
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, after flowering; and to the shedding of ripe fruit. The antonym of deciduous in the botanical sense is evergreen.

The United Kingdom straddles the higher mid-latitudes between 49° and 61°N on the western seaboard of Europe. Since the UK is always in or close to the path of the polar front jet stream, frequent changes in pressure and unsettled weather are typical. Many types of weather can be experienced in a single day.

San Salvador de Jujuy, commonly known as Jujuy and locally often referred to as San Salvador, is the capital and largest city of Jujuy Province in northwest Argentina. Also, it is the seat of the Doctor Manuel Belgrano Department. It lies near the southern end of the Humahuaca Canyon where wooded hills meet the lowlands.

The climate of India consists of a wide range of weather conditions across a vast geographic scale and varied topography. Based on the Köppen system, India encompasses a diverse array of climatic subtypes. These range from arid and semi-arid regions in the west to highland, sub-arctic, tundra, and ice cap climates in the northern Himalayan regions, varying with elevation. The northern lowlands experience subtropical conditions, with some areas at higher altitudes, like Srinagar, touching continental climates. In contrast, much of the south and the east exhibit tropical climate conditions, which support lush rainforests in these territories. Many regions have starkly different microclimates, making it one of the most climatically diverse countries in the world. The country's meteorological department follows the international standard of four seasons with some local adjustments: winter, summer, monsoon or rainy season, and a post-monsoon period.

The Alvord Desert is a desert located in Harney County, in southeastern Oregon in the Western United States. It is roughly southeast of Steens Mountain. The Alvord Desert is a 12-by-7-mile dry lake bed and averages 7 inches (180 mm) of rain a year. Two mountain ranges separate it from the Pacific Ocean—the Coast Range, and the Cascade Mountains. Along with Steens Mountain, these topographical features create a rain shadow. The Alvord Desert lies at an elevation of approximately 4,000 feet (1,200 m).

The climate of Chicago is classified as hot-summer humid continental with hot humid summers and cold, occasionally snowy winters. All four seasons are distinctly represented: Winters are cold and often see snow with below 0 Celsius temperatures and windchills, while summers are warm and humid with temperatures being hotter inland, spring and fall bring bouts of both cool and warm weather and fairly sunny skies. Annual precipitation in Chicago is moderate and relatively evenly distributed, the driest months being January and February and the wettest July and August. Chicago's weather is influenced during all four seasons by the nearby presence of Lake Michigan.

The geography of Toronto, Ontario, covers an area of 630 km2 (240 sq mi) and is bounded by Lake Ontario to the south; Etobicoke Creek, Eglinton Avenue, and Highway 427 to the west; Steeles Avenue to the north; and the Rouge River and the Scarborough–Pickering Townline to the east. In addition to Etobicoke Creek and the Rouge River, the city is trisected by two minor rivers and their tributaries, the Humber River in the west end and the Don River east of downtown. Both flow southward to Lake Ontario at Humber Bay and Toronto Harbour respectively, which are part of the longer Waterfront, as well as Etobicoke Creek and the Rouge River.

Manlleu is municipality in the comarca of Osona, in the province of Barcelona, Catalonia, northern Spain.

The climate of Sydney, Australia is humid subtropical, shifting from mild and cool in winter to warm and occasionally hot in the summer, with no extreme seasonal differences since the weather has some maritime influence. Though more contrasting temperatures are recorded in the inland western suburbs, as Sydney CBD is more affected by the oceanic climate drivers than the hinterland.
Delhi features a monsoon influenced humid subtropical climate bordering a hot semi-arid climate, with high variation between summer and winter temperatures and precipitation. Delhi's version of a humid subtropical climate is markedly different from many other humid subtropical cities such as São Paulo, Houston, and Brisbane in that the city features dust storms and wildfire haze due to its semi-arid climate.
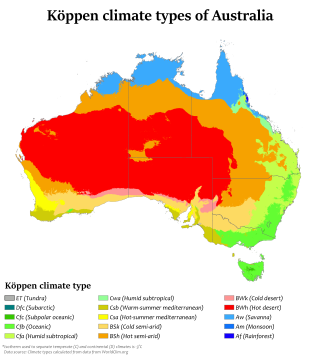
Australia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the farther south one travels, and drier the farther west, until one reaches the West Coast.

