been performed since the 1800s. Popular modern variations are Shadow Coins and Matrix. A variation using playing cards as the objects is known as Sympathetic Aces.

Magic, which encompasses the subgenres of illusion, stage magic, and close-up magic, among others, is a performing art in which audiences are entertained by tricks, effects, or illusions of seemingly impossible feats, using natural means. It is to be distinguished from paranormal magic which are effects claimed to be created through supernatural means. It is one of the oldest performing arts in the world.
The book test is a classic mentalism demonstration used by mentalists to demonstrate telepathy-like effects. The name refers to its early use as a test of mental powers.

Kostya Kimlat is a magician, motivational speaker, entrepreneur, and business consultant. With the use of magic tricks, Kimlat helps companies train employees. As a speaker, he lectures on the importance of perception in daily life through magic and sleight of hand.
The Rising Card is a popular category of magical illusion in which the magician causes randomly selected playing cards to spontaneously rise from the center of a deck. Many variations of this trick exist and are widely performed.The effect can be accomplished using a variety of methods and techniques, ranging from pure sleight of hand to complex electronic and mechanical solutions.











