Related Research Articles
Outsourcing is an agreement in which one company hires another company to be responsible for a planned or existing activity that is or could be done internally, and sometimes involves transferring employees and assets from one firm to another.
Employment is a relationship between two parties, usually based on a contract where work is paid for, where one party, which may be a corporation, for profit, not-for-profit organization, co-operative or other entity is the employer and the other is the employee. Employees work in return for payment, which may be in the form of an hourly wage, by piecework or an annual salary, depending on the type of work an employee does or which sector they are working in. Employees in some fields or sectors may receive gratuities, bonus payment or stock options. In some types of employment, employees may receive benefits in addition to payment. Benefits can include health insurance, housing, disability insurance or use of a gym. Employment is typically governed by employment laws, organisation or legal contracts.

Temporary work or temporary employment refers to an employment situation where the working arrangement is limited to a certain period of time based on the needs of the employing organization. Temporary employees are sometimes called "contractual", "seasonal", "interim", "casual staff", "outsourcing", "freelance"; or the words may be shortened to "temps". In some instances, temporary, highly skilled professionals refer to themselves as consultants.
Freelance, freelancer, and freelance worker, are terms commonly used for a person who is self-employed and is not necessarily committed to a particular employer long-term. Freelance workers are sometimes represented by a company or a temporary agency that resells freelance labor to clients; others work independently or use professional associations or websites to get work.
Self-employment is the state of working for oneself rather than an employer.
An independent contractor is a person, business, or corporation that provides goods or services under a written contract or a verbal agreement. Unlike employees, independent contractors do not work regularly for an employer but work as required, when they may be subject to law of agency. Independent contractors are usually paid on a freelance basis. Contractors often work through a limited company or franchise, which they themselves own, or may work through an umbrella company.
A permatemp is a temporary employee who works for an extended period for a single staffing client. The word is a portmanteau of the words permanent and temporary.
Contingent work, casual work, or contract work, is an employment relationship with limited job security, payment on a piece work basis, typically part time that is considered non-permanent. Although there is less job security, freelancers often report incomes higher than their former traditional jobs.

Freelancers Union is a non-profit organization in the United States of America. The organization provides advocacy and health insurance to its members through its for-profit Freelancers Insurance Company. The union promotes information through monthly meetings.
A vendor management system (VMS) is an Internet-enabled, often Web-based application that acts as a mechanism for business to manage and procure staffing services – temporary, and, in some cases, permanent placement services – as well as outside contract or contingent labor. Typical features of a VMS application include order distribution, consolidated billing and significant enhancements in reporting capability that outperforms manual systems and processes.
Proprietism is an economic system composed of a vast network of sole-proprietorships.
Unreported employment; working under the table, off the books, cash-in-hand or illicit work is illegal employment that is not reported to the government. The employer or the employee often does so for tax evasion or avoiding or violating other laws. The working contract is made without social security costs, and does typically not provide health insurance, paid parental leave, paid vacation or pension funds. It is a part of what has been called the underground economy, shadow economy, black market or the non-observed economy.
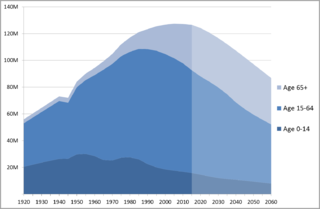
The aging of Japan is thought to outweigh all other nations, with Japan being purported to have the highest proportion of elderly citizens. Japan is experiencing a "super-aging" society both in rural and urban areas. According to 2014 estimates, 33.0% of the Japanese population is above the age of 60, 25.9% are aged 65 or above, and 12.5% are aged 75 or above. People aged 65 and older in Japan make up a quarter of its total population, estimated to reach a third by 2050.
Iowa Workforce Development is a government agency in the American state of Iowa, responsible for overseeing workplace safety, workers' compensation, unemployment insurance and job training services. It was formed in May 1996.
Global workforce refers to the international labor pool of workers, including those employed by multinational companies and connected through a global system of networking and production, immigrant workers, transient migrant workers, telecommuting workers, those in export-oriented employment, contingent work or other precarious employment. As of 2012, the global labor pool consisted of approximately 3 billion workers, around 200 million unemployed.
The Georgia Department of Labor is an administrative agency of the U.S. state of Georgia. With approximately 4,000 employees in 2008, it provides services to the state's current and emerging workforce.

The New Jersey Department of Labor and Workforce Development is a governmental agency of the U.S. state of New Jersey. The New Jersey Civil Service Commission is independent body within the New Jersey state government under the auspices of the Department.
Sharing economy is a term for a way of distributing goods and services, a way that differs from the traditional model of corporations hiring employees and selling products to consumers. In the sharing economy, individuals are said to rent or "share" things like their cars, homes and personal time to other individuals in a peer-to-peer fashion.
Dislocated worker funding is typically used to help workers in events of mass employment loss. A dislocated or displaced worker is defined as an individual who has been laid off or received notice of a potential layoff and has very little chance of finding employment in their current occupation when attempting to return to the workforce. Displaced workers are most frequently found in the manufacturing industry. Legislation addressing training for these workers was first introduced in 1959 through the passing of the Area Redevelopment Act of 1959. Over the years, legislation funding these programs has included wording holding states and private businesses accountable for the roles in the dislocation of workers. Due to the importance of this funding and the negative economic impact of displaced workers, the United States has passed continuing legislation as recent as 2014 and 2015.
Gig worker means independent contractors, online platform workers, contract firm workers, on-call workers and temporary workers. Gig workers enter into formal agreements with on-demand companies, for example Uber, TaskRabbit, to provide services to the company's clients.
References
- ↑ Business & Legal Reports: Study: Free-Agent Workforce Grows
- ↑ "Fast Company: Free Agent Nation". Archived from the original on 2006-10-16. Retrieved 2007-01-19.
- ↑ "Changes in the Labor Market Leads to Increase in Free Agent". Kelly Services. 15 August 2011. Retrieved 15 December 2011.
- ↑ "Free Agent, Free Spirit". Fast Company. Retrieved 17 April 2015.