
In modern usage, hijab generally refers to variety of head coverings conventionally worn by many Muslim women as an expression of faith. Similar to the tichel or snood worn by Orthodox Jewish women, certain headcoverings worn by some Christian women, such as the mantilla, apostolnik and wimple, and the dupatta favored by many Hindu and Sikh women, the hijab comes in various forms. Often, it specifically describes a scarf that is wrapped around the head, covering the hair, neck, and ears while leaving the face visible. The use of the hijab has grown globally since the 1970s, with many Muslims viewing it as a symbol of modesty and faith; it is also worn as a form of adornment. There is consensus among Islamic religious scholars that covering the head is either required or preferred. In practice, most Muslim women choose to wear it.

Anatomy of a Murder is a 1959 American courtroom drama film produced and directed by Otto Preminger. The screenplay by Wendell Mayes was based on the 1958 novel of the same name written by Michigan Supreme Court Justice John D. Voelker under the pen name of Robert Traver. Voelker based the novel on a 1952 murder case in which he was the defense attorney.
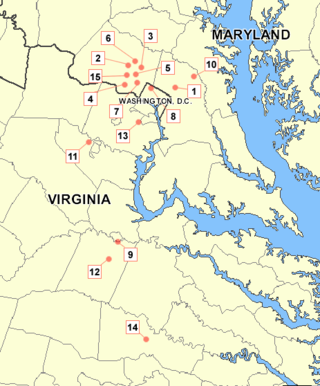
The D.C. sniper attacks were a series of coordinated shootings that occurred during three weeks in October 2002 throughout the Washington metropolitan area, consisting of the District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia, and preliminary shootings, that consisted of murders and robberies in several states, and lasted for six months starting in February 2002. Seven people were killed, and seven others were injured in the preliminary shootings, and ten people were killed and three others were critically wounded in the October shootings. In total, the snipers killed 17 people and wounded 10 others in a 10-month span.

A burqa or a burka is an enveloping outer garment worn by some Muslim women which fully covers the body and the face. Also known as a chadaree or chaadar in Afghanistan, or a paranja in Central Asia, the Arab version of the burqa is called the boshiya and is usually black. The term burqa is sometimes conflated with the niqāb even though, in more precise usage, the niqab is a face veil that leaves the eyes uncovered, while a burqa covers the entire body from the top of the head to the ground, with a mesh screen which only allows the wearer to see in front of her.
Lee Boyd Malvo, also known as John Lee Malvo, is a Jamaican convicted mass murderer who, along with John Allen Muhammad, committed a series of murders dubbed the D.C. sniper attacks over a three-week period in October 2002. Malvo was aged 17 during the span of the shootings. He is serving multiple life sentences at Keen Mountain Correctional Center in Virginia, a maximum security prison.

Islamic clothing is clothing that is interpreted as being in accordance with the teachings of Islam. Muslims wear a wide variety of clothing, which is influenced not only by religious considerations, but also by practical, cultural, social, and political factors. In modern times, some Muslims have adopted clothing based on Western traditions, while others wear modern forms of traditional Muslim dress, which over the centuries has typically included long, flowing garments. Besides its practical advantages in the climate of the Middle East, loose-fitting clothing is also generally regarded as conforming to Islamic teachings, which stipulate that body areas which are sexual in nature must be hidden from public view. Traditional dress for Muslim men has typically covered at least the head and the area between the waist and the knees, while women's islamic dress is to conceal the hair and the body from the ankles to the neck. Some Muslim women also cover their face. However, other Muslims believe that the Quran strictly mandate that women need to wear a hijab or a burqa.

A niqāb or niqaab, also known as a ruband, is a long garment worn by some Muslim women in order to cover their entire body and face, excluding their eyes. It is an interpretation in Islam of the concept of hijab, and is worn in public and in all other places where a woman may encounter non-mahram men. Most prevalent in the Arabian Peninsula, the niqab is a controversial clothing item in many parts of the world, including in some Muslim-majority countries.
Sultaana Lakiana Myke Freeman is a Muslim American, resident in the state of Florida. She garnered media attention and notoriety when she sued the state of Florida over the right to wear a face veil for her driver's license picture.

Mateen Ahmad Cleaves is an American retired basketball player. He played parts of six seasons in the National Basketball Association (NBA). He was an All-American college player for Michigan State, where he led the Spartans to a national championship in 2000. He has also worked as a studio analyst for Fox Sports.

