
Embouchure or lipping is the use of the lips, facial muscles, tongue, and teeth in playing a wind instrument. This includes shaping the lips to the mouthpiece of a woodwind instrument or the mouthpiece of a brass instrument. The word is of French origin and is related to the root bouche, 'mouth'. Proper embouchure allows instrumentalists to play their instrument at its full range with a full, clear tone and without strain or damage to their muscles.
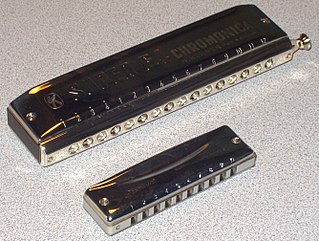
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica include diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, orchestral, and bass versions. A harmonica is played by using the mouth to direct air into or out of one holes along a mouthpiece. Behind each hole is a chamber containing at least one reed. The most common is the diatonic Richter-tuned with ten air passages and twenty reeds, often called the blues harp. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring typically made of brass, stainless steel, or bronze, which is secured at one end over a slot that serves as an airway. When the free end is made to vibrate by the player's air, it alternately blocks and unblocks the airway to produce sound.

The saxophone is a type of single-reed woodwind instrument with a conical body, usually made of brass. As with all single-reed instruments, sound is produced when a reed on a mouthpiece vibrates to produce a sound wave inside the instrument's body. The pitch is controlled by opening and closing holes in the body to change the effective length of the tube. The holes are closed by leather pads attached to keys operated by the player. Saxophones are made in various sizes and are almost always treated as transposing instruments. Saxophone players are called saxophonists.

The trombone is a musical instrument in the brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's vibrating lips cause the air column inside the instrument to vibrate. Nearly all trombones use a telescoping slide mechanism to alter the pitch instead of the valves used by other brass instruments. The valve trombone is an exception, using three valves similar to those on a trumpet, and the superbone has valves and a slide.

The tuba is the lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibration – a buzz – into a mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th century, making it one of the newer instruments in the modern orchestra and concert band. The tuba largely replaced the ophicleide. Tuba is Latin for "trumpet".

A transposing instrument is a musical instrument for which music notation is not written at concert pitch. For example, playing a written middle C on a transposing instrument produces a pitch other than middle C; that sounding pitch identifies the interval of transposition when describing the instrument. Playing a written C on clarinet or soprano saxophone produces a concert B♭, so these are referred to as B♭ instruments. Providing transposed music for these instruments is a convention of musical notation. The instruments do not transpose the music; rather, their music is written at a transposed pitch. Where chords are indicated for improvisation they are also written in the appropriate transposed form.

The melodica is a handheld free-reed instrument similar to a pump organ or harmonica. It features a musical keyboard on top, and is played by blowing air through a mouthpiece that fits into a hole in the side of the instrument. The keyboard usually covers two or three octaves. Melodicas are small, lightweight, and portable, and many are designed for children to play. They are popular in music education programs, especially in Asia. The modern form of the instrument was invented by Hohner in the late 1950s, though similar instruments have been known in Italy since the 19th century.

The tenor horn is a brass instrument in the saxhorn family and is usually pitched in E♭. It has a bore that is mostly conical, like the flugelhorn and euphonium, and normally uses a deep, cornet-like mouthpiece.
Overblowing is the manipulation of supplied air through a wind instrument that causes the sounded pitch to jump to a higher one without a fingering change or the operation of a slide. Overblowing may involve a change in the air pressure, in the point at which the air is directed, or in the resonance characteristics of the chamber formed by the mouth and throat of the player.

The tenor saxophone is a medium-sized member of the saxophone family, a group of instruments invented by Adolphe Sax in the 1840s. The tenor and the alto are the two most commonly used saxophones. The tenor is pitched in the key of B♭ (while the alto is pitched in the key of E♭), and written as a transposing instrument in the treble clef, sounding an octave and a major second lower than the written pitch. Modern tenor saxophones which have a high F♯ key have a range from A♭2 to E5 (concert) and are therefore pitched one octave below the soprano saxophone. People who play the tenor saxophone are known as "tenor saxophonists", "tenor sax players", or "saxophonists".

Hohner Musikinstrumente GmbH & Co. KG is a German manufacturer of musical instruments, founded in 1857 by Matthias Hohner (1833–1902). The roots of the Hohner firm are in Trossingen, Baden-Württemberg. Since its foundation, and though known for its harmonicas, Hohner has manufactured a wide range of instruments, such as kazoos, accordions, recorder flutes, melodicas, banjos, electric, acoustic, resonator and classical guitars, basses, mandolins and ukuleles.

The Richter-tuned harmonica, or 10-hole harmonica or blues harp, is the most widely known type of harmonica. It is a variety of diatonic harmonica, with ten holes which offer the player 19 notes in a three-octave range.
There are numerous techniques available for playing the harmonica, including bending, overbending, and tongue blocking.

A melodeon or diatonic button accordion is a member of the free-reed aerophone family of musical instruments. It is a type of button accordion on which the melody-side keyboard contains one or more rows of buttons, with each row producing the notes of a single diatonic scale. The buttons on the bass-side keyboard are most commonly arranged in pairs, with one button of a pair sounding the fundamental of a chord and the other the corresponding major triad.
The chromatic harmonica is a type of harmonica that uses a button-activated sliding bar to redirect air from the hole in the mouthpiece to the selected reed-plate desired. When the button is not pressed, an altered diatonic major scale of the key of the harmonica is available, while depressing the button accesses the same scale a semitone higher in each hole. Thus, the instrument is capable of playing the 12 notes of the Western chromatic scale. The chromatic harmonica can thus be contrasted with a standard harmonica, which can play only the notes in a given musical key.
Jupiter Band Instruments, Inc. is a manufacturer and distributor of woodwind, brass and percussion instruments. Jupiter was established by its Taiwanese parent company KHS in 1980.

A tremolo harmonica is a type of diatonic harmonica, distinct by having two reeds per note. In a tremolo harmonica, the two reeds are tuned slightly off a reference pitch, one slightly sharp and the other slightly flat. This gives a unique wavering or warbling sound created by the two reeds being not exactly in tune with each other and difference in their subsequent waveforms acting against one another. The degree of beating can be varied depending on the desired effect. Instruments where the beating is faster due to the reeds being farther apart from the reference pitch are called "wet", whereas those where the beating is slower and less noticeable due to the reeds being more closely in tune are called "dry".

Christian August Seydel founded the C. A. Seydel Söhne harmonica factory in Klingenthal, Sachsen in 1847. The firm remains the oldest harmonica factory in the world and manufactures a wide range of harmonicas.
Richter tuning is a system of choosing the reeds for a diatonic wind instrument. It is named after Joseph Richter, a Bohemian instrument maker who adopted the tuning for his harmonicas in the early 19th century and is credited with inventing the blow/draw mechanism that allows the harmonica to play different notes when the air is drawn instead of blown.

A horn is any of a family of musical instruments made of a tube, usually made of metal and often curved in various ways, with one narrow end into which the musician blows, and a wide end from which sound emerges. In horns, unlike some other brass instruments such as the trumpet, the bore gradually increases in width through most of its length—that is to say, it is conical rather than cylindrical. In jazz and popular-music contexts, the word may be used loosely to refer to any wind instrument, and a section of brass or woodwind instruments, or a mixture of the two, is called a horn section in these contexts.
















