Artificial intelligence (AI), in its broadest sense, is intelligence exhibited by machines, particularly computer systems. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to perceive their environment and use learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. Such machines may be called AIs.
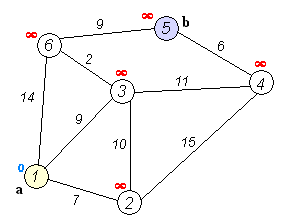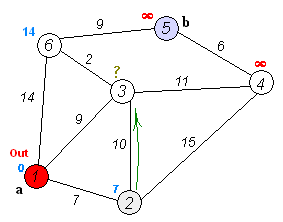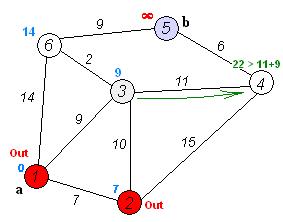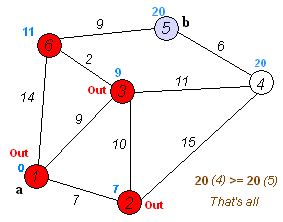
Dijkstra's algorithm is an algorithm for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a weighted graph, which may represent, for example, road networks. It was conceived by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956 and published three years later.
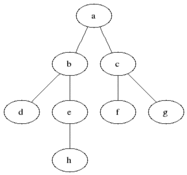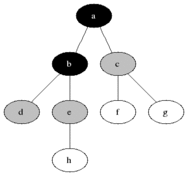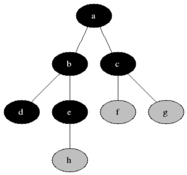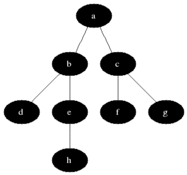
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for searching a tree data structure for a node that satisfies a given property. It starts at the tree root and explores all nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level. Extra memory, usually a queue, is needed to keep track of the child nodes that were encountered but not yet explored.
A* is a graph traversal and pathfinding algorithm, which is used in many fields of computer science due to its completeness, optimality, and optimal efficiency. Given a weighted graph, a source node and a goal node, the algorithm finds the shortest path from source to goal.
Best-first search is a class of search algorithms, which explores a graph by expanding the most promising node chosen according to a specified rule.
Distributed artificial intelligence (DAI) also called Decentralized Artificial Intelligence is a subfield of artificial intelligence research dedicated to the development of distributed solutions for problems. DAI is closely related to and a predecessor of the field of multi-agent systems.
In computer science, iterative deepening search or more specifically iterative deepening depth-first search is a state space/graph search strategy in which a depth-limited version of depth-first search is run repeatedly with increasing depth limits until the goal is found. IDDFS is optimal, meaning that it finds the shallowest goal. Since it visits all the nodes in the search tree down to depth before visiting any nodes at depth , the cumulative order in which nodes are first visited is effectively the same as in breadth-first search. However, IDDFS uses much less memory.
State space search is a process used in the field of computer science, including artificial intelligence (AI), in which successive configurations or states of an instance are considered, with the intention of finding a goal state with the desired property.
Iterative deepening A* (IDA*) is a graph traversal and path search algorithm that can find the shortest path between a designated start node and any member of a set of goal nodes in a weighted graph. It is a variant of iterative deepening depth-first search that borrows the idea to use a heuristic function to conservatively estimate the remaining cost to get to the goal from the A* search algorithm. Since it is a depth-first search algorithm, its memory usage is lower than in A*, but unlike ordinary iterative deepening search, it concentrates on exploring the most promising nodes and thus does not go to the same depth everywhere in the search tree. Unlike A*, IDA* does not utilize dynamic programming and therefore often ends up exploring the same nodes many times.
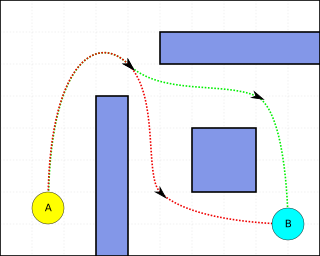
Pathfinding or pathing is the search, by a computer application, for the shortest route between two points. It is a more practical variant on solving mazes. This field of research is based heavily on Dijkstra's algorithm for finding the shortest path on a weighted graph.

In intelligence and artificial intelligence, an intelligent agent (IA) is an agent that perceives its environment, takes actions autonomously in order to achieve goals, and may improve its performance with learning or acquiring knowledge. An intelligent agent may be simple or complex: A thermostat or other control system is considered an example of an intelligent agent, as is a human being, as is any system that meets the definition, such as a firm, a state, or a biome.
Bidirectional search is a graph search algorithm that finds a shortest path from an initial vertex to a goal vertex in a directed graph. It runs two simultaneous searches: one forward from the initial state, and one backward from the goal, stopping when the two meet. The reason for this approach is that in many cases it is faster: for instance, in a simplified model of search problem complexity in which both searches expand a tree with branching factor b, and the distance from start to goal is d, each of the two searches has complexity O(bd/2) (in Big O notation), and the sum of these two search times is much less than the O(bd) complexity that would result from a single search from the beginning to the goal.
In the study of path-finding problems in artificial intelligence, a heuristic function is said to be consistent, or monotone, if its estimate is always less than or equal to the estimated distance from any neighbouring vertex to the goal, plus the cost of reaching that neighbour.
In computer science, specifically in algorithms related to pathfinding, a heuristic function is said to be admissible if it never overestimates the cost of reaching the goal, i.e. the cost it estimates to reach the goal is not higher than the lowest possible cost from the current point in the path. In other words, it should act as a lower bound.
An and–or tree is a graphical representation of the reduction of problems to conjunctions and disjunctions of subproblems.
In computer science, B* is a best-first graph search algorithm that finds the least-cost path from a given initial node to any goal node. First published by Hans Berliner in 1979, it is related to the A* search algorithm.
A hierarchical control system (HCS) is a form of control system in which a set of devices and governing software is arranged in a hierarchical tree. When the links in the tree are implemented by a computer network, then that hierarchical control system is also a form of networked control system.
D* is any one of the following three related incremental search algorithms:
LPA* or Lifelong Planning A* is an incremental heuristic search algorithm based on A*. It was first described by Sven Koenig and Maxim Likhachev in 2001.

The problem of Multi-Agent Pathfinding (MAPF) is an instance of multi-agent planning and consists in the computation of collision-free paths for a group of agents from their location to an assigned target. It is an optimization problem, since the aim is to find those paths that optimize a given objective function, usually defined as the number of time steps until all agents reach their goal cells. MAPF is the multi-agent generalization of the pathfinding problem, and it is closely related to the shortest path problem in the context of graph theory.




