Glycerol phosphate may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Glycerol phosphate may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
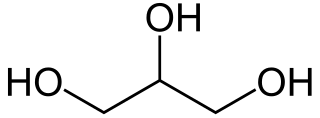
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in many lipids which are known as glycerides. It is widely used in the food industry as a sweetener and humectant and in pharmaceutical formulations. Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups that are responsible for its solubility in water and its hygroscopic nature.

Glyceraldehyde (glyceral) is a triose monosaccharide with chemical formula C3H6O3. It is the simplest of all common aldoses. It is a sweet, colorless, crystalline solid that is an intermediate compound in carbohydrate metabolism. The word comes from combining glycerol and aldehyde, as glyceraldehyde is glycerol with one hydroxymethyl group oxidized to an aldehyde.
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP, also glycerone phosphate in older texts) is the anion with the formula HOCH2C(O)CH2OPO32-. This anion is involved in many metabolic pathways, including the Calvin cycle in plants and glycolysis. It is the phosphate ester of dihydroxyacetone.
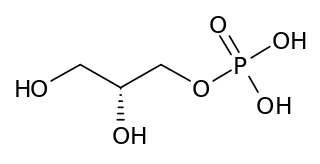
sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate is a phosphoric ester of glycerol, which is a component of glycerophospholipids. Equally appropriate names in biochemical context include glycero-3-phosphate, 3-O-phosphonoglycerol, 3-phosphoglycerol; and Gro3P. From a historical reason, it is also known as L-glycerol 3-phosphate, D-glycerol 1-phosphate, L-α-glycerophosphoric acid. It should not be confused with the similarly named glycerate 3-phosphate or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.

Glycerol kinase, encoded by the gene GK, is a phosphotransferase enzyme involved in triglycerides and glycerophospholipids synthesis.

The glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle is a mechanism that regenerates NAD+ from NADH, a by-product of glycolysis. Its importance in transporting reducing equivalents is secondary to the malate-aspartate shuttle.

Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible redox conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate to sn-glycerol 3-phosphate.

Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant.
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) (EC 1.1.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+] (EC 1.1.1.94) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a poly(glycerol-phosphate) alpha-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sn-glycerol-3-phosphate 2-alpha-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CDP-diacylglycerol—glycerol-3-phosphate 3-phosphatidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a diphosphate-glycerol phosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate-glucose phosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
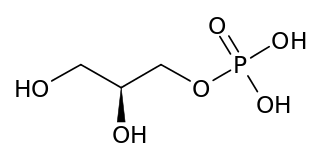
sn-Glycerol 1-phosphate is a phosphoric ester of glycerol, which is a component of archea-specific ether lipids. Equally appropriate names in biochemical context include glycero-1-phosphate, 1-O-phosphonoglycerol, and 1-phosphoglycerol. From a historical reason, it is also known as L-glycerol 1-phosphate, D-glycerol 3-phosphate, and D-α-glycerophosphoric acid.
Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.5.3 is an is an enzyme with systematic name sn-glycerol 3-phosphate:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction