See also
- Gongylodes (γογγυλώδης)
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Gongylus. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Gongylus or Gongylos ( γογγύλος ) may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Gongylus. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Millets are a group of highly variable small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food.

Citrus is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes.
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a number of people from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. After the Battle of Carchemish in 605 BCE, King Nebuchadnezzar of Babylon besieged Jerusalem, resulting in tribute being paid by King Jehoiakim. Jehoiakim refused to pay tribute in Nebuchadnezzar's fourth year, which led to another siege in Nebuchadnezzar's seventh year, culminating with the death of Jehoiakim and the exile to Babylonia of King Jeconiah, his court and many others; Jeconiah's successor Zedekiah and others were exiled in Nebuchadnezzar's eighteenth year; a later deportation occurred in Nebuchadnezzar's twenty-third year. The dates, numbers of deportations, and numbers of deportees given in the biblical accounts vary. These deportations are dated to 597 BCE for the first, with others dated at 587/586 BCE, and 582/581 BCE respectively.

Herod, also known as Herod the Great and Herod I, was a Roman client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. The history of his legacy has polarized opinion, as he is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renovation of the Second Temple in Jerusalem and the expansion of the Temple Mount towards its north, the Tomb of the Patriarchs in Hebron, the construction of the port at Caesarea Maritima, the fortress at Masada, and Herodium. Vital details of his life are recorded in the works of the 1st century CE Roman–Jewish historian Josephus. Herod also appears in the Christian Gospel of Matthew as the ruler of Judea who orders the Massacre of the Innocents at the time of the birth of Jesus, although a majority of Herod biographers do not believe this event to have occurred. Despite his successes, including singlehandedly forging a new aristocracy from practically nothing, he has still garnered criticism from various historians. His reign polarizes opinion amongst scholars and historians, some viewing his legacy as evidence of success, and some as a reminder of his tyrannical rule.
Musaeus, Musaios or Musäus may refer to:

BCE Inc., formerly Bell Canada Enterprises Inc., is a publicly traded telecommunications holding company for the Bell Canada corporate group and for various mass media assets under BCE's subsidiary, Bell Media. Founded through a corporate reorganization in 1983 when Bell Canada, Northern Telecom, and other related companies all became subsidiaries of Bell Canada Enterprises Inc., the company is one of Canada's largest corporations. The company is headquartered at 1 Carrefour Alexander-Graham-Bell in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.

Empusidae is a family of plant-mimicking mantids, consisting of 10 genera, holding almost 30 species. Unlike many other mantid families, the Empusidae are a monophyletic lineage. Empusidae mantids are ambush predators, with mouthparts adapted to feeding on other insects and small animals. The majority of Empusidae species are distributed throughout Africa, but they are also found in Southeast Asia and in the southern parts of Europe.

Gongylus gongylodes, also known as the wandering violin mantis, ornate mantis, or Indian rose mantis, is an insect of the order Mantodea. Characterized by extremely slender limbs with large appendages. It is not a particularly aggressive species and often kept as a pet by hobbyists. The mantis is especially known for swaying its body back and forth to imitate a stick flowing in the wind. It primarily feeds on flying insects. Its native range is in southern India and Sri Lanka. It can reach up to 11 cm long. The males of the species are capable of flight. This species is a communal species in that they live and breed in large groups without unnecessary cannibalism.
Mago may refer to:

Hymenopus coronatus, also called H. bicornis, is a mantis from the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. It is known by various common names including walking flower mantis and (pink) orchid mantis. It is one of several species known as flower mantises from their resemblance and behaviour.

Gongylus is a genus of empusids in the order Mantodea. Characterized by extremely slender limbs with large appendages, at least one species is kept as a pet by hobbyists. Males of the species are capable of flight.
Human prehistory is the period between the use of the first stone tools c. 3.3 million years ago by hominins and the invention of writing systems. The earliest writing systems appeared c. 5,300 years ago, but it took thousands of years for writing to be widely adopted, and it was not used in some human cultures until the 19th century or even until the present. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different dates in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently.

Judea or Judaea, and the modern version of Judah is the ancient Hebrew and Israelite biblical, the contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous southern part of the region of Palestine. The name originates from the Hebrew name Yehudah, a son of the Jewish patriarch Jacob/Israel, and Yehudah's progeny forming the biblical Israelite tribe of Judah (Yehudah) and later the associated Kingdom of Judah, which the 1906 Jewish Encyclopedia dates from 934 until 586 BCE. The name of the region continued to be incorporated through the Babylonian conquest, Persian, Hellenistic, and Roman periods as Yehud, Yehud Medinata, Hasmonean Judea, and consequently Herodian Judea and Roman Judea, respectively.
Phytoscutus is a genus of mites in the family Phytoseiidae.
Phytoscutus gongylus is a species of mite in the family Phytoseiidae.

Gryneium or Gryneion, also Grynium or Grynion (Γρύνιον) and Grynia or Gryneia (Γρύνεια), was a city of ancient Aeolis. It was located 40 stadia from Myrina and 70 from Elaea. In early times it was independent, one of the 12 important cities of Aeolis, but afterwards became subject to Myrina. It contained a sanctuary of Apollo with an ancient oracle and a splendid temple of white marble.
Pericompsus is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae, containing the following species:
Python may refer to:
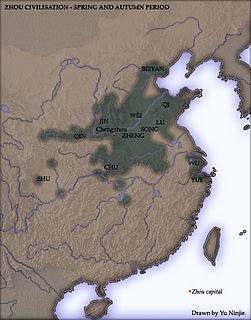
The Eastern Zhou was the second half of the Zhou dynasty of ancient China. It is divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States.