
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) social movements are social movements that advocate for LGBT people in society. Social movements may focus on equal rights, such as the 2000s movement for same-sex marriage, or they may focus on liberation, as in the gay liberation movement of the 1960s and 1970s. Earlier movements focused on self-help and self-acceptance, such as the homophile movement of the 1950s. Although there is not a primary or an overarching central organization that represents all LGBT people and their interests, numerous LGBT rights organizations are active worldwide. The earliest organizations to support LGBT rights were formed in the early 20th century.

Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same sex or gender, entered into in a civil or religious ceremony. There are records of same-sex marriage dating back to the first century. In the modern era, marriage equality was first granted to same-sex couples in the Netherlands on 1 April 2001.
The Federal Marriage Amendment (FMA), also referred to by proponents as the Marriage Protection Amendment, was a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution that would legally define marriage as a union of one man and one woman. The FMA would also prevent judicial extension of marriage rights to same-sex or other unmarried homosexual couples. An amendment to the U.S. Constitution requires the support of two thirds of each house of Congress and ratification by three fourths of the states. The last Congressional vote on the proposed amendment occurred in the House of Representatives on July 18, 2006, when the motion failed 236 to 187, falling short of the 290 votes required for passage in that body. The Senate has only voted on cloture motions with regard to the proposed amendment, the last of which was on June 7, 2006, when the motion failed 49 to 48, falling short of the 60 votes required to allow the Senate to proceed to consideration of the proposal and the 67 votes required to send the proposed amendment to the states for ratification. President Bush endorsed this proposal and made it part of his campaign during the 2004 and 2006 election cycles.

In the United States, the availability of legally recognized same-sex marriage expanded from one state in 2004 to all fifty states in 2015 through various state and federal court rulings, state legislation, and direct popular votes. The fifty states each have separate marriage laws, which must adhere to rulings by the Supreme Court of the United States that recognize marriage as a fundamental right that is guaranteed by both the Due Process Clause and the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as first established in the 1967 landmark civil rights case of Loving v. Virginia.

Jonathan Charles Rauch is an American author, journalist, and activist. After graduating from Yale University, Rauch worked at the Winston-Salem Journal in North Carolina, for National Journal, and later for The Economist and as a freelance writer. He is currently a senior fellow in governance studies at the Brookings Institution and a contributing editor of The Atlantic.

Evan Wolfson is an attorney and gay rights advocate. He is the founder of Freedom to Marry, a group favoring same-sex marriage in the United States, serving as president until its 2015 victory and subsequent wind-down. Wolfson authored the book Why Marriage Matters: America, Equality, and Gay People's Right to Marry, which Time Out New York magazine called, "Perhaps the most important gay-marriage primer ever written..." He was listed as one of Time magazine's 100 Most Influential People in the World. He has taught as an adjunct professor at Columbia Law School, Rutgers Law School, and Whittier Law School and argued before the Supreme Court in Boy Scouts of America v. Dale. He now teaches law and social change at Georgetown Law School and at Yale University; serves as a senior counsel at Dentons, the world’s largest law firm; and primarily provides advice and assistance to other organizations and causes, in the United States and globally, that are seeking to adapt the lessons on ‘how to win’ from the same-sex marriage movement.
This article addresses the history of lesbianism in the United States. Unless otherwise noted, the members of same-sex female couples discussed here are not known to be lesbian, but they are mentioned as part of discussing the practice of lesbianism—that is, same-sex female sexual and romantic behavior.

2006 Virginia Question 1, the Marshall-Newman Amendment is an amendment to the Constitution of Virginia that defines marriage as solely between one man and one woman and bans recognition of any legal status "approximat[ing] the design, qualities, significance, or effects of marriage". The amendment was ratified by 57% of the voters on November 7, 2006. It became part of the state Constitution as Section 15-A of Article 1. In 2014, the amendment was ruled unconstitutional in Bostic v. Schaefer.
Recognition of same-sex unions in the Americas is widespread, with a majority of people in both North America and South America living in jurisdictions providing marriage rights to LGBT citizens.

