Fort Pemberton may refer to:
- Fort Pemberton (Mississippi), a Confederate fort near Greenwood, Mississippi
- Fort Pemberton (South Carolina), a Confederate fort on James Island South Carolina
Fort Pemberton may refer to:

The siege of Vicksburg was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Major General Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mississippi River and drove the Confederate Army of Mississippi, led by Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton, into the defensive lines surrounding the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, leading to the successful siege and Confederate surrender.

Joseph Eggleston Johnston was an American career army officer, serving with distinction in the United States Army during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) and the Seminole Wars. After Virginia declared secession from the United States, he entered the Confederate States Army as one of its most senior general officers. From 1888 to 1889 he was a vice president, from 1889 to 1890 president, of the Aztec Club of 1847.

The Vicksburg campaign was a series of maneuvers and battles in the Western Theater of the American Civil War directed against Vicksburg, Mississippi, a fortress city that dominated the last Confederate-controlled section of the Mississippi River. The Union Army of the Tennessee under Major General Ulysses S. Grant gained control of the river by capturing this stronghold and defeating Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton's forces stationed there.
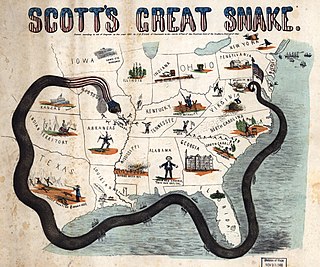
The Anaconda Plan was a strategy outlined by the Union Army for suppressing the Confederacy at the beginning of the American Civil War. Proposed by Union General-in-Chief Winfield Scott, the plan emphasized a Union blockade of the Southern ports and called for an advance down the Mississippi River to cut the South in two. Because the blockade would be rather passive, it was widely derided by a vociferous faction of Union generals who wanted a more vigorous prosecution of the war and likened it to the coils of an anaconda suffocating its victim. The snake image caught on, giving the proposal its popular name.

John Clifford Pemberton was a career United States Army officer who fought in the Seminole Wars and with distinction during the Mexican–American War. He resigned his commission to serve as a Confederate lieutenant-general during the American Civil War. He led the Army of Mississippi from December 1862 to July 1863 and was the commanding officer during the Confederate surrender at the Siege of Vicksburg.

Stephen Dill Lee was an American officer in the Confederate Army, politician, and first president of Mississippi State University from 1880 to 1899. He served as lieutenant general of the Confederate States Army in the Eastern and Western theaters of the American Civil War.

The Battle of Champion Hill of May 16, 1863, was the pivotal battle in the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War (1861–1865). Union Army commander Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and the Army of the Tennessee pursued the retreating Confederate States Army under Lt. Gen. John C. Pemberton and defeated it twenty miles to the east of Vicksburg, Mississippi, leading inevitably to the siege of Vicksburg and surrender. The battle is also known as Baker's Creek.

The Battle of Big Black River Bridge was fought on May 17, 1863, as part of the Vicksburg Campaign of the American Civil War. During the war, the city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, was a key point on the Mississippi River. On April 30, 1863, a Union army commanded by Major General Ulysses S. Grant began crossing onto the east side of the Mississippi River as part of a campaign against Vicksburg. After engaging and defeating Confederate forces in several intermediate battles, Grant's army defeated Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton's Confederates at the decisive Battle of Champion Hill on May 16. During the retreat from Champion Hill, one division of Pemberton's army, commanded by Major General William W. Loring, was cut off from Pemberton's main body. Pemberton did not know the location of Loring's division, and he held a bridgehead on the east side of the Big Black River to cover Loring's anticipated withdrawal across the river on the morning of May 17.

Star of the West was an American merchant steamship that was launched in 1852 and scuttled by Confederate forces in 1863. In January 1861, the ship was hired by the government of the United States to transport military supplies and reinforcements to the U.S. military garrison of Fort Sumter. A battery on Morris Island, South Carolina handled by cadets from the South Carolina Military Academy fired upon the ship, considered by some scholars to have been effectively the first shots fired in the American Civil War.

