Bibliography
- Karl-Ludwig Elvers: [I 79] C. Scipio Hispanus, Cn.. In: Der Neue Pauly . vol. 3 (1997), col. 184.
Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Hispanus of the Scipiones branch of the gens Cornelia, was a Roman politician.
He was the son of Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Hispallus. He served as one of the decemviri stlitibus judicandis and as a military tribune before 150 BC, and became quaestor around that date. He then became aedile, probably in 141 BC. He was a praetor in 139 BC. As praetor, he expelled the astrologers (Chaldaeans and Jews) from the city of Rome.
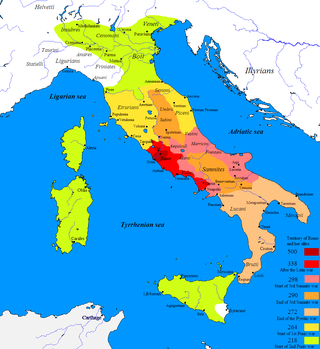
Year 218 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Longus. The denomination 218 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.
Year 212 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Flaccus and Pulcher. The denomination 212 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus was a Roman general and statesman during the third century BC. He played a major part in the Second Punic War, establishing Roman rule in the east of the Iberian peninsula and tying up several Carthaginian armies to keep them from reinforcing Hannibal.

Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus was a two-time consul of the Roman Republic and general, who conquered Macedon in the Third Macedonian War.

The gens Manlia was one of the oldest and noblest patrician houses at Rome, from the earliest days of the Republic until imperial times. The first of the gens to obtain the consulship was Gnaeus Manlius Cincinnatus, consul in 480 BC, and for nearly five centuries its members frequently held the most important magistracies. Many of them were distinguished statesmen and generals, and a number of prominent individuals under the Empire claimed the illustrious Manlii among their ancestors.

Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica was a consul of ancient Rome in 191 BC. He was a son of Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus.
Gnaeus, also spelled Cnaeus, was a Roman praenomen derived from the Latin naevus, a birthmark. It was a common name borne by many individuals throughout Roman history, including:
This is a historical timeline of Portugal.

The gens Cornelia was one of the greatest patrician houses at ancient Rome. For more than seven hundred years, from the early decades of the Republic to the third century AD, the Cornelii produced more eminent statesmen and generals than any other gens. At least seventy-five consuls under the Republic were members of this family, beginning with Servius Cornelius Maluginensis in 485 BC. Together with the Aemilii, Claudii, Fabii, Manlii, and Valerii, the Cornelii were almost certainly numbered among the gentes maiores, the most important and powerful families of Rome, who for centuries dominated the Republican magistracies. All of the major branches of the Cornelian gens were patrician, but there were also plebeian Cornelii, at least some of whom were descended from freedmen.
Publius Aelius Paetus was a Roman consul of the late 3rd century BC. He was a prominent supporter of Scipio Africanus, and was elected censor with Africanus in 199.

The Roman Republic conquered and occupied territories in the Iberian Peninsula that were previously under the control of native Celtic, Iberian, Celtiberian and Aquitanian tribes and the Carthaginian Empire. The Carthaginian territories in the south and east of the peninsula were conquered in 206 BC during the Second Punic War. Control was gradually extended over most of the peninsula without annexations. It was completed after the end of the Roman Republic, by Augustus, the first Roman emperor, who annexed the whole of the peninsula to the Roman Empire in 19 BC.
Lucius Cornelius Scipio was a statesman of the Roman Republic. He was the second son of Scipio Africanus, but despite this illustrious background, his career was cut short by his demotion from the senate by the censors in 174 BC.
This section of the timeline of Hispania concerns Spanish and Portuguese history events from the Carthaginian conquests to before the barbarian invasions.

Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet Africanus, literally meaning "the African", but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa.
Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Hispallus was a Roman politician in the second century BC.