See also
Topics referred to by the same term
This disambiguation page lists articles about people with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article.
Haakon Magnusson or Håkon Magnusson may refer to:

Haakon VI, also known as Håkan Magnusson, was King of Norway from 1343 until his death and King of Sweden between 1362 and 1364. He is sometimes known as Haakon Magnusson the Younger to distinguish him from his great-grandfather, Haakon V.

Haakon V Magnusson was King of Norway from 1299 until 1319.

Haakon, also spelled Håkon, Hakon, Håkan, or Háukon or Hákon, is an older spelling of the modern Norwegian form of the Old Norwegian masculine first name Hákon meaning "High Son" from há and konr. An old English form is Hacon as in Haconby, Hacon's Village. The name appears in Scottish Gaelic as Àcainn, as seen in the place-name Kyleakin, meaning 'Haakon's Narrows', being named after King Haakon IV of Norway.
Guttorm Sigurdsson was the king of Norway from January to August 1204, during the Norwegian civil war era. As a grandson of King Sverre, he was proclaimed king by the Birkebeiner faction when he was just four years old. Although obviously not in control of the events surrounding him, Guttorm's accession to the throne under the effective regency of Haakon the Crazy led to renewed conflict between the Birkebeiner and the Bagler factions, the latter supported militarily by Valdemar II of Denmark.

Tønsberg Fortress was a medieval fortress and castle, located in Tønsberg, Norway which was defended by the fortress for over 300 years.

Euphemia of Sweden was a Swedish princess. She was Duchess consort of Mecklenburg, heiress of Sweden and of Norway, and mother of King Albert of Sweden. (c. 1338-1412) .

The Bagli Party or Bagler was a faction or party during the Norwegian Civil Wars. The Bagler faction was made up principally of the Norwegian aristocracy, clergy and merchants.

The Fairhair dynasty was a family of kings founded by Harald I of Norway which united and ruled Norway with few interruptions from the latter half of the 9th century. In the traditional view, this lasted until 1387, however, many modern scholars view this rule as lasting only three generations, ending with Harald Greycloak in the late 10th century. The moniker "Fairhair dynasty" is a retrospective construction: in their lifetime what little traces there are refer to them consistently as "Ynglings".

Eric Magnusson was a Swedish duke and the second son of Magnus Ladulås. His duchy consisted of large parts of Sweden, as well as smaller parts of Norway and Denmark. He had a troubled relationship with his brother, King Birger Magnusson, with several uprisings as a result. His son, Magnus, became the king of Norway and Sweden. The Eric's Chronicle, the oldest Swedish chronicle, is named for him.

Ingeborg of Norway was a Norwegian princess and by marriage a Swedish royal duchess with a position in the regency governments in Norway (1319–1327) and Sweden (1319–1326) during the minority of her son, King Magnus Eriksson. In 1318–1319, she was Sweden's de facto ruler, and from 1319 until 1326, she was Sweden's first de jure female regent. Her role in northern European history is considered of major importance.
Magnusson, or Magnússon, is a surname of Scandinavian origin, meaning son of Magnus. It may refer to:
Haakon may refer to:

Ingeborg, Duchess of Öland was a Norwegian princess and a Swedish duchess. She was Duchess of Uppland, Öland and Finland. As a widow, she had a seat in the regency government of her nephew Magnus, who reigned as king of both Sweden and Norway.

The House of Sverre was a royal house or dynasty which ruled, at various times in history, the Kingdom of Norway, hereunder the kingdom's realms, and the Kingdom of Scotland. The house was founded with King Sverre Sigurdsson. It provided the rulers of Norway from 1184 to 1319.
Events in the year 1319 in Norway.
Events in the year 1380 in Norway.

The Old Town of Oslo is a neighbourhood in the inner city of Oslo, Norway, belonging to the borough of Gamle Oslo and is the oldest urban area within the current capital. This part of the capital of Norway was simply called Oslo until 1925 while the city as a whole was called Kristiania. Oslo's old town was established with the urban structure around the year 1000 and was the capital of Norway's dominion in 1314. The main Old Town area has several ruins of stone and brick lying above ground, and large amounts of protected culture underground. The core area also has listed 1700s buildings. Towards Ekeberg slope and further up are some 17th and 18th-century wooden houses that are zoned for conservation under the Planning and Building Act, though there exist in the Old Town many four-storey brick houses, built at the end of the 1800s, and some heritage railway buildings from different eras.
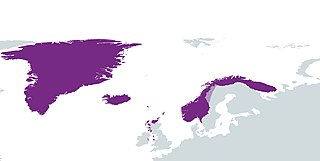
The term Norwegian Realm and Old Kingdom of Norway refer to the Kingdom of Norway's peak of power at the 13th century after a long period of civil war before 1240. The kingdom was a loosely unified nation including the territory of modern-day Norway, modern-day Swedish territory of Jämtland, Herjedalen, Ranrike (Bohuslän) and Idre and Särna, as well as Norway's overseas possessions which had been settled by Norwegian seafarers for centuries before being annexed or incorporated into the kingdom as 'tax territories'. To the North, Norway also bordered extensive tax territories on the mainland. Norway, whose expansionism starts from the very foundation of the Kingdom in 872, reached the peak of its power in the years between 1240 and 1319.