Background
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
A glycosyl acceptor is any suitable nucleophile-containing molecule that will react with a glycosyl donor to form a new glycosidic bond. By convention, the acceptor is the member of this pair which did not contain the resulting anomeric carbon of the new glycosidic bond. Since the nucleophilic atom of the acceptor is typically an oxygen atom, this can be remembered using the mnemonic of the acceptor is the alcohol. A glycosyl acceptor can be a mono- or oligosaccharide that contains an available nucleophile, such as an unprotected hydroxyl.
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
glucose to haemoglobin
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate, i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology, glycosylation usually refers to an enzyme-catalysed reaction, whereas glycation may refer to a non-enzymatic reaction. Glycosylation is a form of co-translational and post-translational modification. Glycans serve a variety of structural and functional roles in membrane and secreted proteins. The majority of proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum undergo glycosylation. Glycosylation is also present in the cytoplasm and nucleus as the O-GlcNAc modification. Aglycosylation is a feature of engineered antibodies to bypass glycosylation. Five classes of glycans are produced:

In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of Heliconius butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body.
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions differ from electrophilic additions in that the former reactions involve the group to which atoms are added accepting electron pairs, whereas the latter reactions involve the group donating electron pairs.
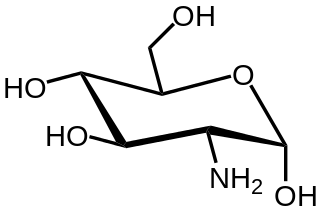
In organic chemistry, an amino sugar is a sugar molecule in which a hydroxyl group has been replaced with an amine group. More than 60 amino sugars are known, with one of the most abundant being N-Acetyl-d-glucosamine, which is the main component of chitin.

In biochemistry and molecular genetics, an AP site, also known as an abasic site, is a location in DNA that has neither a purine nor a pyrimidine base, either spontaneously or due to DNA damage. It has been estimated that under physiological conditions 10,000 apurinic sites and 500 apyrimidinic may be generated in a cell daily.
Glycal is a name for cyclic enol ether derivatives of sugars having a double bond between carbon atoms 1 and 2 of the ring. The term “glycal” should not be used for an unsaturated sugar that has a double bond in any position other than between carbon atoms 1 and 2.
An Endoglycosidase is an enzyme that releases oligosaccharides from glycoproteins or glycolipids. It may also cleave polysaccharide chains between residues that are not the terminal residue, although releasing oligosaccharides from conjugated protein and lipid molecules is more common.

Glycosyltransferases are enzymes that establish natural glycosidic linkages. They catalyze the transfer of saccharide moieties from an activated nucleotide sugar to a nucleophilic glycosyl acceptor molecule, the nucleophile of which can be oxygen- carbon-, nitrogen-, or sulfur-based.
The term Glycosynthase refers to a class of proteins that have been engineered to catalyze the formation of a glycosidic bond. Glycosynthase are derived from glycosidase enzymes, which catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds. They were traditionally formed from retaining glycosidase by mutating the active site nucleophilic amino acid to a small non-nucleophilic amino acid. More modern approaches use directed evolution to screen for amino acid substitutions that enhance glycosynthase activity.

Glycoside hydrolases catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are extremely common enzymes with roles in nature including degradation of biomass such as cellulose (cellulase), hemicellulose, and starch (amylase), in anti-bacterial defense strategies, in pathogenesis mechanisms and in normal cellular function. Together with glycosyltransferases, glycosidases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of glycosidic bonds.
Carbohydrate chemistry is a subdiscipline of chemistry primarily concerned with the detection, synthesis, structure, and function of carbohydrates. Due to the general structure of carbohydrates, their synthesis is often preoccupied with the selective formation of glycosidic linkages and the selective reaction of hydroxyl groups; as a result, it relies heavily on the use of protecting groups.
A chemical glycosylation reaction involves the coupling of a glycosyl donor, to a glycosyl acceptor forming a glycoside. If both the donor and acceptor are sugars, then the product is an oligosaccharide. The reaction requires activation with a suitable activating reagent. The reactions often result in a mixture of products due to the creation of a new stereogenic centre at the anomeric position of the glycosyl donor. The formation of a glycosidic linkage allows for the synthesis of complex polysaccharides which may play important roles in biological processes and pathogenesis and therefore having synthetic analogs of these molecules allows for further studies with respect to their biological importance.
Oligosaccharides and polysaccharides are an important class of polymeric carbohydrates found in virtually all living entities. Their structural features make their nomenclature challenging and their roles in living systems make their nomenclature important.
Intramolecular aglycon delivery is a synthetic strategy for the construction of glycans. This approach is generally used for the formation of difficult glycosidic linkages.

The armed/disarmed approach to glycosylation is an effective way to prevent sugar molecules from self-glycosylation when synthesizing disaccharides. This approach was first recognized when acetylated sugars only acted as glycosyl acceptors when reacted with benzylated sugars. The acetylated sugars were termed “disarmed” while the benzylated sugars were termed “armed”.
The Crich β-mannosylation in organic chemistry is a synthetic strategy which is used in carbohydrate synthesis to generate a 1,2-cis-glycosidic bond. This type of linkate is generally very difficult to make, and specific methods like the Crich β-mannosylation are used to overcome these issues.
A glycosyl donor is a carbohydrate mono- or oligosaccharide that will react with a suitable glycosyl acceptor to form a new glycosidic bond. By convention, the donor is the member of this pair that contains the resulting anomeric carbon of the new glycosidic bond. The resulting reaction is referred to as a glycosylation or chemical glycosylation.

An oxocarbeniumion is a chemical species characterized by a central sp2-hybridized carbon, an oxygen substituent, and an overall positive charge that is delocalized between the central carbon and oxygen atoms. An oxocarbenium ion is represented by two limiting resonance structures, one in the form of a carbenium ion with the positive charge on carbon and the other in the form of an oxonium species with the formal charge on oxygen. As a resonance hybrid, the true structure falls between the two. Compared to neutral carbonyl compounds like ketones or esters, the carbenium ion form is a larger contributor to the structure. They are common reactive intermediates in the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds, and are a commonly used strategy for chemical glycosylation. These ions have since been proposed as reactive intermediates in a wide range of chemical transformations, and have been utilized in the total synthesis of several natural products. In addition, they commonly appear in mechanisms of enzyme-catalyzed biosynthesis and hydrolysis of carbohydrates in nature. Anthocyanins are natural flavylium dyes, which are stabilized oxocarbenium compounds. Anthocyanins are responsible for the colors of a wide variety of common flowers such as pansies and edible plants such as eggplant and blueberry.
Carbohydrate synthesis is a sub-field of organic chemistry concerned specifically with the generation of natural and unnatural carbohydrate structures. This can include the synthesis of monosaccharide residues or structures containing more than one monosaccharide, known as oligosaccharides.