
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is the integrated management of main business processes, often in real-time and mediated by software and technology. ERP is usually referred to as a category of business management software—typically a suite of integrated applications—that an organization can use to collect, store, manage and interpret data from many business activities. ERP systems can be local-based or cloud-based. Cloud-based applications have grown in recent years due to the increased efficiencies arising from information being readily available from any location with Internet access.
A management information system (MIS) is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of information in an organization. The study of the management information systems involves people, processes and technology in an organizational context.

The Buenos Aires Underground, locally known as Subte, is a rapid transit system that serves the area of the city of Buenos Aires, Argentina. The first section of this network opened in 1913, making it the 13th subway in the world and the first underground railway in Latin America, the Southern Hemisphere, and the Spanish-speaking world, with the Madrid Metro opening five years later, in 1919. As of 2023, Buenos Aires is the only Argentine city with a metro system.

Business process modeling (BPM) in business process management and systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current business processes may be analyzed, improved, and automated. BPM is typically performed by business analysts, who provide expertise in the modeling discipline; by subject matter experts, who have specialized knowledge of the processes being modeled; or more commonly by a team comprising both. Alternatively, the process model can be derived directly from events' logs using process mining tools.

Nuevo Laredo is a city in the Municipality of Nuevo Laredo in the Mexican state of Tamaulipas. The city lies on the banks of the Rio Grande, across from Laredo, United States. The 2010 census population of the city was 373,725. Nuevo Laredo is part of the Laredo-Nuevo Laredo Metropolitan Area with a population of 636,516. The municipality has an area of 1,334.02 km2 (515.07 sq mi). Both the city and the municipality rank as the third largest in the state.
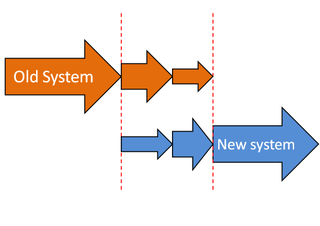
Phased adoption or phased implementation is a strategy of implementing an innovation in an organization in a phased way, so that different parts of the organization are implemented in different subsequent time slots. Phased implementation is a method of System Changeover from an existing system to a new one that takes place in stages. Other concepts that are used are: phased conversion, phased approach, phased strategy, phased introduction and staged conversion. Other methods of system changeover include direct changeover and parallel running.

SAP ERP is an enterprise resource planning software developed by the German company SAP SE. SAP ERP incorporates the key business functions of an organization. The latest version of SAP ERP (V.6.0) was made available in 2006. The most recent SAP enhancement package 8 for SAP ERP 6.0 was released in 2016. It is now considered legacy technology, having been superseded by SAP S/4HANA.
The Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS) designs, develops, implements and maintains most of the important information systems of Indian Railways. It is under the ownership of Government of India and administrative control of the Ministry of Railways. It is located in Chanakyapuri, New Delhi. CRIS was established in 1986.
XHMNU-TDT is an educational television station owned and operated by the Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León (UANL) in Monterrey, Nuevo Leon.

Operativo Independencia was a 1975 Argentine military operation in Tucumán Province to crush the People's Revolutionary Army (ERP), a Guevarist guerrilla group which tried to create a Vietnam-style war front in the northwestern province. It was the first large-scale military operation of the Dirty War.

The System of Cooperation Among the American Air Forces is an apolitical voluntary international organization among the North and South American air forces.
The Interactive Policy Making, or IPM, is an online opinion poll management system launched in 2001, which is used to gather the opinion of European Union citizens and entreprises regarding policy development The software is part of the Interactive Policy Making Initiative and is made of various modules which assist in the creation of such questionnaires - including a creation, translation, test, launch and analysis module.
ERP5 is an open source ERP based on Python and Zope. It has the particularity of being based on a unified model to describe its implementation.

GNU Health is a free/libre health and hospital information system with strong focus on public health and social medicine. Its functionality includes management of electronic health records and laboratory information management system.
The Digital Firm is a kind of organization that has enabled core business relationships through digital networks In these digital networks are supported by enterprise class technology platforms that have been leveraged within an organization to support critical business functions and services. Some examples of these technology platforms are Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Supply Chain Management (SCM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Knowledge Management System (KMS), Enterprise Content Management (ECM), and Warehouse Management System (WMS) among others. The purpose of these technology platforms is to digitally enable seamless integration and information exchange within the organization to employees and outside the organization to customers, suppliers, and other business partners.
SAP implementation refers to the name of the German company SAP SE, and is the whole of processes that defines a method to implement the SAP ERP enterprise resource planning software in an organization. The SAP implementation method described in this entry is a generic method and not a specific implementation method as such. It is based on best practices and case studies from various literature sources and presents a collection of processes and products that make up a complete implementation method to allow any organization to plan and execute the implementation of SAP software.
A human resources management system (HRMS) or Human Resources Information System (HRIS) or Human Capital Management (HCM) is a form of Human Resources (HR) software that combines a number of systems and processes to ensure the easy management of human resources, business processes and data. Human resources software is used by businesses to combine a number of necessary HR functions, such as storing employee data, managing payroll, recruitment, benefits administration, time and attendance, employee performance management, and tracking competency and training records.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a cloud-based enterprise software platform developed by Microsoft that bundles its ERP and CRM business applications and services. announced by Microsoft in July 2016 and released on November 1, 2016.

The ERP-22 de Agosto was an Argentinian guerrilla faction split in 1973 of the Military Committee of the Federal Capital of the People's Revolutionary Army (ERP), as a result of tactical divergences regarding the organization's position before the electoral act of March 11, 1973.
Food labeling in Mexico refers to the official norm that mainly consists of placing labels on processed food sold in the country in order to help consumers make a better purchasing decision based on nutritional criteria. The system was approved in 2010 under the Norma Oficial Mexicana (NOM) NOM-051-SCFI/SSA1-2010. The standards, denominated as Daily Dietary Guidelines, were based on the total amount of saturated fats, fats, sodium, sugars and energy or calories represented in kilocalories per package, the percentage they represented per individual portion, as well as the percentage that they would represent in a daily intake.