The western theater of the American Civil War encompassed major military operations in the states of Alabama, Georgia, Florida, Mississippi, North Carolina, Kentucky, South Carolina and Tennessee, as well as Louisiana east of the Mississippi River. Operations on the coasts of these states, except for Mobile Bay, are considered part of the Lower Seaboard Theater. Most other operations east of the Appalachian Mountains are part of the eastern theater. Operations west of the Mississippi River took place in the trans-Mississippi theater.

The Battle of Grand Gulf was fought on April 29, 1863, during the American Civil War. Union Army forces commanded by Major General Ulysses S. Grant had failed several times to bypass or capture the Confederate-held city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, during the Vicksburg campaign. Grant decided to move his army south of Vicksburg, cross the Mississippi River, and then advance on the city. A Confederate division under Brigadier General John S. Bowen prepared defenses—Forts Wade and Cobun—at Grand Gulf, Mississippi, south of Vicksburg. To clear the way for a Union crossing, seven Union Navy ironclad warships from the Mississippi Squadron commanded by Admiral David Dixon Porter bombarded the Confederate defenses at Grand Gulf on April 29. Union fire silenced Fort Wade and killed its commander, but the overall Confederate position held. Grant decided to cross the river elsewhere.

John Stevens Bowen was a career United States Army officer who later became a general in the Confederate Army and a commander in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. He fought at the battles of Shiloh, Corinth, and the Vicksburg Campaign. He is often said to have died just as his abilities were gaining attention.

William Wing Loring was an American soldier who served in the armies of the United States, the Confederacy, and Egypt.

USS Rattler was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.

The Yazoo Pass expedition was a joint operation of Major General Ulysses S. Grant's Army of the Tennessee and Rear Admiral David D. Porter's Mississippi River Squadron in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. Grant's objective was to get his troops into a flanking position against the Rebel defenders. The expedition was an effort to bypass the Confederate defenses on the bluffs near the city by using the backwaters of the Mississippi Delta as a route from the Mississippi River to the Yazoo River. Once on the Yazoo, the Army would be able to cross the river unopposed and thus achieve their goal. The operation would require a deep penetration into enemy territory that was dominated by water, so cooperation between the two services was necessary. The Army was led by Brigadier General Leonard F. Ross. Naval commander was Lieutenant Commander Watson Smith, whose extremely poor health was an important factor in the ultimate failure of the expedition.
Fort Pemberton Site may refer to:
Fort Pemberton was one of the larger confederate forts was constructed in the defense of Charleston, South Carolina during the American Civil War. At the war's outset in 1861, it became evident that control of the western regions of James Island and the Stono River was to be an important element in the defense of the city. Confederate military authorities of the time believed that Union occupation of James Island would leave Charleston subject to attack from the southeast. From this position the city would assuredly fall to the Union. Although there were many gun batteries in place along the south and east side of James Island, Fort Pemberton was the only fortress in defense of this region.

The 9th Arkansas Infantry Regiment was a regiment of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. It served in the Western Theater, seeing action in the Vicksburg, Tennessee and Georgia campaigns. Due to attrition; the 9th Arkansas was consolidated several times with other Arkansas regiments, finally merging in 1865 into the 1st Arkansas Consolidated Mounted Rifles.

The 1st Georgia Sharpshooter Battalion was a sharpshooter unit of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. It was authorized by an act in April 1862 by the Confederate Congress, and was formed in Savannah, Georgia. The 1st Battalion Sharpshooters served at Fort McAllister defending the coast of Georgia in the Battle of Fort McAllister (1863). They also saw action at the Battle of Jackson, Mississippi, as well as the Battle of Chickamauga, and the Chattanooga Campaign. The battalion fought to the end of the war, their last engagement being at the Battle of Bentonville in March 1865.

Landis's Missouri Battery, also known as Landis's Company, Missouri Light Artillery, was an artillery battery that served in the Confederate States Army during the early stages of the American Civil War. The battery was formed when Captain John C. Landis recruited men from the Missouri State Guard in late 1861 and early 1862. The battery fielded two 12-pounder Napoleon field guns and two 24-pounder howitzers for much of its existence, and had a highest reported numerical strength of 62 men. After initially serving in the Trans-Mississippi Theater, where it may have fought in the Battle of Pea Ridge, the unit was transferred east of the Mississippi River. The battery saw limited action in 1862 at the Battle of Iuka and at the Second Battle of Corinth.