Davina Kotulski is a clinical psychologist, writer and same-sex marriage activist and leader in the Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Transgender Equal Rights movement. Kotulski began publicly advocating for same-sex marriage in 1999. Kotulski is the author of It's Never Too Late to Be Your Self,Why You Should give a Damn About Gay Marriage and Love Warriors: The Rise of the Marriage Equality Movement and Why it Will Prevail.

Proposition 8, known informally as Prop 8, was a California ballot proposition and a state constitutional amendment intended to ban same-sex marriage; it passed in the November 2008 California state elections and was later overturned in court. The proposition was created by opponents of same-sex marriage in advance of the California Supreme Court's May 2008 appeal ruling, In re Marriage Cases, which followed the short-lived 2004 same-sex weddings controversy and found the previous ban on same-sex marriage unconstitutional. Proposition 8 was ultimately ruled unconstitutional by a federal court in 2010, although the court decision did not go into effect until June 26, 2013, following the conclusion of proponents' appeals.

A same-sex relationship is a romantic or sexual relationship between people of the same sex. Same-sex marriage refers to the institutionalized recognition of such relationships in the form of a marriage; civil unions may exist in countries where same-sex marriage does not.
Many views are held or have been expressed by religious organizations in relation to same-sex marriage. Arguments both in favor of and in opposition to same-sex marriage are often made on religious grounds and/or formulated in terms of religious doctrine. Although many of the world's religions are opposed to same-sex marriage, the number of religious denominations that are conducting same-sex marriages have been increasing since 2010. Religious views on same-sex marriage are closely related to religious views on homosexuality.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S. state of Maine since December 29, 2012. A bill for the legalization of same-sex marriages was approved by voters, 53–47 percent, on November 6, 2012, as Maine, Maryland and Washington became the first U.S. states to legalize same-sex marriage by popular vote. Election results were certified by the Maine Secretary of State's office and the Governor of Maine on November 29.

Concerns regarding same-sex marriage and the family are at the forefront of the controversies over legalization of same-sex marriage. In the United States, an estimated 1 million to 9 million children have at least one lesbian, gay, bi, trans, intersex, or queer parent. Concern for these children and others to come are the basis for both opposition to and support for marriage for LGBT couples.
David Blankenhorn is the founder and president of the Institute for American Values and its initiative Braver Angels. He is also co-director of The Marriage Opportunity Council and the author of Fatherless America and The Future of Marriage. A noted figure in the campaign against same-sex marriage in the United States, his position changed and he voiced support of legalizing same-sex marriage in June 2012.

LGBT history in the United States spans the contributions and struggles of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender individuals as well as the coalitions they've built. States like California, New Jersey, Colorado, Oregon, and Illinois have public school curricula that legally require LGBT history lessons, including prominent gay people and LGBT-rights milestones, in history classes.
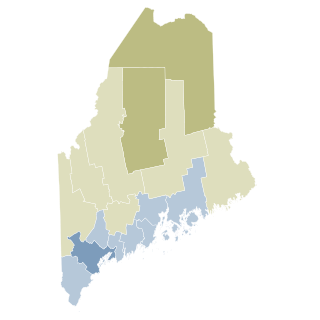
Maine Question 1 was a voter referendum on an initiated state statute that occurred November 6, 2012. The title of the citizen initiative is "An Act to Allow Marriage Licenses for Same-Sex Couples and Protect Religious Freedom". The question that appeared on the ballot was: "Do you want to allow the State of Maine to issue marriage licenses to same-sex couples?"

This article addresses the history of gay men in the United States. Unless otherwise noted, the members of same-sex male couples discussed here are not known to be gay, but they are mentioned as part of discussing the practice of male homosexuality—that is, same-sex male sexual and romantic behavior.

Gay Marriage: Why It Is Good for Gays, Good for Straights, and Good for America is a 2004 book by the journalist Jonathan Rauch in which the author advocates the legal and social recognition of same-sex marriage.












