A graser or gamma-ray laser is a hypothetical device that would produce coherent gamma rays.
Graser may also refer to:

A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow.
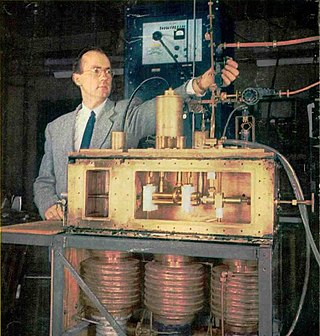
A maser is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, James P. Gordon, and Herbert J. Zeiger at Columbia University in 1953. Townes, Nikolay Basov and Alexander Prokhorov were awarded the 1964 Nobel Prize in Physics for theoretical work leading to the maser. Masers are also used as the timekeeping device in atomic clocks, and as extremely low-noise microwave amplifiers in radio telescopes and deep-space spacecraft communication ground stations.

Compton scattering, discovered by Arthur Holly Compton, is the scattering of a high frequency photon after an interaction with a charged particle, usually an electron. If it results in a decrease in energy of the photon, it is called the Compton effect. Part of the energy of the photon is transferred to the recoiling electron. Inverse Compton scattering occurs when a charged particle transfers part of its energy to a photon.
Enrico Fermi (1901–1954) was an Italian physicist who created the world's first nuclear reactor.

A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the 180m
73Ta
nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by 180m
73Ta
as well as 192m2
77Ir
, 210m
83Bi
, 242m
95Am
and multiple holmium isomers.
Terrestrial refers to things related to land or the planet Earth.
GLAST may refer to:
Gamma ray observatory or Gamma Ray Observatory can refer to:

A free-electron laser (FEL) is a light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions and behaves in many ways like a laser, but instead of using stimulated emission from atomic or molecular excitations, it employs relativistic electrons as a gain medium. Radiation is generated by a bunch of electrons passing through a magnetic structure. In an FEL, this radiation is further amplified as the radiation re-interacts with the electron bunch such that the electrons start to emit coherently, thus allowing an exponential increase in overall radiation intensity.
Lust for Life may refer to:
In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators. Amplification of ultrashort pulses almost always requires the technique of chirped pulse amplification, in order to avoid damage to the gain medium of the amplifier.
Gaser may refer to:
Gamma is the third letter of the Greek alphabet.
Land of the Free may refer to:
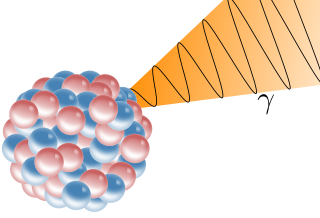
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz (3×1019 Hz), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation gamma rays based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power.
Gamma rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation.

The Breit–Wheeler process or Breit–Wheeler pair production is a proposed physical process in which a positron–electron pair is created from the collision of two photons. It is the simplest mechanism by which pure light can be potentially transformed into matter. The process can take the form γ γ′ → e+ e− where γ and γ′ are two light quanta.
A gamma-ray laser, or graser, is a hypothetical device that would produce coherent gamma rays, just as an ordinary laser produces coherent rays of visible light. Potential applications for gamma-ray lasers include medical imaging, spacecraft propulsion, and cancer treatment.
George Curriden Baldwin was an American theoretical and experimental physicist. He was a professor of nuclear engineering at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and a scientist working at the General Electric Research Laboratory and at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. He wrote a book on Nonlinear Optics and authored or co-authored over 130 technical papers.
A gravity laser, also sometimes referred to as a Gaser, Graser, or Glaser, is a hypothetical device for stimulated emission of coherent gravitational radiation or gravitons, much in the same way that a standard laser produces coherent electromagnetic radiation.