Lahn-Dill is a Kreis (district) in the west of Hesse, Germany. Neighboring districts are Siegen-Wittgenstein, Marburg-Biedenkopf, Gießen, Wetteraukreis, Hochtaunuskreis, Limburg-Weilburg, Westerwaldkreis.
Rhein-Lahn-Kreis is a district (Kreis) in the east of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Neighboring districts are Westerwaldkreis, Limburg-Weilburg, Rheingau-Taunus, Mainz-Bingen, Rhein-Hunsrück, Mayen-Koblenz, and the district-free city Koblenz.

Leun is a small town in the Lahn-Dill-Kreis in Hesse, Germany.

This division of Germany into major natural regions takes account primarily of geomorphological, geological, hydrological, and pedological criteria in order to divide the country into large, physical units with a common geographical basis. Political boundaries play no part in this, apart from defining the national border.

The West Hesse Highlands, also known as the West Hessian Lowlands and Highlands, refers to a heavily forested region of the Central Uplands in Germany that lies mostly within the state of Hesse, between those elements of the Rhenish Massif right of the Rhine in the west, the Weser Uplands to the north, the Hessian Central Uplands to the east and the Wetterau to the south.
The East Hesse Highlands describes a heavily wooded range of hills lying mainly in the German state of Hesse, but also extending a little way into Lower Saxony to the north, Thuringia to the east and Bavaria to the southeast. The region is sandwiched between the West Hesse Depression to the west, the Weser Uplands to the north, the Thuringian Basin to the northeast, the northwestern edge of the Thuringian Forest to the east, the Spessart to the south and the Wetterau to the southwest.
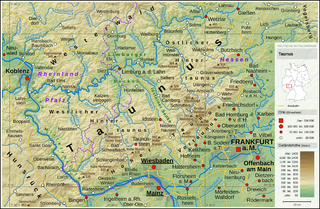
The Gladenbach Uplands, named after their central town of Gladenbach, is a range of hills up to 609 m high in the Rhine Massif in Germany, on the junction of the Rothaar Mountains, Westerwald (southwest), (Eastern) Hintertaunus and West Hesse Highlands in the east.
It lies in Central Hesse within the districts of Marburg-Biedenkopf, Lahn-Dill and Gießen within the so-called Lahn-Dill-(Dietzhölze-) loop. Small parts of the Upper Lahn Valley in the northwest belong, together with the town of Bad Laasphe, also to the district of Siegen-Wittgenstein, North Rhine-Westphalia.

The Lahn Valley Railway is a railway line between Niederlahnstein in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate to Wetzlar in Hesse. Its western terminus was originally in Oberlahnstein. Trains now mostly operate between Koblenz and Gießen. The line was opened by the Nassau Rhine and Lahn Railway Company and the Nassau State Railway between 1858 and 1863 and is one of the oldest railways in Germany.

Eschhofen station lies on the Lahn Valley Railway in the town of Limburg an der Lahn in the German state of Hesse. In addition, just east of the station, the Main-Lahn Railway (Main-Lahn-Bahn) branches off to Frankfurt. The station was opened in 1863. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 5 station.

The region of Middle Hesse is one of three planning regions in the German state of Hesse, alongside North and South Hesse. Its territory is identical with that of the administrative province of Gießen and covers the counties of Limburg-Weilburg, Lahn-Dill-Kreis, Gießen, Marburg-Biedenkopf and Vogelsbergkreis. The Middle Hesse Regional Assembly, which decides on the regional plan, currently consists of 31 members chosen by the five counties and the three towns with special status: Gießen, Marburg and Wetzlar. The regional assembly has tasked the governing president (Regierungspräsident) with delivering regional management. The Mid-Hesse Regional Management Association was founded on 22 January 2003.

The Upper Hessian Ridge or Upper Hesse Ridge is a hill chain in the West Hesse Highlands in North and Middle Hesse, which lies on the Rhine-Weser watershed and links the montane Central Upland ranges of the Kellerwald and the Vogelsberg in a north-south direction. The swell is divided into the Gilserberg Heights in the north, the central Neustadt Saddle and the Northern Vogelsberg Foreland in the south.

The Lahn-Eifel-Bahn is a rail passenger service in the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse that runs as the RB 23 from Limburg an der Lahn via Koblenz and Andernach to Mayen, as RE 25 from Gießen via Limburg to Koblenz and as RB 38 from Andernach via Mayen to Kaisersesch.

Weilburg is a station in the town of Weilburg in the German state of Hesse on the Lahn Valley Railway (Lahntalbahn). The Weil Valley Railway (Weiltalbahn) branched off towards Weilmünster immediately after the station from 1890 to 1988.

Leun/Braunfels is a heritage-listed station in the district of Lahnbahnhof in the town of Leun in the German state of Hesse. It is in the fare zone of the Rhein-Main-Verkehrsverbund (RMV) and is located on the Lahn Valley Railway (Lahntalbahn). Directly next to the entrance building was the Braunfels terminus of the Ernst Railway (Ernstbahn) to Philippstein of which only a few remains are visible. It operated from 1875 to 1962.

The Taunus Nature Park is a nature park in Central Germany with an area of 134,775 hectares (1347.75 km²) in the Central Upland range of the Taunus. It is one of two Hessian nature parks in the Taunus and the second largest nature park in Hesse.

The Middle Rhine Basin is the central landscape region of the Middle Rhine in Germany and, along with the Limburg Basin, forms one of the biggest intra-montane lowland regions within the Rhenish Massif. The basin is divided into the valley bottom of the Neuwied Basin, the Neuwied Basin Perimeter east of the Rhine and the Lower Moselle Valley west of the Rhine in the south, and the Maifeld-Pellenz Hills in the north.
As well as being a low mountain range, the Westerwald is also a natural region in the system of natural regional division of Germany. Within that it is a major unit group with the number "32". According to this system the major unit group of the Westerwald belongs to the basement plate (Grundgebirgsschollenland), which describes the type of mountain-building process by which it was formed. The major unit group extends across the states of Hesse, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate. It is roughly bounded by the valleys of the Lahn, Rhine and Sieg, whereby the hills immediately south of the Heller and Sieg are not considered to be part of it.