A handle is a grip attached to an object for using or moving the object.
Contents
Handle may also refer to:
A handle is a grip attached to an object for using or moving the object.
Handle may also refer to:
C is a general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems.
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes which together represent a sequence. In its most basic form, each node contains data, and a reference to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing more efficient insertion or removal of nodes at arbitrary positions. A drawback of linked lists is that data access time is linear in respect to the number of nodes in the list. Because nodes are serially linked, accessing any node requires that the prior node be accessed beforehand. Faster access, such as random access, is not feasible. Arrays have better cache locality compared to linked lists.
Null may refer to:
In computer science, reference counting is a programming technique of storing the number of references, pointers, or handles to a resource, such as an object, a block of memory, disk space, and others.
In computer programming, a reference is a value that enables a program to indirectly access a particular data, such as a variable's value or a record, in the computer's memory or in some other storage device. The reference is said to refer to the datum, and accessing the datum is called dereferencing the reference. A reference is distinct from the datum itself.

Historically, the classic Mac OS used a form of memory management that has fallen out of favor in modern systems. Criticism of this approach was one of the key areas addressed by the change to Mac OS X.
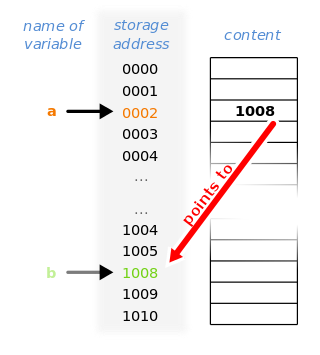
In computer science, a pointer is an object in many programming languages that stores a memory address. This can be that of another value located in computer memory, or in some cases, that of memory-mapped computer hardware. A pointer references a location in memory, and obtaining the value stored at that location is known as dereferencing the pointer. As an analogy, a page number in a book's index could be considered a pointer to the corresponding page; dereferencing such a pointer would be done by flipping to the page with the given page number and reading the text found on that page. The actual format and content of a pointer variable is dependent on the underlying computer architecture.
A function pointer, also called a subroutine pointer or procedure pointer, is a pointer referencing executable code, rather than data. Dereferencing the function pointer yields the referenced function, which can be invoked and passed arguments just as in a normal function call. Such an invocation is also known as an "indirect" call, because the function is being invoked indirectly through a variable instead of directly through a fixed identifier or address.
In computer science, type safety and type soundness are the extent to which a programming language discourages or prevents type errors. Type safety is sometimes alternatively considered to be a property of facilities of a computer language; that is, some facilities are type-safe and their usage will not result in type errors, while other facilities in the same language may be type-unsafe and a program using them may encounter type errors. The behaviors classified as type errors by a given programming language are usually those that result from attempts to perform operations on values that are not of the appropriate data type, e.g., adding a string to an integer when there's no definition on how to handle this case. This classification is partly based on opinion.
Pointer may refer to:
On the Amiga, the Old File System was the filesystem for AmigaOS before the Amiga Fast File System. Even though it used 512-byte blocks, it reserved the first small portion of each block for metadata, leaving an actual data block capacity of 488 bytes per block. It wasn't very suitable for anything except floppy disks, and it was soon replaced.
In computer science, dynamic dispatch is the process of selecting which implementation of a polymorphic operation to call at run time. It is commonly employed in, and considered a prime characteristic of, object-oriented programming (OOP) languages and systems.
In computing, a null pointer or null reference is a value saved for indicating that the pointer or reference does not refer to a valid object. Programs routinely use null pointers to represent conditions such as the end of a list of unknown length or the failure to perform some action; this use of null pointers can be compared to nullable types and to the Nothing value in an option type.
In computer science, a call stack is a stack data structure that stores information about the active subroutines of a computer program. This type of stack is also known as an execution stack, program stack, control stack, run-time stack, or machine stack, and is often shortened to simply "the stack". Although maintenance of the call stack is important for the proper functioning of most software, the details are normally hidden and automatic in high-level programming languages. Many computer instruction sets provide special instructions for manipulating stacks.
C++/CLI is a variant of the C++ programming language, modified for Common Language Infrastructure. It has been part of Visual Studio 2005 and later, and provides interoperability with other .NET languages such as C#. Microsoft created C++/CLI to supersede Managed Extensions for C++. In December 2005, Ecma International published C++/CLI specifications as the ECMA-372 standard.
Fat is an oily or greasy organic substance.
Dynamic loading is a mechanism by which a computer program can, at run time, load a library into memory, retrieve the addresses of functions and variables contained in the library, execute those functions or access those variables, and unload the library from memory. It is one of the 3 mechanisms by which a computer program can use some other software; the other two are static linking and dynamic linking. Unlike static linking and dynamic linking, dynamic loading allows a computer program to start up in the absence of these libraries, to discover available libraries, and to potentially gain additional functionality.
In computer programming, a handle is an abstract reference to a resource that is used when application software references blocks of memory or objects that are managed by another system like a database or an operating system.
Component Object Model (COM) is a binary-interface standard for software components introduced by Microsoft in 1993. It is used to enable inter-process communication (IPC) object creation in a large range of programming languages. COM is the basis for several other Microsoft technologies and frameworks, including OLE, OLE Automation, Browser Helper Object, ActiveX, COM+, DCOM, the Windows shell, DirectX, UMDF and Windows Runtime.
In computing or computer programming, delegation refers generally to one entity passing something to another entity, and narrowly to various specific forms of relationships. These include: