
Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE), also known as 2.75G, Enhanced GPRS (EGPRS), IMT Single Carrier (IMT-SC), and Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution, is a 2G digital mobile phone technology for data transmission. It is a subset of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) on the GSM network and improves upon it offering speeds close to 3G technology, hence the name 2.75G.

The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. GSM is also a trade mark owned by the GSM Association. GSM may also refer to the Full Rate voice codec.

General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), also called 2.5G, is a mobile data standard on the 2G cellular communication network's global system for mobile communications (GSM). Networks and mobile devices with GPRS started to roll out around the year 2001. At the time of introduction it offered for the first time seamless mobile data transmission using packet data for an "always-on" connection, providing improved Internet access for web, email, WAP services, and Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS).
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP, UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.

The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is an umbrella term for a number of standards organizations which develop protocols for mobile telecommunications. Its best known work is the development and maintenance of:
In the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) and 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE), user equipment (UE) is any device used directly by an end-user to communicate. It can be a hand-held telephone, a laptop computer equipped with a mobile broadband adapter, or any other device. It connects to the base station Node B/eNodeB as specified in the ETSI 125/136-series and 3GPP 25/36-series of specifications. It roughly corresponds to the mobile station (MS) in GSM systems.
The GPRS core network is the central part of the general packet radio service (GPRS) which allows 2G, 3G and WCDMA mobile networks to transmit Internet Protocol (IP) packets to external networks such as the Internet. The GPRS system is an integrated part of the GSM network switching subsystem.
Network switching subsystem (NSS) is the component of a GSM system that carries out call out and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations. It is owned and deployed by mobile phone operators and allows mobile devices to communicate with each other and telephones in the wider public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture contains specific features and functions which are needed because the phones are not fixed in one location.
In communications, Circuit Switched Data (CSD) is the original form of data transmission developed for the time-division multiple access (TDMA)-based mobile phone systems like Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM). After 2010 many telecommunication carriers dropped support for CSD, and CSD has been superseded by GPRS and EDGE (E-GPRS).
Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (AMR-WB) is a patented wideband speech audio coding standard developed based on Adaptive Multi-Rate encoding, using a similar methodology to algebraic code-excited linear prediction (ACELP). AMR-WB provides improved speech quality due to a wider speech bandwidth of 50–7000 Hz compared to narrowband speech coders which in general are optimized for POTS wireline quality of 300–3400 Hz. AMR-WB was developed by Nokia and VoiceAge and it was first specified by 3GPP.
In telecommunications networks, RANAP is a protocol specified by 3GPP in TS 25.413 and used in UMTS for signaling between the Core Network, which can be a MSC or SGSN, and the UTRAN. RANAP is carried over Iu-interface.
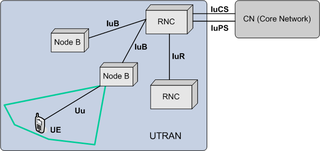
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) is a collective term for the network and equipment that connects mobile handsets to the public telephone network or the Internet. It contains the base stations, which are called Node B's and Radio Network Controllers (RNCs) which make up the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) radio access network. This communications network, commonly referred to as 3G, can carry many traffic types from real-time Circuit Switched to IP based Packet Switched. The UTRAN allows connectivity between the UE and the core network.
Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Services (MBMS) is a point-to-multipoint interface specification for existing 3GPP cellular networks, which is designed to provide efficient delivery of broadcast and multicast services, both within a cell as well as within the core network. For broadcast transmission across multiple cells, it defines transmission via single-frequency network configurations. The specification is referred to as Evolved Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Services (eMBMS) when transmissions are delivered through an LTE network. eMBMS is also known as LTE Broadcast.
A radio access network (RAN) is part of a mobile telecommunication system implementing a radio access technology (RAT). Conceptually, it resides between a device such as a mobile phone, a computer, or any remotely controlled machine and provides connection with its core network (CN). Depending on the standard, mobile phones and other wireless connected devices are varyingly known as user equipment (UE), terminal equipment, mobile station (MS), etc. RAN functionality is typically provided by a silicon chip residing in both the core network as well as the user equipment. See the following diagram:
CN / ⧵ / ⧵ RAN RAN / ⧵ / ⧵ UE UE UE UE
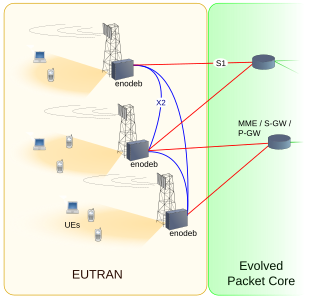
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access, also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and a Node B.

Wi-Fi calling, also called VoWiFi, refers to mobile phone voice calls and data that are made over IP networks using Wi-Fi, instead of the cell towers provided by cellular networks. Using this feature, compatible handsets are able to route regular cellular calls through a wireless LAN (Wi-Fi) network with broadband Internet, while seamlessly change connections between the two where necessary. This feature makes use of the Generic Access Network (GAN) protocol, also known as Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA).
Radio Base Station (RBS) is the commercial name given to the family of Base Stations developed by Ericsson, typically constituting a sizable part of the Radio Access Network (RAN). Radio Base Station is also the generic name to be used instead of BTS which are typically denoting GSM-era radio base station technology. For other vendors, specific equipment names are used such as Huawei DBS or NSN Flexi base stations.
System Architecture Evolution (SAE) is the core network architecture of mobile communications protocol group 3GPP's LTE wireless communication standard.
HNBAP is a control protocol found in Home Node B networks on the Iu-h interface.

E-UTRAN Node B, also known as Evolved Node B, is the element in E-UTRA of LTE that is the evolution of the element Node B in UTRA of UMTS. It is the hardware that is connected to the mobile phone network that communicates directly wirelessly with mobile handsets (UEs), like a base transceiver station (BTS) in GSM networks.







