
C++ is a general-purpose programming language created by Bjarne Stroustrup as an extension of the C programming language, or "C with Classes". The language has expanded significantly over time, and modern C++ now has object-oriented, generic, and functional features in addition to facilities for low-level memory manipulation. It is almost always implemented as a compiled language, and many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, LLVM, Microsoft, Intel, Oracle, and IBM, so it is available on many platforms.

Indigenous languages of the Americas are spoken by indigenous peoples from Alaska, Nunavut, and Greenland to the southern tip of South America, encompassing the land masses that constitute the Americas. These indigenous languages consist of dozens of distinct language families, as well as many language isolates and unclassified languages.
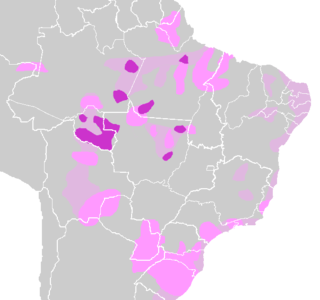
The Tupi or Tupian language family comprises some 70 languages spoken in South America, of which the best known are Tupi proper and Guarani.

The Cariban languages are a family of languages indigenous to northeastern South America. They are widespread across northernmost South America, from the mouth of the Amazon River to the Colombian Andes, and they are also spoken in small pockets of central Brazil. The languages of the Cariban family are relatively closely related. There are about three dozen of them, but most of them are only spoken by a few hundred people—the only one with more than a few thousand speakers is Macushi, which has 30,000. The Cariban family is well known among linguists partly because one language in the family—Hixkaryana—has a default word order of object–verb–subject, which had previously been believed to not exist in any spoken natural language.

Amerind is a hypothetical higher-level language family proposed by Joseph Greenberg in 1960 and elaborated by his student Merritt Ruhlen. Greenberg proposed that all of the indigenous languages of the Americas belong to one of three language families, the previously established Eskimo–Aleut and Na–Dene, and with everything else—otherwise classified by specialists as belonging to dozens of independent families—as Amerind. Due to a large number of methodological flaws in the 1987 book Language in the Americas, the relationships he proposed between these languages have been rejected by the majority of historical linguists as spurious.

Luiz Roberto de Barros Mott or Luiz Mott in São Paulo, is an anthropologist and a gay rights activist in Brazil.

This article is a list of different language classification proposals developed for indigenous languages of the Americas. The article is divided into North, Central, and South America sections; however, the classifications do not neatly correspond to these divisions.
The Guató are an indigenous people living on the upper Paraguay River, along the border of modern-day Brazil and Bolivia. They aided the Brazilians in the war with Paraguay 1865–70.

The Borôroan languages of Brazil are Borôro and the extinct Umotína and Otuke. They are sometimes considered to form part of the proposed Macro-Jê language family, though this has been disputed.

Google Translate is a free multilingual neural machine translation service developed by Google, to translate text and websites from one language into another. It offers a website interface, a mobile app for Android and iOS, and an application programming interface that helps developers build browser extensions and software applications. As of January 2021, Google Translate supports 109 languages at various levels and as of April 2016, claimed over 500 million total users, with more than 100 billion words translated daily.

Portuguese is the official and national language of Brazil and is widely spoken by most of the population. The Portuguese dialects spoken in Brazil are collectively known as Brazilian Portuguese. The Brazilian Sign Language also has official status at the federal level.
English is a West Germanic language first spoken in early medieval England which eventually became the leading language of international discourse in today's world. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name, England. Both names derive from Anglia, a peninsula on the Baltic Sea. English is most closely related to Frisian and Low Saxon, while its vocabulary has been significantly influenced by other Germanic languages, particularly Old Norse, as well as Latin and French.

The languages of South America can be divided into three broad groups:

Guató is a possible language isolate spoken by 1% of the Guató people of Brazil.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.












