Government of Punjab may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Government of Punjab. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Government of Punjab may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Government of Punjab. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Punjab is Pakistan's most populous province, with an estimated population of 110,012,442 as of 2017. Forming the bulk of the transnational Punjab region, it is bordered by the Pakistani provinces of Sindh, Balochistan, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, the enclave of Islamabad, and Azad Kashmir. It also shares borders with the Indian states of Punjab, Rajasthan, and the Indian-administered territory of Jammu and Kashmir. The capital is Lahore, a cultural, historical, economic and cosmopolitan centre of Pakistan where the country's cinema industry, and much of its fashion industry, are based.

Sikhs are people associated with Sikhism, a monotheistic religion that originated in the 15th century, in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term Sikh has its origin in the words शिष्य, meaning a "disciple" or a "student". According to Article I of the Sikh Rehat Maryada, a Sikh is:
Any human being who faithfully believes in One Immortal Being; ten Gurus, from Guru Nanak to Guru Gobind Singh; Guru Granth Sahib; the teachings of the ten Gurus and the baptism bequeathed by the tenth Guru.
The Khalistan movement is a Sikh separatist movement seeking to create a separate country called Khalistān in the Punjab region as a homeland for Sikhs. The proposed country would consist of both the Punjab, India along with Punjab, Pakistan and include parts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Balochistan and Sindh in Pakistan; as well as Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and parts of Jammu and Kashmir, and Rajasthan in India. According to Jagjit Singh Chohan, Zulfikar Ali Bhutto the Prime Minister of Pakistan had proposed to make Nankana Sahib, as the capital of Khalistan during his talks with Chohan after the conclusion of the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971.

The Partition of India of 1947 was the division of British India into two independent dominion states, India and Pakistan by an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. India is today the Republic of India; Pakistan is today the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition involved the division of two provinces, Bengal and Punjab, based on district-wise non-Muslim or Muslim majorities. The partition also saw the division of the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Indian Civil Service, the railways, and the central treasury. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947 and resulted in the dissolution of the British Raj, or Crown rule in India. The two self-governing countries of India and Pakistan legally came into existence at midnight on 15 August 1947.
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.

Faisalabad, formerly known as Lyallpur, is the third-most-populous city in Pakistan, and the second-largest in the eastern province of Punjab. Historically one of the first planned cities within British India, it has long since developed into a cosmopolitan metropolis. Faisalabad was restructured into city district status; a devolution promulgated by the 2001 local government ordinance (LGO). The total area of Faisalabad District is 5,856 km2 (2,261 sq mi) while the area controlled by the Faisalabad Development Authority (FDA) is 1,280 km2 (490 sq mi). Faisalabad has grown to become a major industrial and distribution centre because of its central location in the region and connecting roads, rails, and air transportation. It has been referred to as the "Manchester of Pakistan". As of 2013, GDP (PPP) of Faisalabad was estimated as $43 billion and projected to rise to $87 billion in 2025 at a growth rate of 5.7%. Faisalabad contributes over 20 percent to the Pakistan's GDP, and has an average annual GDP (nominal) of $20.5 billion. Agriculture and industry remain its hallmark.

The administrative units of Pakistan consist of four provinces, two autonomous territories and one federal territory. Each province and territory is subdivided into divisions, which are further subdivided into districts, which are further subdivided into tehsils, or taluka, which are further subdivided into union councils.

The Districts of Pakistan, are the third-order administrative divisions of Pakistan, below provinces and divisions, but forming the first-tier of local government. In total, there are 154 districts in Pakistan including the Capital Territory and the districts of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit Baltistan. These districts are further divided into tehsils or talukas.

The University of Punjab, also referred to as Punjab University, is a public research university located in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Punjab University is the oldest public university in Pakistan. With multiple campuses in Gujranwala, Jhelum, and Khanspur, the university was formally established by the British Government after convening the first meeting for establishing higher education institutions in October 1882 at Simla. Punjab University was the fourth university to be established by the British colonial authorities in the Indian subcontinent; the first three universities were established in other parts of British India. There are 45,678 Students who attend the university, and Punjab University has a total of 13 faculties within which there are 83 academic departments, research centers, and institutes. Punjab University has ranked first among large-sized multiple faculty universities by the HEC in 2012. There are also two Nobel Laureates among the university's alumni and former staff. Additionally, the university is also a member of the Association of Commonwealth Universities of the United Kingdom. In the recently issued rankings of Asian universities by QS World Universities Rankings, Punjab University jumped from the 232nd to 193rd position, improving its position by 39 places. Punjab University also ranks 251-300 in the subject of Agriculture and Forestry, 501-550 in the subject of Physics & Astronomy and 501-550 in the subject of Chemistry according to QS World University Rankings by Subject 2019.

