The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. It came into being mostly because the city of Baltimore wanted to compete with the newly constructed Erie Canal and another canal being proposed by Pennsylvania, which would have connected Philadelphia and Pittsburgh. At first this railroad was located entirely in the state of Maryland, with an original line built from the port of Baltimore west to Sandy Hook.

The Ontario Northland Railway is a Canadian railway operated by the Ontario Northland Transportation Commission, a provincial Crown agency of the government of Ontario.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes region of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

The Central Railroad of New Jersey, also known as the Jersey Central or Jersey Central Lines, was a Class I railroad with origins in the 1830s. It filed for bankruptcy three times; in 1939, 1947 and on March 22, 1967, the CNJ filed for bankruptcy for the final time. It foreshadowed the rest of New Jersey's railroads, but not by much. It then pulled out of Pennsylvania completely in 1972. While most of the passenger services, structures and equipment were picked up by the State of New Jersey, later NJ Transit, it was absorbed into Conrail in April 1976 along with several other prominent bankrupt railroads of the northeastern United States. Only two of the railroad's steam locomotives were preserved: CNJ No. 592 & CNJ No. 113; the latter is the only one that is still operational.

The Richmond, Fredericksburg, and Potomac Railroad was a railroad connecting Richmond, Virginia, to Washington, D.C. The track is now the RF&P Subdivision of the CSX Transportation system; the original corporation is no longer a railroad company.

The Central New England Railway was a railroad from Hartford, Connecticut and Springfield, Massachusetts west across northern Connecticut and across the Hudson River on the Poughkeepsie Bridge to Maybrook, New York. It was part of the Poughkeepsie Bridge Route, an alliance between railroads for a passenger route from Washington to Boston, and was acquired by the New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad in 1904.

The Delaware and Hudson Railway (D&H) is a railroad that operates in the northeastern United States. In 1991, after more than 150 years as an independent railroad, the D&H was purchased by Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). CP operates D&H under its subsidiary Soo Line Corporation which also operates Soo Line Railroad.

The Lehigh and Hudson River Railway (L&HR) was the smallest of the six railroads that were merged into Conrail in 1976. It was a bridge line running northeast-southwest across northwestern New Jersey, connecting the line to the Poughkeepsie Bridge at Maybrook, New York with Easton, Pennsylvania, where it interchanged with various other companies.
The Geneva and Lyons Railroad was a railroad in New York State, constructed and owned by the New York Central Railroad. Chartered in 1877 and opened in 1878, it served as an outlet for coal trains on the Syracuse, Geneva and Corning Railroad to reach the main line of the New York Central. The Fall Brook Coal Company, which operated the Syracuse, Geneva and Corning, and the Lehigh Valley Railroad both used the line to deliver coal to Lyons. A branch of the New York Central since its completion, the Geneva and Lyons was formally absorbed by the New York Central in 1890.
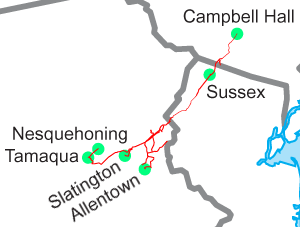
The Lehigh & New England Railroad was a Class I railroad located in Northeastern United States that acted as a bridge line. It was the second notable U.S. railroad to file for abandonment in its entirety, the first being the New York, Ontario & Western Railway.

Pearl River is a railroad station in Pearl River, New York. It serves NJ Transit and Metro-North Railroad trains on the Pascack Valley Line. It is located at 35 South Main Street between West Central Avenue and Jefferson Avenue. Pearl River is the last station in New York, heading from Spring Valley towards Hoboken Terminal. The land donated for the station came from Julius Braunsdorf, a local entrepreneur, who won a lawsuit against the Singer Corporation. Braunsdorf opened Central Avenue, the local post office, and the railroad station. Known as Muddy Brook, Braunsdorf suggested the hamlet be renamed for the pearls in the local river. Braunsdorf built originally two facilities at Pearl River, but some time after 1880, these were merged into one structure.
The Lebanon and Tremont Branch of the Philadelphia & Reading Railroad was a railroad line in Lebanon and Schuylkill County, Pennsylvania, built to tap the coal fields in the West End of Schuylkill County and send coal southward to Lebanon.
The Jersey Shore, Pine Creek and Buffalo Railway was a railroad built in the early 1880s to give the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad access to the coal regions around Clearfield, Pennsylvania, United States. It was originally planned as part of a connecting line between the East Coast of the United States and Buffalo, New York.

The Sussex Railroad was a short-line railroad in northwestern New Jersey. It replaced its predecessor, the Sussex Mine Railroad, in 1853 and operated under the Sussex Railroad Company until 1945 when it was fully merged into the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (DL&W) system. The Sussex Railroad was important in the economic development of Sussex County as it supplied a route for early local industries, such as dairy farms and ore mines, to export their products. It was the last independently operated New Jersey railroad to be incorporated into the DL&W system. The last train travelled on the Sussex Railroad tracks on October 2, 1966. The tracks were removed soon after and the right-of-way was transformed into a rail trail known as the Sussex Branch trail.

Crescent Junction is a small unincorporated community within Grand County in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Utah. The community is located at 4,882 feet (1,488 m) above sea level. Crescent Junction is the more common name of the town for road transport, as the name of junction of Interstate 70 and U.S. Route 191 in Utah law, while Brendel is more common in rail transport, as the name given by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad to rail siding and junction at the same location.

The Utah Division of the former Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad (D&RGW) is a rail line that connects Grand Junction, Colorado and Salt Lake City, Utah in the Western United States. It is now incorporated into the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) system as its Green River and Provo Subdivisions, forming a portion of the Denver-Nevada Central Corridor. Daily passenger service is provided by Amtrak's California Zephyr, and the BNSF Railway and Utah Railway have trackage rights over the line.
The Williamsport and North Branch Railroad was a short line that operated in north-central Pennsylvania between 1872 and 1937. After a long struggle to finance its construction, it was completed in 1893. It derived most of its freight revenue from logging and to a certain extent from anthracite coal traffic. It also carried many passengers to mountain resorts in Sullivan County, Pennsylvania. With the decline of the logging industry and increased accessibility of the region by automobile in the 1910s and 1920s, the railroad's business rapidly declined. The economic blow of the Great Depression proved insurmountable, and it was abandoned as unprofitable in 1937.

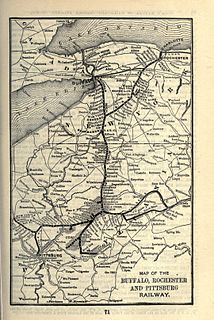
The Buffalo and Susquehanna Railroad was a railroad company that formerly operated in western and north central Pennsylvania and western New York. It was created in 1893 by the merger and consolidation of several smaller logging railroads. It operated independently until 1929, when a majority of its capital stock was purchased by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. At the same time, the B&O also purchased control of the neighboring Buffalo, Rochester, and Pittsburgh Railway. The Baltimore and Ohio officially took over operations of both roads in 1932.