Gunner Bay is a large bay in the far north of Bermuda. It contains the entrance to St. George's Harbor and Paget Island, and is overlooked by St. David's Head in the far north of St. David's Island.
Gunner Bay is a large bay in the far north of Bermuda. It contains the entrance to St. George's Harbor and Paget Island, and is overlooked by St. David's Head in the far north of St. David's Island.

The Gulf of St. Lawrence fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in North America.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

St. Margarets Bay is a bay located on the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia, Canada on the border of Halifax County and Lunenburg County.

Southampton Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named for Henry Wriothesley, 3rd Earl of Southampton (1573-1624).

Warwick Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after Robert Rich, 2nd Earl of Warwick (1587-1658).
Pembroke Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after English aristocrat William Herbert, 3rd Earl of Pembroke (1580–1630).

Devonshire Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. Originally named Cavendish Tribe and later Devonshire Tribe, for William Cavendish, 1st Earl of Devonshire (1552–1626). Devonshire Redoubt, on Castle Island, one of the Castle Harbour fortifications of St. George's Parish, was also named after him.

Hamilton Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It was renamed for Scottish aristocrat James Hamilton, 2nd Marquess of Hamilton (1589–1625) when he purchased the shares originally held in the Virginia Company by Lucy Russell, Countess of Bedford.
St. George's Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after the founder of the Bermuda colony, Admiral Sir George Somers.

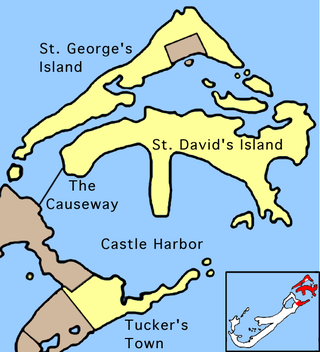
The Causeway is a narrow strip of reclaimed land and bridges in the north of Bermuda linking Hamilton Parish on the mainland in the southwest and Bermuda International Airport on St. David's Island in St. George's Parish in the northeast, which are otherwise divided by Castle Harbour.

Castle Harbour is a large natural harbour in Bermuda. It is located between the northeastern end of the main island and St. David's Island. Originally called Southampton Port, it was renamed as a result of its heavy fortification in the early decades of the Seventeenth century.

Nonsuch Island is part of the chain of islands which make up Bermuda. It is in St George's Parish, in the northeast of Bermuda. It is 5.7 ha in area and is at the east entrance to Castle Harbour, close to the south-easternmost point of Cooper's Island. Among the island's charted features is a bay called Nonsuch Bay.

Cooper's Island is part of the chain which makes up Bermuda. It is located in St. George's Parish, in the northeast of the territory.
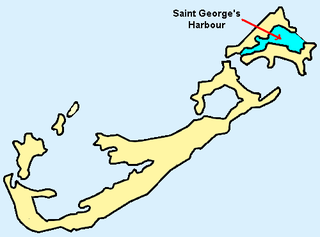
St. George's Harbour is a natural harbour in the north of Bermuda. It serves as the port for the town of St. George's, located on St. George's Island, to its north. To its south is St. David's Island. The harbour and both islands lie within St. George's Parish. It was for two centuries the primary harbour of the British Overseas Territory.
St. David's Head is a headland in the northeast of St. David's Island, Bermuda. It is the easternmost point of the territory, and is located in St. George's Parish. Actually two headlands, it is the site of Great Head Battery, one of the many forts that surround the site of the territory's first settlement in the early 17th century, which is now open to the public as a national monument.

Ferry Reach is a three mile long channel in the north-east of Bermuda, which lies between St. George's Island in the north and St. David's Island in the south, south-west of the town of St. George's.

St. David's Island is one of the main islands of the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is located in the far north of the territory, one of the two similarly sized islands that make up the majority of St. George's Parish.

Tobacco Bay is located in the far north of Bermuda. It lies on the Atlantic Ocean coast, close to the town of St. George's and to the historic Fort St. Catherine. One of Bermuda's national parks, it is a popular public beach. Snorkeling is a popular activity, as the bay has impressive underwater coral reefs, which explains its popularity with those who snorkel.

Several of the islands strung across the South entrance of Castle Harbour, Bermuda were fortified in the early days of the territory, hence the harbour's name. When official settlement of the archipelago by England began in 1612 the first permanent town, St. George's was placed on the North side of St. George's Harbour. St. George's Harbour could be accessed directly by channels from the East. Those channels, however, were shallow, suitable, originally, only for small ships. As a consequence, and despite any major settlement on its shores, Castle Harbour was an important anchorage in the early years of the colony, with its main entrance, Castle Roads being an important route in from the open Atlantic for shipping. It was also a weak point, as it was remote from the defences of St. George's Harbour, and difficult to reach. It was quickly fortified and garrisoned by a standing militia.
Bailey's Bay is a long shallow indentation in the northeastern shore of the main island of Bermuda. It stretches for about 1,500 metres (1,600 yd) along the north coast of Hamilton Parish. The settlement which stretches along the bay's coast is also called Bailey's Bay.
32°22′21″N64°39′14″W / 32.3725°N 64.6539°W