Punjab was a province of British India. Most of the Punjab region was annexed by the East India Company in 1849, and was one of the last areas of the Indian subcontinent to fall under British control. In 1858, the Punjab, along with the rest of British India, came under the direct rule of the British crown. The province comprised five administrative divisions, Delhi, Jullundur, Lahore, Multan and Rawalpindi and a number of princely states. In 1947, the partition of India led to the province being divided into East Punjab and West Punjab, in the newly independent dominions of India and Pakistan respectively.

The Government of the Punjab, a provincial government in the federal structure of Pakistan, is based in Lahore, the capital of the Punjab Province.

The Punjab Legislative Assembly or the Punjab Vidhan Sabha is the unicameral legislature of the state of Punjab in India. At present, it consists of 117 members, directly elected from 117 single-seat constituencies. The tenure of the Legislative Assembly is five years unless dissolved sooner. The current Speaker of the Assembly is Rana K. P. Singh. The meeting place of the Legislative Assembly since 6 March 1961 is the Vidhan Bhavan in Chandigarh.

The Green Revolution in India refers to a period when Indian agriculture was converted into an industrial system due to the adoption of modern methods and technology such as the use of high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, tractors, irrigation facilities, pesticides, and fertilizers. It was mainly found by M.S. Swaminathan. This was part of the larger Green revolution endeavor initiated by Norman Borlaug, which leveraged agricultural research and technology to increase agricultural productivity in the developing world.

The Government of Punjab, also known as the State Government of Punjab or locally as the State Government, is the supreme governing authority of the Indian state of Punjab and its 22 districts. It consists of an executive, led by the Governor of Punjab, a judiciary and a legislative branch.

Punjab is a state in northern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir to the north, and the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south and southeast, and Rajasthan to the southwest. It is bordered by the Pakistani province of Punjab to the west. The state covers an area of 50,362 square kilometres, 1.53% of India's total geographical area. It is the 20th-largest Indian state by area. With 27,704,236 inhabitants at the 2011 census, Punjab is the 16th-largest state by population, comprising 22 districts. Punjabi is the most widely spoken and official language of the state. The main ethnic group are the Punjabis, with Sikhs (58%) and Hindus (38%) as the dominant religious groups. The state capital is Chandigarh, a Union Territory and also the capital of the neighbouring state of Haryana. The five tributary rivers of the Indus River from which the region took its name are Sutlej, Ravi, Beas, Chenab and Jhelum Rivers; Sutlej, Ravi and Beas are part of the Indian Punjab.

Parkash Singh Badal is an Indian politician who was Chief Minister of Punjab state from 1970 to 1971, from 1977 to 1980, from 1997 to 2002, and from 2007 to 2017. He is also the patron of Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD), a Sikh-centered regional political party. He was the president of the party from 1995 to 2008, when he was replaced by his son Sukhbir Singh Badal. As the patron of SAD he exercises a strong influence on the Shiromani Gurdwara Parbandhak Committee and Delhi Sikh Gurdwara Management Committee. The Government of India awarded him the second-highest civilian award, Padma Vibhushan, in 2015.

Sardara Singh Johl is an Indian agriculture economist, writer, politician and the chancellor of the Central University of Punjab. A former National Professor of Agricultural Economics of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, he served as the vice chancellor of the Punjabi University and Punjab Agricultural University during different tenures and chaired the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices set up by the Government of India. He is a former director of the Central Board of Governors of the Reserve Bank of India and a former consultant to international bodies such as Food and Agriculture Organization, World Bank and United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia. The Government of India awarded him the third highest civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan, in 2004, for his contributions to Agriculture and agriculture education.
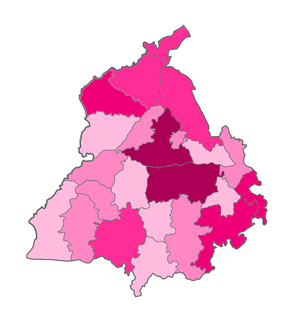
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have spread to the Indian state of the Punjab on 9 March 2020, when an Indian man returning from Italy was tested positive. As of 16 May 2020, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has confirmed a total of 1932 cases, including 33 deaths and 305 recoveries in the Punjab.