Haarlem is a city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the province of North Holland. Haarlem is situated at the northern edge of the Randstad, one of the more populated metropolitan areas in Europe; it is also part of the Amsterdam metropolitan area. Haarlem had a population of 162,543 in 2021.

Haarlemmermeer is a municipality in the west of the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland. Haarlemmermeer is a polder, consisting of land reclaimed from water. The name Haarlemmermeer means 'Haarlem's lake', referring to the body of water from which the region was reclaimed in the 19th century.

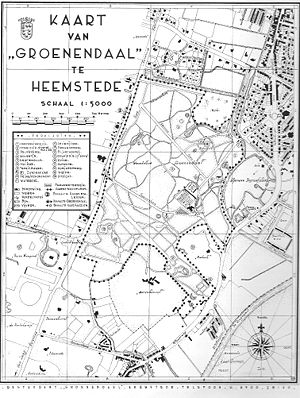
Heemstede is a town and a municipality in the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland. It is the fourth richest municipality of the Netherlands.

De Adriaan is a windmill in the Netherlands that burnt down in 1932 and was rebuilt in 2002. The original windmill dates from 1779 and the mill has been a distinctive part of the skyline of Haarlem for centuries.

The Spaarne is a river in North Holland, Netherlands. This partially canalized river connects the Ringvaart to a side branch of the North Sea Canal. It runs through Haarlem, Heemstede, and Spaarndam.

The Ringvaart is a canal in the province of North Holland, the Netherlands. The Ringvaart is a true circular canal surrounding the Haarlemmermeer polder and forms the boundary of the Haarlemmermeer municipality. Ringvaart is also the name of the dike bordering the canal.

Floriade was an international exhibition and garden festival, held every 10 years in the Netherlands. All the Floriades were World Horticultural Expositions and they were listed as A1 category exhibitions by the International Association of Horticultural Producers and hence recognised by the Bureau International des Expositions. The last event, Floriade 2022, was held in Almere.
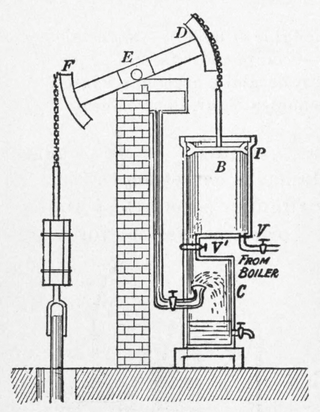
A beam engine is a type of steam engine where a pivoted overhead beam is used to apply the force from a vertical piston to a vertical connecting rod. This configuration, with the engine directly driving a pump, was first used by Thomas Newcomen around 1705 to remove water from mines in Cornwall. The efficiency of the engines was improved by engineers including James Watt, who added a separate condenser; Jonathan Hornblower and Arthur Woolf, who compounded the cylinders; and William McNaught, who devised a method of compounding an existing engine. Beam engines were first used to pump water out of mines or into canals but could be used to pump water to supplement the flow for a waterwheel powering a mill.

Villa Welgelegen is a historical building in Haarlem, the Netherlands, which currently houses the offices of the provincial executives of North Holland. Located at the north end of a public park in the city, it is an example of neoclassical architecture, designed by Abraham van der Hart and unusual for its style in the Netherlands.

Cruquius is a village in the Dutch province of North Holland. It is a part of the municipality of Haarlemmermeer and lies about 4 km northwest of Hoofddorp.

A buitenplaats was a summer residence for rich townspeople in the Netherlands. During the Dutch Golden Age of the 17th century, many traders and city administrators in Dutch towns became very wealthy. Many of them bought country estates, at first mainly to collect rents, however soon mansions started to be built there, which were used only during the summer.

A Cornish engine is a type of steam engine developed in Cornwall, England, mainly for pumping water from a mine. It is a form of beam engine that uses steam at a higher pressure than the earlier engines designed by James Watt. The engines were also used for powering man engines to assist the underground miners' journeys to and from their working levels, for winching materials into and out of the mine, and for powering on-site ore stamping machinery.

De Naald is a monument in Heemstede, Netherlands, erected in 1817 by the city council to commemorate two battles on the Manpad road running next to the site. The site is at the corner of the Manpad, and Herenweg, on property belonging to the estate 'Huis te Manpad'.

The Leidsevaart is a canal between the cities of Haarlem and Leiden in the Netherlands. It was dug in 1657, making it one of the oldest canals in the Netherlands. It was the major means of transport between Leiden and Haarlem for almost two centuries until the rail connection was established in the 19th century. The original stops along the railway mirrored the toll bridges of the canal.

The Museum De Cruquius occupies the old Cruquius steam pumping station in Cruquius, the Netherlands. It derives its name from Nicolaas Kruik (1678–1754), a Dutch land-surveyor and one of many promoters of a plan to pump the Haarlemmermeer dry. Like many well-educated men of his time, he latinized his name to Nicolaus Samuel Cruquius. During his lifetime the issue of the Haarlem Lake and how to pump it dry was international news, as the following excerpt from the Virginia Gazette on 31 May 1751 illustrates:

John Hope, also known as Jan Hope, was a wealthy Dutch banker, participating in Hope & Co., a member of the city council and an art collector. In 1770 he was appointed as manager of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He is also known today for his Groenendaal Park in Heemstede, where he summered on his estate. Shortly before he died he bought the nearby "Bosbeek". This estate became one of the first examples of a large garden in the 'English Style' in the Netherlands, and shaped by his second son Adrian Elias. His oldest son Thomas Hope became a designer of neoclassical interior decoration, and his youngest son Henry Philip Hope a gem collector and jewelry specialist.

The Duin- en Bollenstreek is a region in the Western Netherlands, that features coastal dunes and the cultivation of flower bulbs. Situated at the heart of historical Holland nearby the city of Leiden, South Holland, it is bordered by The Hague to the west and Haarlem to the north. The combination of beaches, flower fields, lakes and history makes this area attractive to tourists.

Flower bulb cultivation is an economic activity in the provinces of North Holland, South Holland and Flevoland. The colourful flower fields that have come to symbolise Holland can be seen in these areas around April.

The Huis te Manpad is an historical villa and former summer home of Jacob van Lennep in Heemstede, the Netherlands; bordered by the Leidsevaart canal, the Manpadslaan, and the Herenweg. It neighbors the estate of Hartekamp, famed for the gardens described by Carl Linnaeus. Both estates still have trees and other flora dating from that period.

The Dutch Windmill is the northern of two functioning windmills, the other being Murphy Windmill, on the western edge of Golden Gate Park in San Francisco, California. It was completed in 1903, and placed on the San Francisco Designated Landmark list on December 6, 1981.