
The Austrian People's Party is a Christian-democratic and liberal-conservative political party in Austria.

The German People's Party was a conservative-liberal political party during the Weimar Republic that was the successor to the National Liberal Party of the German Empire. Along with the left-liberal German Democratic Party (DDP), it represented political liberalism in Germany between 1918 and 1933.

The Centre Party, officially the German Centre Party and also known in English as the Catholic Centre Party, is a Christian democratic political party in Germany. It was most Influential in the German Empire and Weimar Republic. Formed in 1870, it successfully battled the Kulturkampf waged by Chancellor Otto von Bismarck against the Catholic Church. It soon won a quarter of the seats in the Reichstag, and its middle position on most issues allowed it to play a decisive role in the formation of majorities. The party name Zentrum (Centre) originally came from the fact that Catholic representatives would take up the middle section of seats in parliament between the social democrats and the conservatives.

The Christian Democratic People's Party of Switzerland, also called the Christian Democratic Party, Democratic People's Party and Swiss Christian Democratic Party, was a Christian democratic political party in Switzerland. On 1 January 2021, it merged with the Conservative Democratic Party of Switzerland (BDP/PBD) to form The Centre, which now operates at the federal level. The Christian Democratic People's Party will continue to exist at the cantonal level as individual local and regional parties determine their status. Its 28 seats in the National Council and 13 seats in the Council of States were transferred to the new party, as was its sole seat on the Federal Council, held by Viola Amherd.

Herbert Czaja was a German Christian democratic politician. Czaja was born to a multi-ethnic and multilingual family in Cieszyn in Poland, which was part of Austria-Hungary at the time of his birth. During the Second Polish Republic he was politically active in the German Christian People's Party, a centrist party representing German-speaking Catholics in Poland, and obtained a doctorate in philology from the Jagiellonian University. In 1946 he was expelled from his native Poland by the communist regime during the expulsion of Germans after World War II and came as a refugee to Stuttgart in West Germany, where he worked as a teacher and became active in politics for the Christian Democratic Union.

The Bavarian People's Party was a Catholic political party in Bavaria during the Weimar Republic. After the collapse of the German Empire in 1918, it split away from the national-level Catholic Centre Party and formed the BVP in order to pursue a more conservative and particularist Bavarian course. It consistently had more seats in the Bavarian state parliament than any other party and provided all Bavarian minister presidents from 1920 on. In the national Reichstag it remained a minor player with only about three percent of total votes in all elections. The BVP disbanded shortly after the Nazi seizure of power in early 1933.

Wojciech Korfanty was a Polish activist, journalist and politician, who served as a member of the German parliaments, the Reichstag and the Prussian Landtag, and later, in the Polish Sejm. Briefly, he also was a paramilitary leader, known for organizing the Polish Silesian Uprisings in Upper Silesia, which after World War I was contested by Germany and Poland. Korfanty fought to protect Poles from discrimination and the policies of Germanisation in Upper Silesia before the war and sought to join Silesia to Poland after Poland regained its independence.
The Free Conservative Party was a liberal-conservative political party in Prussia and the German Empire which emerged from the Prussian Conservative Party in the Prussian Landtag in 1866. In the federal elections to the Reichstag parliament from 1871, it ran as the German Reich Party. DRP was classified as centrist or centre-right by political standards at the time, and it also put forward the slogan "conservative progress".
This article aims to give a historical outline of liberalism in Germany. The liberal parties dealt with in the timeline below are, largely, those which received sufficient support at one time or another to have been represented in parliament. Not all parties so included, however, necessarily labeled themselves "liberal". The sign ⇒ denotes another party in that scheme.

Franz Matt was a German lawyer, politician and minister, who belonged to the Bavarian People's Party (BVP). Following the revolution, he substantially defined and put through Bavarian cultural and educational policy.
The Party of the Right, abbreviated to PD, was a political party in Luxembourg between 1914 and 1944. It was the direct predecessor of the Christian Social People's Party (CSV), which has ruled Luxembourg for all but fifteen years since.

The All-German People's Party was a minor political party in West Germany active between 1952 and 1957. It was a Christian, pacifist, centre-left party that opposed the re-armament of West Germany because it believed that the remilitarisation and NATO integration would make German reunification impossible, deepen the division of Europe and pose a danger to peace.

Eduard Müller was a German Roman Catholic priest and politician from the Prussian Province of Silesia.

Eduard Pant (29 January 1887 in Witkowitz, Austria-Hungary – 20 October 1938 in Katowice was a journalist and politician of the Catholic German minority in the Silesian Voivodeship of Poland in the interwar period. He was Deputy Speaker of the Silesian Parliament from 1922 to 1935 and a Senator of the Second Polish Republic from 1928 to 1935.
Thomas Szczeponik was a German-Polish Catholic politician.

The Union of Upper Silesians was an early 20th-century movement for the independence of Upper Silesia. The movement had its genesis during the revolutions of 1848. Allied with the Silesian People's Party, it dissolved in 1924 but has influenced the present-day Silesian Autonomy Movement.
Away from Rome! was a religious movement founded in Austria by the Pan-German politician Georg Ritter von Schönerer aimed at conversion of all Roman Catholic German-speaking people in Austria to Lutheran Protestantism or, in some cases, an Old Catholic Church. It was founded amid the ensuing Kulturkampf in Imperial Germany.
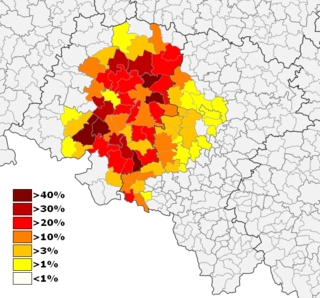
The German Minority Electoral Committee is an electoral committee in Poland which represents the German minority. Since 2008, its representative has been Ryszard Galla. In the 2023 Polish parliamentary election, Galla lost his seat in the Sejm, leaving the party with no national representation.

Joseph Joos (1878–1965) was a prominent German intellectual and politician. As a Member of Parliament in Weimar, Joseph Joos grew to become one of the leading voices of the Christian Democratic Union in Germany. His convictions led him to become a political prisoner in the Dachau concentration camp from 1941 to 1945. After World War II, Joseph Joos became a close advisor to West Germany's Chancellor Konrad Adenauer.
The Catholic People's Party was the name of two conservative parties active concurrently in the two components of the Austria-Hungary dual monarchy.