In France, there is an ongoing social, political, and legal debate concerning the wearing of the hijab and other forms of Islamic coverings in public. The cultural framework of the controversy can be traced to France's history of colonization in North Africa, but escalated into a significant public debate in 1989 when three girls were suspended from school for refusing to remove their headscarves. That incident, referred to in France as l'affaire du foulard or l'affaire du voile, initially focused the controversy on the wearing of the hijab in French public schools. Because of the wide-ranging social debates caused by the controversy, l'affaire du foulard has been compared to the Dreyfus affair in its impact on French culture.
Woo Bih Li is a Singaporean lawyer who has been serving as a judge of the Supreme Court of Singapore since 2003.

The British debate over veils began in October 2006 when the MP and government minister Jack Straw wrote in his local newspaper, the Lancashire Evening Telegraph, that, while he did not want to be "prescriptive", he preferred talking to women who did not wear a niqab as he could see their face, and asked women who were wearing such items to remove them when they spoke to him, making clear that they could decline his request and that a female member of staff was in the room.
Hijab and burka controversies in Europe revolve around the variety of headdresses worn by Muslim women, which have become prominent symbols of the presence of Islam in especially Western Europe. In several countries, the adherence to hijab has led to political controversies and proposals for a legal partial or full ban in some or all circumstances. Some countries already have laws banning the wearing of masks in public, which can be applied to veils that conceal the face. Other countries are debating similar legislation, or have more limited prohibitions. Some of them apply only to face-covering clothing such as the burqa, boushiya, or niqab; some apply to any clothing with an Islamic religious symbolism such as the khimar, a type of headscarf. The issue has different names in different countries, and "the veil" or hijab may be used as general terms for the debate, representing more than just the veil itself, or the concept of modesty embodied in Hijab.

Various styles of head coverings, most notably the khimar, hijab, chador, niqab, paranja, yashmak, tudong, shayla, safseri, carşaf, haik, dupatta, boshiya and burqa, are worn by Muslim women around the world, where the practice varies from mandatory to optional or restricted in different majority Muslim and non-Muslim countries.

Marwa Ali El-Sherbini, was an Egyptian woman and German resident who was killed in 2009 during an appeal hearing at a court of law in Dresden, Germany, when she was three months pregnant. She was stabbed by Alex Wiens, an ethnic German immigrant from Russia against whom she had testified in a criminal case for verbal abuse. El-Sherbini's husband, who was present at the hearing, tried to intervene. He too was repeatedly stabbed by Wiens and was then mistakenly shot and wounded by a police officer who was called to the court room. Wiens was arrested at the crime scene and subsequently tried for murder and attempted murder. He was found guilty of both charges; it was also found that Wiens's actions constituted a heinous crime, because they were committed in front of a child, against two people, in a court of law, and fulfilled the murder criterion of treacherousness, such as hatred against foreigners. Wiens was sentenced to life imprisonment.

In a predominantly Muslim society, as many as 90% of women in Egypt have adopted a form of veiling. A majority of Egyptian women cover at least their hair with the hijab. A hijab refers to a head covering that is worn by Muslim women. Although the phenomenon of wearing the niqāb, a veil which covers the face is not as common, the niqab in Egypt has become more prevalent. While a few women in Egypt wear a black niqab along with a billowing black abaya as seen in countries such as Saudi Arabia, many choose to wear different colors of the niqab or manipulate the hijab to cover their face. Regardless, the growing trend of munaqqabat, or women who wear the niqab, has alarmed the authorities. They have begun to see this dress as a security threat, because it hides the face, and because it is perceived as a political statement, a rejection of the state in favor of a strict Islamic system.
Anti-mask or anti-masking laws are legislative or penal initiatives prohibiting the concealment of one's face in public. Anti-mask laws vary widely between jurisdictions in their intent, scope, and penalties.
S.A.S. v. France was a case brought before the European Court of Human Rights which ruled by a vote of fifteen to two that the French ban on face covering did not violate European Convention on Human Rights's (ECHR) provisions on right to privacy or freedom of religion. The two judges in the minority expressed their partly dissenting opinion. The Court was unanimous in dismissing other related claims of the plaintiff, S.A.S.

Hijabophobia is a type of religious and cultural discrimination against Muslim women who wear the hijab. The discrimination has had manifestations in public, working and educational places, although most people against the Hijab are in favor of women's freedom.

The burqa is worn by women in various countries. Some countries have banned it in government offices, schools, or in public places and streets.













