This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies smooth muscle and glands, and thus influences the function of internal organs. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions such as the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response.

The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the other being the parasympathetic nervous system.

A dorsal root ganglion, is a cluster of neurons in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.

The pterygopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion found in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is largely innervated by the greater petrosal nerve ; and its axons project to the lacrimal glands and nasal mucosa. The flow of blood to the nasal mucosa, in particular the venous plexus of the conchae, is regulated by the pterygopalatine ganglion and heats or cools the air in the nose. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck, the others being the submandibular ganglion, otic ganglion, and ciliary ganglion.
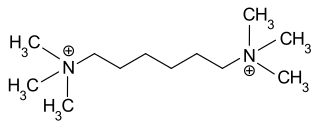
Hexamethonium is a non-depolarising ganglionic blocker, a nicotinic nACh (NN) receptor antagonist that acts in autonomic ganglia by binding mostly in or on the NN receptor, and not the acetylcholine binding site itself. It does not have any effect on the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR) located on target organs of the parasympathetic nervous system but acts as antagonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors located in sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia (NN).

Prevertebral ganglia are sympathetic ganglia which lie between the paravertebral ganglia and the target organ.

The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is part of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), more specifically it is part of the sympathetic nervous system, a division of the ANS most commonly associated with the fight or flight response. The ANS is composed of pathways that lead to and from ganglia, groups of nerve cells. A ganglion allows a large amount of divergence in a neuronal pathway and also enables a more localized circuitry for control of the innervated targets. The SCG is the only ganglion in the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. It is the largest and most rostral (superior) of the three cervical ganglia. The SCG innervates many organs, glands and parts of the carotid system in the head.

The submandibular ganglion is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck..
Each spinal nerve receives a branch called a gray ramus communicans from the adjacent paravertebral ganglion of the sympathetic trunk. The gray rami communicantes contain postganglionic nerve fibers of the sympathetic nervous system and are composed of largely unmyelinated neurons. This is in contrast to the white rami communicantes, in which heavily myelinated neurons give the rami their white appearance.

In the autonomic nervous system, fibers from the CNS to the ganglion are known as preganglionic fibers. All preganglionic fibers, whether they are in the sympathetic division or in the parasympathetic division, are cholinergic and they are myelinated.

The celiac ganglia or coeliac ganglia are two large irregularly shaped masses of nerve tissue in the upper abdomen. Part of the sympathetic subdivision of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), the two celiac ganglia are the largest ganglia in the ANS, and they innervate most of the digestive tract.

Parasympathetic ganglia are the autonomic ganglia of the parasympathetic nervous system. Most are small terminal ganglia or intramural ganglia, so named because they lie near or within (respectively) the organs they innervate. The exceptions are the four paired parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck.

Sympathetic ganglia are the ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. They deliver information to the body about stress and impending danger, and are responsible for the familiar fight-or-flight response. They contain approximately 20,000–30,000 nerve cell bodies and are located close to and on either side of the spinal cord in long chains. Sympathetic ganglia are the tissue from which neuroblastoma tumours arise.

The cervical ganglia are paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Preganglionic nerves from the thoracic spinal cord enter into the cervical ganglions and synapse with its postganglionic fibers or nerves. The cervical ganglion has three paravertebral ganglia:
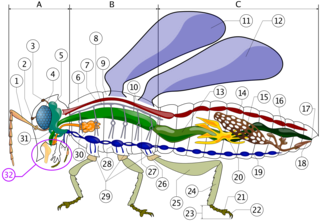
The suboesophageal ganglion of arthropods and in particular insects is part of the arthropod central nervous system (CNS). As indicated by its name, it is located below the oesophagus, inside the head. As part of the ventral nerve cord, it is connected to the brain and to the first thoracic ganglion. Its nerves innervate the sensory organs and muscles of the mouthparts and the salivary glands.
A ganglionic blocker is a type of medication that inhibits transmission between preganglionic and postganglionic neurons in the Autonomic Nervous System, often by acting as a nicotinic receptor antagonist. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are found on skeletal muscle, but also within the route of transmission for the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system. More specifically, nicotinic receptors are found within the ganglia of the autonomic nervous system, allowing outgoing signals to be transmitted from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells. Thus, for example, blocking nicotinic acetylcholine receptors blocks both sympathetic (excitatory) and parasympathetic (calming) stimulation of the heart. The nicotinic antagonist hexamethonium, for example, does this by blocking the transmission of outgoing signals across the autonomic ganglia at the postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.

A ganglion cell is a cell found in a ganglion. The term is also sometimes used to refer specifically to:
In neuroanatomy, the cranial nerve ganglia are either parasympathetic or sensory ganglia of the cranial nerves.
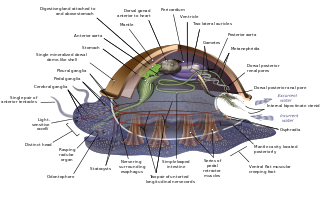
A circumesophageal or circumpharyngeal nerve ring is an arrangement of nerve ganglia around the esophagus/ pharynx of an animal. It is a common feature of nematodes, molluscs, and many other invertebrate animals, though it is absent in all vertebrate animals and is not structurally possible in simpler one such as water bears.