See also
- Grey's Anatomy , American television series
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Gray's Anatomy. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Gray's Anatomy is a classic human anatomy textbook, first edition (1858) by Henry Gray and Henry Carter.
Gray's Anatomy may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Gray's Anatomy. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Gray's Anatomy is an English written textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.

A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

Gray's Anatomy is an 80-minute concert film directed by Steven Soderbergh in 1996 involving a dramatized monologue by actor/writer Spalding Gray. The title is taken from the classic human anatomy textbook, Gray's Anatomy, originally written by Henry Gray in 1858. It was shot in ten days in late January 1996 during a break Soderbergh had from post-production on his previous film, Schizopolis.

Henry Gray was a British anatomist and surgeon most notable for publishing the book Gray's Anatomy. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS) at the age of 25.
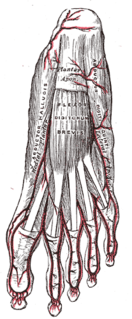
The abductor digiti minimi is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.

The perforating cutaneous nerve is a cutaneous nerve that supplies skin over the gluteus maximus muscle.
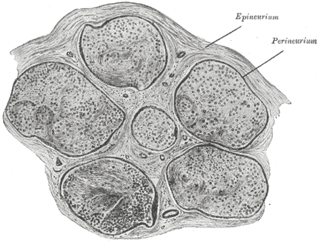
A funiculus is a small bundle of axons, enclosed by the perineurium. A small nerve may consist of a single funiculus, but a larger nerve will have several funiculi collected together into larger bundles known as fascicles. Fascicles are bound together in a common membrane, the epineurium.

The antitragus is a feature of mammalian ear anatomy.

The appendicular artery commonly arises from terminal branch of the ileocolic artery less commonly from the posterior cecal artery or an ileal artery. It descends behind the termination of the ileum and enters the mesoappendix of the vermiform appendix. It runs near the free margin of the mesoappendix and ends in branches which supply the appendix.

The palmar branch of the ulnar nerve arises about five cm proximal to the wrist from where the ulnar nerve splits into palmar and dorsal branches.

The palmar branch of the median nerve is a branch of the median nerve which arises at the lower part of the forearm.

The interspinous ligaments are thin and membranous ligaments, that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine. They extend from the root to the apex of each spinous process. They meet the ligamenta flava in front and blend with the supraspinous ligament behind.

A nerve fascicle, or fasciculus is a bundle of funiculi. A funiculus is a bundle of axons.
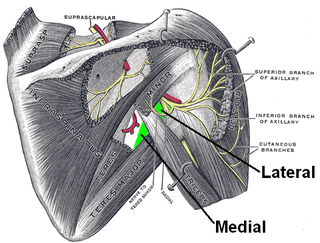
The quadrangular space is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: triangular space and triangular interval.

The deep branch of the ulnar nerve is a terminal, primarily motor branch of the ulnar nerve. It is accompanied by the deep palmar branch of ulnar artery.

The superficial branch of the ulnar nerve is a terminal branch of the ulnar nerve. It supplies the palmaris brevis and the skin on the ulnar side of the hand, and divides into a common palmar digital nerve and a proper palmar digital nerve.

The superficial cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes that lie near the surface of the neck.
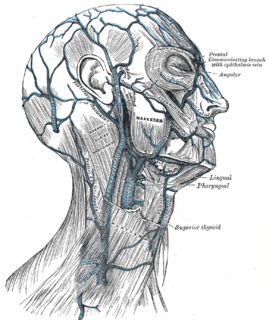
The anterior auricular veins are veins which drain the anterior aspect of the external ear. The veins drains to the superficial temporal vein.

Henry Vandyke Carter was an English anatomist, surgeon, and anatomical artist most notable for his illustrations of the book Gray's Anatomy.