Washington most commonly refers to:
Rochambeau or Ro-Sham-Bo may refer to:

Rhode Island Avenue station is a Washington Metro station in Washington, D.C., on the Red Line. The station is located in the Brentwood neighborhood of Northeast, on an elevated platform crossing Rhode Island Avenue NE

An old soldiers' home is a military veterans' retirement home, nursing home, or hospital, or sometimes an institution for the care of the widows and orphans of a nation's soldiers, sailors, and marines, etc.

Fort Kearny was a historic outpost of the United States Army founded in 1848 in the Western United States during the middle and late 19th century. The fort was named after Colonel and later General Stephen Watts Kearny. The outpost was located along the Oregon Trail near Kearney, Nebraska. The town of Kearney took its name from the fort. The "e" was added to Kearny by postmen who consistently misspelled the town name. A portion of the original site is preserved as Fort Kearny State Historical Park by the Nebraska Game and Parks Commission.

Woodridge is a residential neighborhood located in Ward 5 of Northeast Washington, D.C. Woodridge is contained between Eastern Avenue N.E. to the east, Taylor Street N.E. to the north, South Dakota Avenue N.E. to the west, and Bladensburg Road N.E. to the south. Its central commercial strips are Rhode Island Avenue NE and Bladensburg Road N.E. Woodridge borders the adjacent neighborhoods of Brookland, Langdon, North Michigan Park, and Fort Lincoln in Northeast Washington D.C. In addition to these neighborhoods in the District of Columbia, Woodridge borders the city of Mount Rainier and town of Cottage City in Maryland. In terms of public transportation, residents of Woodridge have access to the Brookland-CUA and Rhode Island Avenue Metro stations.
Washington Park may refer to the following, all in the United States:

Rhode Island Avenue is a diagonal avenue in the Northwest and Northeast quadrants of Washington, D.C., and the capital's inner suburbs in Prince George's County, Maryland. Paralleling New York Avenue, Rhode Island Avenue was one of the original streets in Pierre L'Enfant's plan for the capital. It became a major commuter route, carrying U.S. Route 1 traffic into the city from Prince George's County.
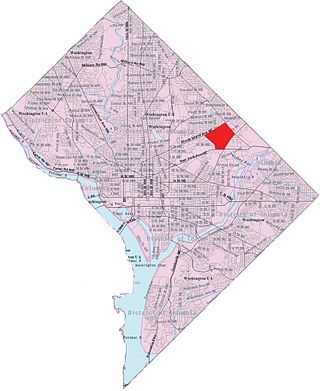
Langdon, is a neighborhood located in Ward 5 of Northeast Washington, D.C. Historical surveys of D.C. recognize Langdon as a neighborhood dating back to at least 1903. Langdon is bounded by Montana Ave. NE to the west/southwest, New York Ave. NE to the south, Bladensburg Rd. NE to the southeast, South Dakota Ave. NE to the northeast, and Rhode Island Ave. NE to the north/northwest. Langdon is adjacent to the Northeast D.C. neighborhoods of Brentwood (west), Woodridge (east), Fort Lincoln (southeast), Gateway (south), and Brookland (north).
College Hill is a common name for the neighborhood where a college or university is located.

Fort Kearny was a fort constructed during the American Civil War as part of the defenses of Washington, D.C. Located near Tenleytown, in the District of Columbia, it filled the gap between Fort Reno and Fort DeRussy north of the city of Washington. The fort was named in honor of Maj. Gen. Philip Kearny of the Union Army, who was killed at the Battle of Chantilly on September 1, 1862. Three batteries of guns supported the fort, and are considered part of the fort's defenses.
Commandant's Quarters or Commandant's House may refer to:
Quality Hill or Quality Hill Historic District may refer to:
Patterson House, or Patterson Farmhouse or Patterson Farm may refer to:

Major General Nathanael Greene is a bronze equestrian statue honoring Nathanael Greene, a military leader during the American Revolutionary War. Greene was from modern-day Rhode Island and after laws passed by the Kingdom of Great Britain, along with the burning of one of his ships, Greene formed a state militia. He was later promoted to brigadier general in the Continental Army where he became a trusted adviser to Commander-in-Chief General George Washington. Greene played an active role during the war, participating in battles, sieges, and campaigns from New England to the Southern Colonies. For his service to the war, Greene was offered free land and settled in Georgia with his family. He died a few years later from a heatstroke.

Fort Kearny was a coastal defense fort in the Saunderstown area of Narragansett, Rhode Island from 1901 to 1943. It was a prisoner-of-war camp for German prisoners in 1945. It is now the Narragansett Bay Campus of the University of Rhode Island. In many sources it is spelled Fort Kearney.

The Harbor Defenses of Narragansett Bay was a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps harbor defense command. It coordinated the coast defenses of Narragansett Bay and Rhode Island from 1895 to 1950, beginning with the Endicott program. These included both coast artillery forts and underwater minefields. The command originated circa 1895 as an Artillery District, was renamed Coast Defenses of Narragansett Bay in 1913, and again renamed Harbor Defenses of Narragansett Bay in 1925.

Fort Saratoga was one of seven temporary earthwork forts part of the Civil War Defenses of Washington, D.C., during the Civil War built in the Northeast quadrant of the city at the beginning of the Civil War by the Union Army to protect the city from the Confederate Army. From west to east, the forts were as follow: Fort Slocum, Fort Totten, Fort Slemmer, Fort Bunker Hill, Fort Saratoga, Fort Thayer and Fort Lincoln. Unlike other forts, nothing remains of the structure.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.










