
Four-in-a-row (or four-in-a-line, Yonmoku-Narabe) is the name for several games in which the object is to line up four things in a row. Some of these games are:

Four-in-a-row (or four-in-a-line, Yonmoku-Narabe) is the name for several games in which the object is to line up four things in a row. Some of these games are:

Gomoku, also called Five in a Row, is an abstract strategy board game. It is traditionally played with Go pieces on a 15×15 Go board while in the past a 19×19 board was standard. Because pieces are typically not moved or removed from the board, gomoku may also be played as a paper-and-pencil game. The game is known in several countries under different names.

Mancala refers to a family of two-player turn-based strategy board games played with small stones, beans, or seeds and rows of holes or pits in the earth, a board or other playing surface. The objective is usually to capture all or some set of the opponent's pieces.
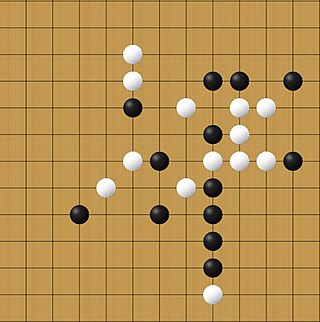
Pente is an abstract strategy board game for two or more players, created in 1977 by Gary Gabrel. A member of the m,n,k game family, Pente stands out for its custodial capture mechanic, which allows players to "sandwich" pairs of stones and capture them by flanking them on either side. This changes the overall tactical assessments players face when compared to pure placement m,n,k games such as Gomoku.

Tic-tac-toe, noughts and crosses, or Xs and Os is a paper-and-pencil game for two players who take turns marking the spaces in a three-by-three grid with X or O. The player who succeeds in placing three of their marks in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row is the winner. It is a solved game, with a forced draw assuming best play from both players.

Nine men's morris is a strategy board game for two players dating at least to the Roman Empire. The game is also known as nine-man morris, mill, mills, the mill game, merels, merrills, merelles, marelles, morelles, and ninepenny marl in English. In North America, the game has also been called cowboy checkers, and its board is sometimes printed on the back of checkerboards. Nine men's morris is a solved game, that is, a game whose optimal strategy has been calculated. It has been shown that with perfect play from both players, the game results in a draw.
Three men's morris is an abstract strategy game played on a three by three board that is similar to tic-tac-toe. It is also related to six men's morris and nine men's morris. A player wins by forming a mill, that is, three of their own pieces in a row.

Twister is a game of physical skill produced by Milton Bradley Company and Winning Moves Games USA. It is played on a large plastic mat that is spread on the floor or ground. The mat has four rows of six large colored circles on it with a different color in each row: red, yellow, green and blue. A spinner tells players where they have to place their hand or foot. The game promotes itself as "the game that ties you up in knots".
Mak-yek is a two-player abstract strategy board game played in Thailand and Myanmar. Players move their pieces as in the rook in Chess and attempt to capture their opponent's pieces through custodian and intervention capture. The game may have been first described in literature by Captain James Low a writing contributor in the 1839 work Asiatic Researches; or, Transactions of the Society, Instituted in Bengal, For Inquiring into The History, The Antiquities, The Arts and Sciences, and Literature of Asian, Second Part of the Twentieth Volume in which he wrote chapter X On Siamese Literature and documented the game as Maak yék. Another early description of the game is by H.J.R. Murray in his 1913 work A History of Chess, and the game was written as Maak-yek.

In the United States and Canada, bingo is a game of chance in which each player matches the numbers printed in different arrangements on cards. The game host draws balls at random, marking the selected numbers with tiles. When a player finds that the selected numbers are arranged on their card in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal line, they call out "Bingo!" to alert all participants to a winning card, which prompts the game host to examine the card for verification of the win. Players compete against one another to be the first to have a winning arrangement for the prize or jackpot. After a winner is declared, the players clear their number cards of the tiles and the game host begins a new round of play.

Mastermind or Master Mind is a code-breaking game for two players invented in Israel. It resembles an earlier pencil and paper game called Bulls and Cows that may date back a century.

Connect Four is a game in which the players choose a color and then take turns dropping colored tokens into a six-row, seven-column vertically suspended grid. The pieces fall straight down, occupying the lowest available space within the column. The objective of the game is to be the first to form a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal line of four of one's own tokens. It is therefore a type of M,n,k-game with restricted piece placement. Connect Four is a solved game. The first player can always win by playing the right moves.

3D tic-tac-toe, also known by the trade name Qubic, is an abstract strategy board game, generally for two players. It is similar in concept to traditional tic-tac-toe but is played in a cubical array of cells, usually 4×4×4. Players take turns placing their markers in blank cells in the array. The first player to achieve four of their own markers in a row wins. The winning row can be horizontal, vertical, or diagonal on a single board as in regular tic-tac-toe, or vertically in a column, or a diagonal line through four boards.

GIPF is an abstract strategy board game by Kris Burm, the first of seven games in his series of games called the GIPF Project. GIPF was recommended by Spiel des Jahres in 1998.

Four-player chess is a family of chess variants played with four people. The game features a special board typically made of a standard 8×8 square, with 3 rows of 8 cells each extending from each side, and requires two sets of differently colored pieces. The rules are similar to, but not the same as, regular chess. There are a variety of different rule variations; most variations, however, share a somewhat similar board and piece setup.
Brain Chain is a strategy-driven trivia board game played by two or three players or teams. The object is to be the first player or team to connect an unbroken row of six "links" horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. The game is played on a 10x10 category grid surrounded by an exterior track. Brain Chain has been described as Trivial Pursuit with a Go-Moku win mechanic plus a dash of Pueblo added in.
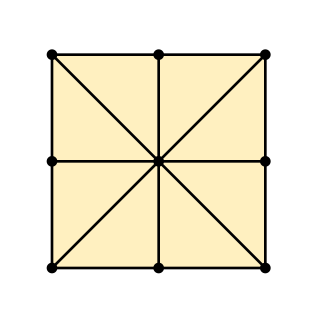
Achi is a two-player abstract strategy game from Ghana. It is also called tapatan. It is related to tic-tac-toe, but even more related to three men's morris, Nine Holes, Tant Fant, Shisima, and Dara, because pieces are moved on the board to create the 3-in-a-row. Achi is an alignment game.
Shisima is a two-player abstract strategy game from Kenya. It is related to tic-tac-toe, and even more so to three men's morris, Nine Holes, Achi, Tant Fant, and Dara, because pieces are moved on the board to create the 3-in-a-row. Unlike those other games, Shisima uses an octagonal board.

Speed Circuit is a Formula I racing game published by 3M in 1971, and then republished by Avalon Hill in 1977.
Order and Chaos is a variant of the game tic-tac-toe on a 6×6 gameboard. It was invented by Stephen Sniderman and introduced by him in Games magazine in 1981. The player Order strives to create a five-in-a-row of either Xs or Os. The opponent Chaos endeavors to prevent this.

Tic-tac-toe is an instance of an m,n,k-game, where two players alternate taking turns on an m×n board until one of them gets k in a row. Harary's generalized tic-tac-toe is an even broader generalization. The game can also be generalized as a nd game. The game can be generalised even further from the above variants by playing on an arbitrary hypergraph where rows are hyperedges and cells are vertices.