Related Research Articles

The organized International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 16 million volunteers, members, and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human suffering.

A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hostages, unnecessarily destroying civilian property, deception by perfidy, wartime sexual violence, pillaging, and for any individual that is part of the command structure who orders any attempt to committing mass killings including genocide or ethnic cleansing, the granting of no quarter despite surrender, the conscription of children in the military and flouting the legal distinctions of proportionality and military necessity.

The law of war is a component of international law that regulates the conditions for initiating war and the conduct of hostilities. Laws of war define sovereignty and nationhood, states and territories, occupation, and other critical terms of law.

A hospital ship is a ship designated for primary function as a floating medical treatment facility or hospital. Most are operated by the military forces of various countries, as they are intended to be used in or near war zones. In the 19th century, redundant warships were used as moored hospitals for seamen.

Non-combatant is a term of art in the law of war and international humanitarian law to refer to civilians who are not taking a direct part in hostilities; persons, such as combat medics and military chaplains, who are members of the belligerent armed forces but are protected because of their specific duties ; combatants who are placed hors de combat; and neutral persons, such as peacekeepers, who are not involved in fighting for one of the belligerents involved in a war. This particular status was first recognized under the Geneva Conventions with the First Geneva Convention of 1864.

The Second Geneva Convention, officially the Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea, is one of the four treaties of the Geneva Conventions. The Geneva Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea was first adopted in 1949, replacing the Hague Convention (X) of 1907. It adapts the main protective regime of the First Geneva Convention to combat at sea.

The First Geneva Convention, officially the Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded in Armies in the Field, held on 22 August 1864, is the first of four treaties of the Geneva Conventions. It defines "the basis on which rest the rules of international law for the protection of the victims of armed conflicts."

Disarmed Enemy Forces is a US designation for soldiers who surrender to an adversary after hostilities end, and for those POWs who had already surrendered and were held in camps in occupied German territory at the time. It was General Dwight D. Eisenhower's designation of German prisoners in post–World War II occupied Germany.
International humanitarian law (IHL), also referred to as the laws of armed conflict, is the law that regulates the conduct of war. It is a branch of international law that seeks to limit the effects of armed conflict by protecting persons who are not participating in hostilities and by restricting and regulating the means and methods of warfare available to combatants.

A combat medic is responsible for providing emergency medical treatment at a point of wounding in a combat or training environment, as well as primary care and health protection and evacuation from a point of injury or illness. Additionally, medics may also be responsible for the creation, oversight, and execution of long-term patient care plans in consultation with or in the absence of a readily available doctor or advanced practice provider. Combat medics may be used in hospitals and clinics, where they have the opportunity to work in additional roles, such as operating medical and laboratory equipment and performing and assisting with procedures.

Under the Geneva Conventions, the emblems of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement are to be worn by all medical and humanitarian personnel and also displayed on their vehicles and buildings while they are in an active warzone, and all military forces operating in an active warzone must not attack entities displaying these emblems. The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement recognizes four protection emblems, three of which are in use: the Red Cross, the Red Crescent, the Red Lion and Sun, and the Red Crystal.

The Geneva Convention on Prisoners of War was signed at Geneva, July 27, 1929. Its official name is the Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War. It entered into force 19 June 1931. It is this version of the Geneva Conventions which covered the treatment of prisoners of war during World War II. It is the predecessor of the Third Geneva Convention signed in 1949.

The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) is a humanitarian organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, and is a three-time Nobel Prize laureate. The organization has played an instrumental role in the development of rules of war and promoting humanitarian norms.
Protective signs are legally protected symbols to be used during an armed conflict to mark persons and objects under the protection of various treaties of international humanitarian law. While their essential meaning can be summarized as "don't shoot" or "don't attack", the exact conditions implied vary depending on the respective sign and the circumstances of its use. The form, shape and color of these signs are defined by the rules of international humanitarian law. Usually, they are easy to draw in order to make even an improvised use as easy as possible, and they were chosen to be as concise, recognizable and visible as possible under all circumstances.
There are differences from one country to another regarding the definition of Japanese war crimes. War crimes have been broadly defined as violations of the laws or customs of war, which involves acts using prohibited weapons, violating battlefield norms while engaging in combat with the enemy combatants, or against protected persons, including enemy civilians and citizens and property of neutral states as in the case of the attack on Pearl Harbor. Military personnel from the Empire of Japan have been accused and/or convicted of committing many such acts during the period of Japanese imperialism from the late 19th to mid-20th centuries. They have been accused of conducting a series of human rights abuses against civilians and prisoners of war (POWs) throughout east Asia and the western Pacific region. These events reached their height during the Second Sino-Japanese War of 1937–45 and the Asian and Pacific campaigns of World War II (1941–45).
The Rule of Law in Armed Conflicts Project is an initiative of the Geneva Academy of International Humanitarian Law and Human Rights to support the application and implementation of the international law of armed conflict.

The Geneva Conventions are international humanitarian laws consisting of four treaties and three additional protocols that establish international legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war. The singular term Geneva Convention colloquially denotes the agreements of 1949, negotiated in the aftermath of the Second World War (1939–1945), which updated the terms of the two 1929 treaties and added two new conventions. The Geneva Conventions extensively define the basic rights of wartime prisoners, civilians and military personnel; establish protections for the wounded and sick; and provide protections for the civilians in and around a war-zone.

The Algerian Red Crescent is an Algerian humanitarian volunteer organization founded in 1957. It has been recognized by the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement only since 1963.
The following is a list of events, births, and deaths in 1929 in Switzerland.
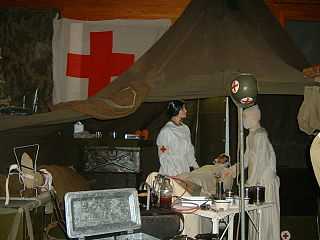
Protected persons is a legal term under international humanitarian law and refers to persons who are under specific protection of the 1949 Geneva Conventions, their 1977 Additional Protocols, and customary international humanitarian law during an armed conflict.