This article concerns the period 379 BC – 370 BC.
This article concerns the period 199 BC – 190 BC.

Lysander was a Spartan admiral who commanded the Spartan fleet in the Hellespont which defeated the Athenians at Aegospotami in 405 BC. The following year, he was able to force the Athenians to capitulate, bringing the Peloponnesian War to an end. He then played a key role in Sparta's domination of Greece for the next decade until his death at the Battle of Haliartus.
Year 195 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Flaccus and Cato. The denomination 195 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 196 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Purpureo and Marcellus. The denomination 196 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 192 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Flamininus and Ahenobarbus. The denomination 192 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Chabrias was an Athenian general of the 4th century BC.

Gytheio or Gythio, also the ancient Gythium or Gytheion, is a town on the eastern shore of the Mani Peninsula, and a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality East Mani, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 197.313 km2. It was the seaport of Sparta, some 40 kilometres north. Gytheio is the site of ancient Cranae, a tiny island where according to legend Paris of Troy and Helen from Sparta spent their first night together before departing for Troy, thus igniting the Trojan War.

Philopoemen was a skilled Greek general and statesman, who was Achaean strategos on eight occasions.
The Maniots or Maniates are the inhabitants of the Mani Peninsula, Laconia, in the southern Peloponnese, Greece. They were also formerly known as Mainotes and the peninsula as Maina. Maniots are described as descendants of the ancient Dorian population of the Peloponnese and as such related to the ancient Spartans. The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible, and the regional name "Mani" is thought to have meant originally "dry" or "barren". The name "Maniot" is a derivative meaning "of Mani". In the early modern period, Maniots had a reputation as fierce and proudly independent warriors, who practiced piracy and fierce blood feuds. For the most part, the Maniots lived in fortified villages where they defended their lands against the armies of William II Villehardouin and later against those of the Ottomans.
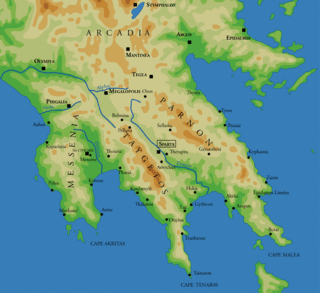
The Siege of Gythium was fought in 195 BC between Sparta and the coalition of Rome, Rhodes, the Achaean League and Pergamum. As the port of Gythium was an important Spartan base the allies decided to capture it before they advanced inland to Sparta. The Romans and the Achaeans were joined outside the city by the Pergamese and Rhodian fleets. The Spartans held out but one of the joint commanders, Dexagoridas, decided to surrender the city to the Roman legate. When Gorgopas, the other commander, found out, he killed Dexagoridas and took sole command of the city. After Dexagoridas' murder the Spartans held out more vigorously. However, Titus Quinctius Flamininus of the allied forces arrived with 4,000 more men and the Spartans decided to surrender the city on the condition that the garrison could leave unharmed. The result of this siege forced Nabis, the tyrant of Sparta, to abandon the surrounding land and withdraw to the city of Sparta. Later that year, Sparta capitulated to the allies.
Philoces was Philip V of Macedon's prefect and commander on the island of Euboea. In 200 BC he was ordered by Philip to ravage Attica with 2,000 infantry and 200 cavalry. According to Polybius the ravaging that Philoces gave Attica was the worst since the Persian War. In 197 BC he tried to relieve the city of Eretria but he was driven off by the Roman army besieging the city. He was then put in charge of a group of 1,500 who went to Achaea and relieved Corinth and had Argos surrendered to them. Philioces later gave Argos to Nabis of Sparta in return for a Spartan alliance with Macedon. Philoces still remained commander of the Macedonian garrison at Argos after the exchange and when Nabis deserted the Macedonians and went over to the Romans, Philoces was offered by the Romans to surrender the city to them. Philoces surrendered the city and was allowed free passage to Macedon. This is the last that is heard about Philoces.

The War against Nabis, or the Laconian War, of 195 BC was fought between the Greek city-state of Sparta and a coalition composed of Rome, the Achaean League, Pergamum, Rhodes, and Macedon.
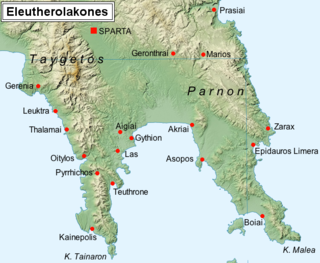
The League of Free Laconians was established in southern Greece in 21 BC by the Emperor Augustus, giving formal structure to a group of cities that had been associated for almost two centuries.

The Cleomenean War was fought by Sparta and its ally, Elis, against the Achaean League and Macedon. The war ended in a Macedonian and Achaean victory.
Gorgopas was a Spartan commander during the Corinthian War. In 388 BC Hierax was dispatched by Sparta to Aegina to take over the Spartan fleet. The Spartans under the command of Teleutias had earlier driven off the Athenian fleet blockading Aegina. Soon after taking over, Hierax departed for Rhodes with most of the fleet leaving Gorgopas, his vice-admiral with twelve triremes as governor in Aegina, replacing Eteonicus who held the post before. Gorgopas continued operations against the Athenian army led by Pamphilius who was still laying siege to the city. He ultimately forced Athens to send ships to evacuate their land forces from the area. Gorgopas then went on to harass the Athenian territory from his base in Aegina.
Eunomus was an Athenian admiral during the Corinthian War. In 389 BC he was put in charge of a fleet of 13 triremes to check the operation of the Spartan commander Gorgopas operating out of Aegina.
Demaenetus was an Athenian commander during the Corinthian War. In 389 BC he was one of the commanders in an engagement close to Aegina that resulted in a Spartan defeat and the death of the Spartan commander Gorgopas. One Athenian unit under Chabrias prepared an ambush while another under Demaenetus drew Gorgopas out of Aegina and into the trap by openly marching through the area.









