Germanium oxide may refer to:
- Germanium dioxide, GeO2, the best known and most commonly encountered oxide of germanium containing germanium(IV)
- Germanium monoxide, GeO, a stable but not well characterised compound containing germanium(II)
Germanium oxide may refer to:

Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Pure germanium is a semiconductor with an appearance similar to elemental silicon. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature.
A metalloid is a type of chemical element which has a preponderance of properties in between, or that are a mixture of, those of metals and nonmetals. There is no standard definition of a metalloid and no complete agreement on which elements are metalloids. Despite the lack of specificity, the term remains in use in the literature of chemistry.

The carbon group is a periodic table group consisting of carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), and flerovium (Fl). It lies within the p-block.
SiGe, or silicon–germanium, is an alloy with any molar ratio of silicon and germanium, i.e. with a molecular formula of the form Si1−xGex. It is commonly used as a semiconductor material in integrated circuits (ICs) for heterojunction bipolar transistors or as a strain-inducing layer for CMOS transistors. IBM introduced the technology into mainstream manufacturing in 1989. This relatively new technology offers opportunities in mixed-signal circuit and analog circuit IC design and manufacture. SiGe is also used as a thermoelectric material for high-temperature applications (>700 K).

Germanium tetrachloride is a colourless, fuming liquid with a peculiar, acidic odour. It is used as an intermediate in the production of purified germanium metal. In recent years, GeCl4 usage has increased substantially due to its use as a reagent for fiber optic production.

Germane is the chemical compound with the formula GeH4, and the germanium analogue of methane. It is the simplest germanium hydride and one of the most useful compounds of germanium. Like the related compounds silane and methane, germane is tetrahedral. It burns in air to produce GeO2 and water. Germane is a group 14 hydride.

Bismuth germanium oxide or bismuth germanate is an inorganic chemical compound of bismuth, germanium and oxygen. Most commonly the term refers to the compound with chemical formula Bi4Ge3O12 (BGO), with the cubic evlitine crystal structure, used as a scintillator. (The term may also refer to a different compound with formula Bi12GeO20, an electro-optical material with sillenite structure, and Bi2Ge3O9.)
Germanium dioxide, also called germanium(IV) oxide, germania, and salt of germanium, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula GeO2. It is the main commercial source of germanium. It also forms as a passivation layer on pure germanium in contact with atmospheric oxygen.

Organogermanium compounds are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to germanium or hydrogen to germanium chemical bond. Organogermanium chemistry is the corresponding chemical science. Germanium shares group 14 in the periodic table with silicon, tin and lead, and not surprisingly the chemistry of organogermanium is in between that of organosilicon compounds and organotin compounds.
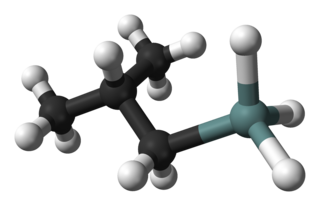
Isobutylgermane (IBGe, Chemical formula: (CH3)2CHCH2GeH3, is an organogermanium compound. It is a colourless, volatile liquid that is used in MOVPE (Metalorganic Vapor Phase Epitaxy) as an alternative to germane. IBGe is used in the deposition of Ge films and Ge-containing thin semiconductor films such as SiGe in strained silicon application, and GeSbTe in NAND Flash applications.

Germanium monoxide, GeO, is a chemical compound of germanium and oxygen. It can be prepared as a yellow sublimate at 1000 °C by reacting GeO2 with Ge metal. The yellow sublimate turns brown on heating at 650 °C. GeO is not well characterised. It is amphoteric dissolving in acids to form germanium(II) salts and in alkali to form "trihydroxogermanates" or "germanites" containing the Ge(OH)3− ion.
Germanium dichloride is a chemical compound of germanium and chlorine with the formula GeCl2. It is a solid and contains germanium in the +2 oxidation state.

In chemistry, germanate is a compound containing an oxyanion of germanium. In the naming of inorganic compounds it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central germanium atom, for example potassium hexafluorogermanate, K2GeF6.

Germanium tetrafluoride (GeF4) is a chemical compound of germanium and fluorine. It is a colorless gas.

Digermane is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ge2H6. One of the few hydrides of germanium, it is a colourless liquid. Its molecular geometry is similar to ethane.
Germanium(II) hydroxide, normally written as Ge(OH)2, is a poorly characterised compound, sometimes called hydrous germanium(II) oxide or germanous hydroxide. It was first reported by Winkler in 1886.

Sodium germanate is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2GeO3. It is a colorless solid. Sodium germanate is primarily used for the synthesis of other germanium compounds.
Germanium(II) hydrides, also called germylene hydrides, are a class of Group 14 compounds consisting of low-valent germanium and a terminal hydride. They are also typically stabilized by an electron donor-acceptor interaction between the germanium atom and a large, bulky ligand.
The nitridogermanates are chemical compounds containing germanium atoms bound to nitrogen. The simplest anion is GeN48−, but these are often condensed, with the elimination of nitrogen.