Tasmania has a cool temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The highest recorded maximum temperature in Tasmania is 42.2 °C (108.0 °F) at Scamander on 30 January 2009, during the 2009 southeastern Australia heat wave. Tasmania's lowest recorded minimum temperature is −14.2 °C (6.4 °F) on 7 August 2020, at Central Plateau.
The province of Sindh is situated in a tropical region, with subtropical regions in the northern sections; it is hot, humid and very rainy in the summer and cold and dry in winter. Temperatures frequently rise above 46 °C (115 °F) between May and August, and the minimum average temperature of 2 °C (36 °F) occurs during December and January. The annual rainfall averages about nearly 13 inches (330 mm), falling mainly during June and September. The southwesterly monsoon wind begins to blow in mid-February and continues until the end of September, whereas the cool northerly wind blows during the winter months from October to January.
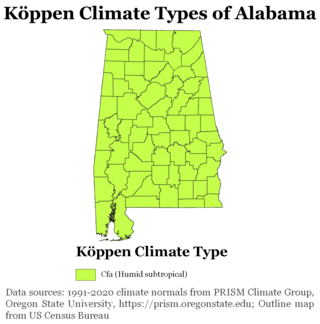
The state of Alabama is classified as humid subtropical (Cfa) under the Köppen climate classification. The state's average annual temperature is 64 °F (18 °C). Temperatures tend to be warmer in the state's southern portion with its proximity to the Gulf of Mexico, while its northern portions, especially in the Appalachian Mountains in the northeast, tend to be slightly cooler. Alabama generally has hot, humid summers and mild winters with copious precipitation throughout the year. The state receives an average of 56 inches (1,400 mm) of rainfall each year and experiences a lengthy growing season of up to 300 days in its southern portion. Hailstorms occur occasionally during the spring and summer here, but they are seldom destructive. Heavy fogs are rare, and they are confined chiefly to the coast. Thunderstorms also occur year-around. They are most common in the summer, but they are most commonly severe during the spring and late autumn. That is when destructive winds and tornadoes occur frequently, especially in the northern and central parts of the state. Central and northern Alabama are squarely within Dixie Alley, the primary area in the U.S. outside the Southern Plains with relatively high tornado risk. Alabama is ranked second in the U.S for the deadliest tornadoes. Hurricanes are quite common in the state, especially in the southern part. Major hurricanes occasionally strike the coast, such as Hurricane Frederic in September 1979 and Hurricane Ivan in September 2004; both storms resulted in significant to devastating damage in the Mobile area.

The south of Sweden has a temperate climate, despite its northern latitude, with largely four distinct seasons and mild temperatures throughout the year. The winter in the far south is usually weak and is manifested only through some shorter periods with snow and sub-zero temperatures, autumn may well turn into spring there, without a distinct period of winter. The northern parts of the country have a subarctic climate while the central parts have a humid continental climate. The coastal south can be defined as having either a humid continental climate using the 0 °C isotherm, or an oceanic climate using the –3 °C isotherm.

Birkenfeld is an unincorporated community in Columbia County, Oregon, United States, in the Nehalem Valley on Oregon Route 202 between Jewell and Mist.
The climate of Hyderabad is semi-arid, featuring too little rain to feature the tropical savanna climate. The days are hot and dry, usually going up to extreme highs of 40 °C (104 °F), while the nights are cool and breezy. Winds usually bring along clouds of dust, and people prefer staying indoors in the daytime, while the breezes at night are pleasant and clean.

Dubai features a tropical desert, hot arid climate. Dubai has two seasons – winter and summer. Rainfall has been increasing over the past few decades in the city accumulating to more than 130 mm (5.12 in) per year.
Rawalpindi features a humid subtropical climate with hot summers, and cool to cold winters. Its climate is classified as very similar to its twin city Islamabad, but the geographical location and extreme urbanization of Rawalpindi has led to weather and climatic conditions that are notably different from its twin. Rawalpindi's weather has historically been known to change rather quickly due to its proximity to Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. These mountains not only influence the weather of the city, but also provide great recreation during the hot months. Furthermore, Its warm comfortable mean annual temperature of 21.3 °C (70 °F) attracts people to live here permanently from all over Pakistan. The average annual rainfall is abundant at 1,346.8 millimetres (53.02 in), most of which falls in the monsoon season. However, frontal cloud bands also bring significant rainfall in the winter. In summers, June is the hottest with record maximum temperature at a blistering 48.3 °C (119 °F) recorded on 13 June 1953. On the other hand, January is the coldest month of the year when temperature can drop to a minimum −3.9 °C (25 °F) in the winter recorded on 17 January 1967. Throughout the year, Rawalpindi and Islamabad experience an average of about 98 thunderstorms, which is the highest frequency of thunderstorms in Punjab province of any plane station. In fact, most rainfall in the city is accompanied by a thunderstorm with peak activity experienced in August. Record rainfall was experienced in the year 2013 at a massive 1,988 millimetres (78.3 in) mostly due to an unusually wet monsoon season. On a typical day, the city hosts breezy afternoons, but usually calm to light breeze wind conditions are observed after midnight. The mean annual wind speed of Rawalpindi is roughly 10 kilometres per hour (6.2 mph) at 14 m height. Moreover, just a few kilometers southwest of Rawalpindi, the potential power generation has been identified by U.S. Aid to be between marginal to good at 50 m height.
















