Germanium selenide may refer to:
Germanium selenide may refer to:
German(s) may refer to:

Germanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature.

The carbon group is a periodic table group consisting of carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), and flerovium (Fl). It lies within the p-block.

Germanium tetrachloride is a colourless, fuming liquid with a peculiar, acidic odour. It is used as an intermediate in the production of purified germanium metal. In recent years, GeCl4 usage has increased substantially due to its use as a reagent for fiber optic production.

The point-contact transistor was the first type of transistor to be successfully demonstrated. It was developed by research scientists John Bardeen and Walter Brattain at Bell Laboratories in December 1947. They worked in a group led by physicist William Shockley. The group had been working together on experiments and theories of electric field effects in solid state materials, with the aim of replacing vacuum tubes with a smaller device that consumed less power.
GES or Gęś may refer to:
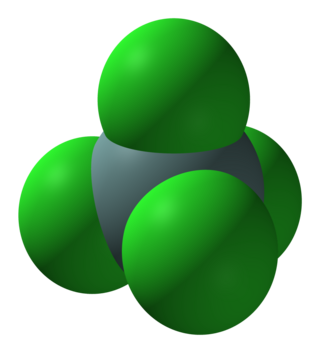
Germanium chloride may refer to:
Germanium oxide may refer to:
Germanium dioxide, also called germanium(IV) oxide, germania, and salt of germanium, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula GeO2. It is the main commercial source of germanium. It also forms as a passivation layer on pure germanium in contact with atmospheric oxygen.
Argentium silver is a brand of modern tarnish-resistant silver alloys, containing either 93.5%, 94% or 96% silver. Argentium alloys replace some of the copper in the traditional sterling silver with the metalloid germanium. Argentium 935, Argentium 940 and Argentium 960 alloys exceed the standard required for hallmarking as sterling silver, and Argentium 960 silver meets the standard for hallmarking as Britannia silver.
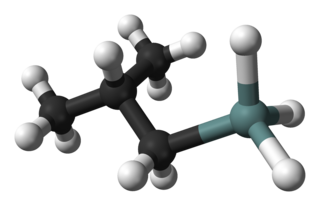
Isobutylgermane (IBGe, Chemical formula: (CH3)2CHCH2GeH3, is an organogermanium compound. It is a colourless, volatile liquid that is used in MOVPE (Metalorganic Vapor Phase Epitaxy) as an alternative to germane. IBGe is used in the deposition of Ge films and Ge-containing thin semiconductor films such as SiGe in strained silicon application, and GeSbTe in NAND Flash applications.
Galex may refer to:
Germanium sulfide may refer to:
Amorphous semiconductor may refer to :
Tetrachloride may refer to:
tetraiodide may refer to:
Germanium fluoride is a chemical compound of germanium and fluorine which exists in the following forms:
32 may refer to:
Gese may refer to:
Germanium bromide may refer to: